

Background: Rituximab (RTX) is being increasingly used in treatment of several autoimmune diseases, including Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).RTX induces a deep depletion of all peripheral B-Cell subsets (memory and naïve B-cells). During the B-Cell repopulation phase, occurring approximately after 3 months of RTX administration, B-precursors and naïve cells reappear.Several studies have shown that relapsing RA patients are characterized by a relative expansion of memory B cells during the B-Cell repopulation phase
Objectives: The aim of this study was to quantify the memory B-Cell compartment in RA patients with different disease activity scores, evaluated by DAS28, during RTX treatment
Methods: 26 RA patients under RTX treatment were studied. At the end of th treatment 8/26 showed high-to-moderate activity risk (median DAS28=4.8) and 18 low activity risk or remission (median DAS28=2.69). After a median of 3 months from last RTX infusion, B-Cell subsets (precursors, naïve, memory B cells and plasma cells) were quantified in peripheral blood by flow cytometry, using a panel of 8 markers (CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, CD20, CD27, CD38 and CD45). B naïve cells were identified as CD19+ CD20+ CD27-, B memory cells were identified as CD19+ CD20+ CD27+, plasma cells as CD19+ CD38++ CD27++ CD20- and B precursors as CD19+ CD38++ CD20- CD27-, respectively. Percent and absolute values were calculated for each subset. In adition 10 healthy subjects were included as negative control group (NC).
Results: The median percent and absolute values of B naïve cells, B memory cells and plasma cells identified in NC, non-responder RA patients with high/moderate disease activity and responder RA patients with low disease activity or in remission are reported in
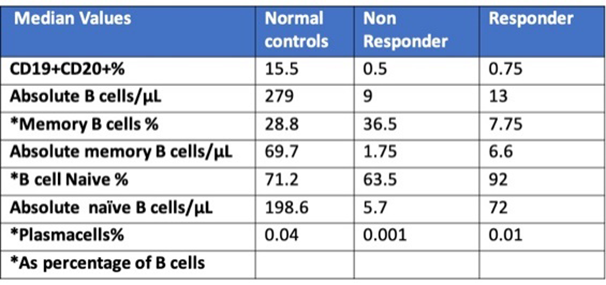
The virtual absence of peripheral B-Cell was defined as <0.1 B-Cell/μL. In the responder group, 5/18 cases showed absolute B-Cell levels <0.1 cell/μL, while only in 1/8 of the non responder group a similar B-Cell depletion was found. The memory B-Cell% was significantly higher in non responder than in responders (p<0.05); the memory B-Cell level in non responders was similar to that of the NC group.
Conclusion: We used a sensitive and easily applicable flow cytometric multicolor panel that allowed the accurate and standardized identification and enumeration of peripheral blood B-Cell subsets. As reported by other studies, higher levels of memory B-Cells were found in non responder RA patients treated by RTX, approaching those of healthy individuals.
REFERENCES:
[1] Lòpez J. Clin Exp Rheumatol2018; Dec 19. Sellam J. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 3692-3701.Dass S. Arthritis Rheum2008; 58: 2993-2999
Disclosure of Interests: None declared
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.7914