

Background: Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) DM patients have an increased risk of interstitial lung disease (ILD), with a potentially fatal course.1 Viral infection has been speculated to be the putative trigger for anti-MDA5 DM.2 3 The molecular pathogenesis remains largely unknown.
Objectives: In this study, we aimed to explore the role of type I interferon (IFN) system in the pathogenesis of anti-MDA5 DM.
Methods: We studied 20 anti-MDA5 DM patients and compared them with anti- aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) DM patients (n=10) and seronegative DM patients (n=30). The levels of IL-1b, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18, TNF-a, IFN-a, IFN-b, IFN-g, B cell activating factor (BAFF), Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) in blood were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and multiplex assay. Expressions of mRNA for sensor molecules (TLR3, TLR4, TLR7, TLR9, MDA5, RIG-1) and type I IFN inducible genes (IRF7, STAT1, MxA, ISG15) in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) were detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. Expressions of STAT1, MxA, ISG15 proteins in skin lesions from anti-MDA5 DM were analysed by immunohistochemistry technique.
Results: Anti-MDA5 DM patients had higher levels of plasma type I IFN (IFN-a, IFN-b), IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-a than seronegative-DM patients. In comparison to anti-ARS DM patients, IFN-a alone displayed heightened level in anti-MDA5 DM patients. Among these 3 subsets of patients, PBMC from anti-MDA5 DM patients have the significant upregulation of TLR3, TLR7, MDA5, RIG-1 sensors as well as IRF7, STAT1, MxA, ISG15 genes. And skin biopsies from anti-MDA5 DM patients were characterised by strong expression of STAT1, MxA, ISG15 proteins. Furthermore, overexpression of plasma BAFF was observed in anti-MDA5 DM patients. BAFF level was showed to be positively correlated with IFN-a level. Additionally, BAFF level, synergizing with IFN-a, was of great relevance to KL-6 in anti-MDA5 DM patients with higher plasma IFNa concentration.
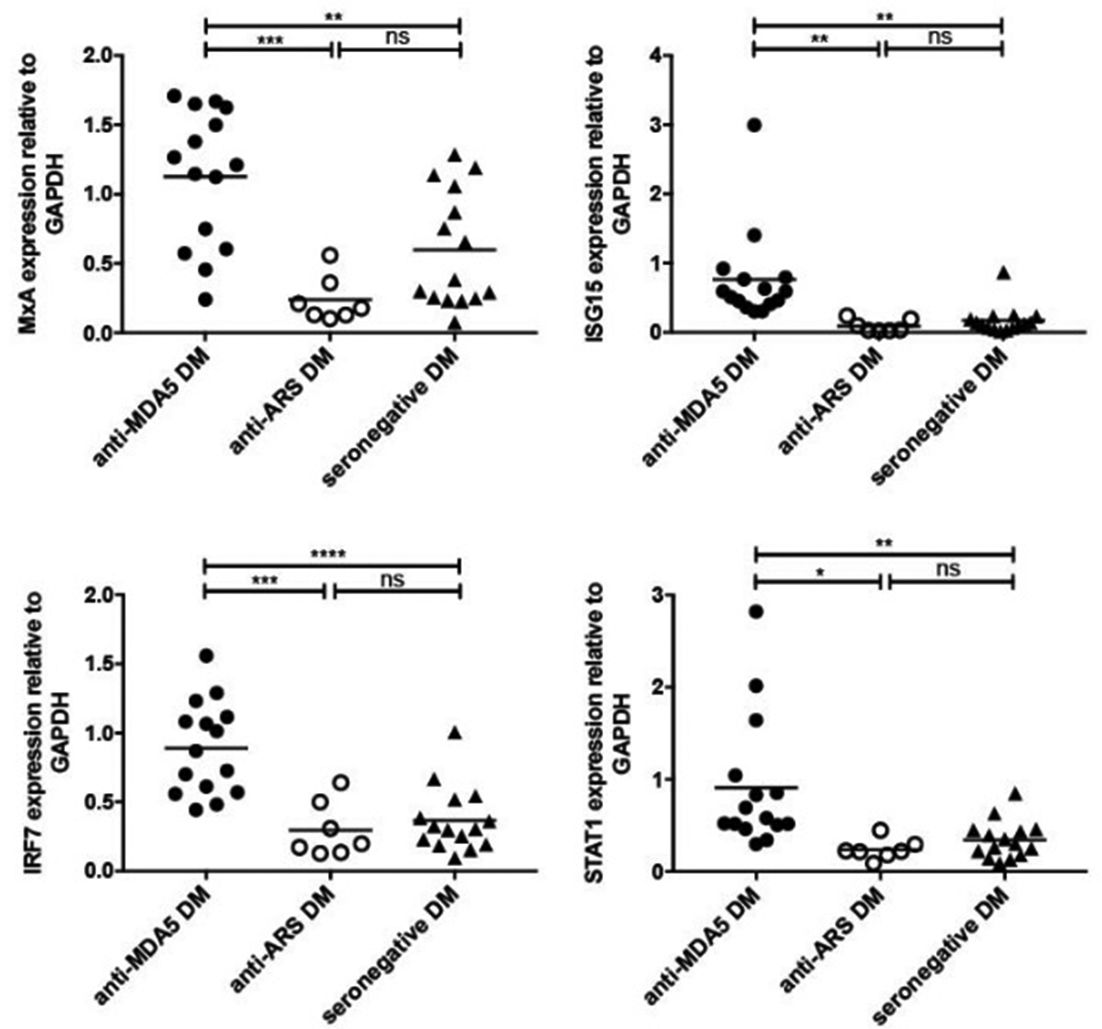
Conclusions: Our data suggest that aberrant activation of the type I IFN system associated with BAFF may be implicated in the pathogenesis of ILD in anti-MDA5 DM. The discovery may drive the development of new therapeutic strategies for the type of DM patients.
References
Acknowledgements: The authors are grateful to Wangdong Xu for his help with statistical analysis
Disclosure of Interest: None declared
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-eular.5363