

Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a highly disabling autoimmune disease. T lymphocyte subsets imbalance causeing immune dysfunction is essential stages in the occurrence and development of RA diseases. Recent studies show that the interaction of both follicular helper T (Tfh) cells and follicular regulatory T (Tfr) cells are important frontier scientific direction to maintain autoimmune tolerance, and Tfr/Tfh balance may play a pivotal role in the formation of lymphoid germinal center and the production of autoantibodies [1-2] .
Objectives: The aim of this study was to explore the clinical characteristic of peripheral follicular T cell subsets in patients with RA and healthy individuals,and the effects of Tfr/Tfh balance on autoantibody formation and disease activity. Searching for new immunomodulatory targets from it.
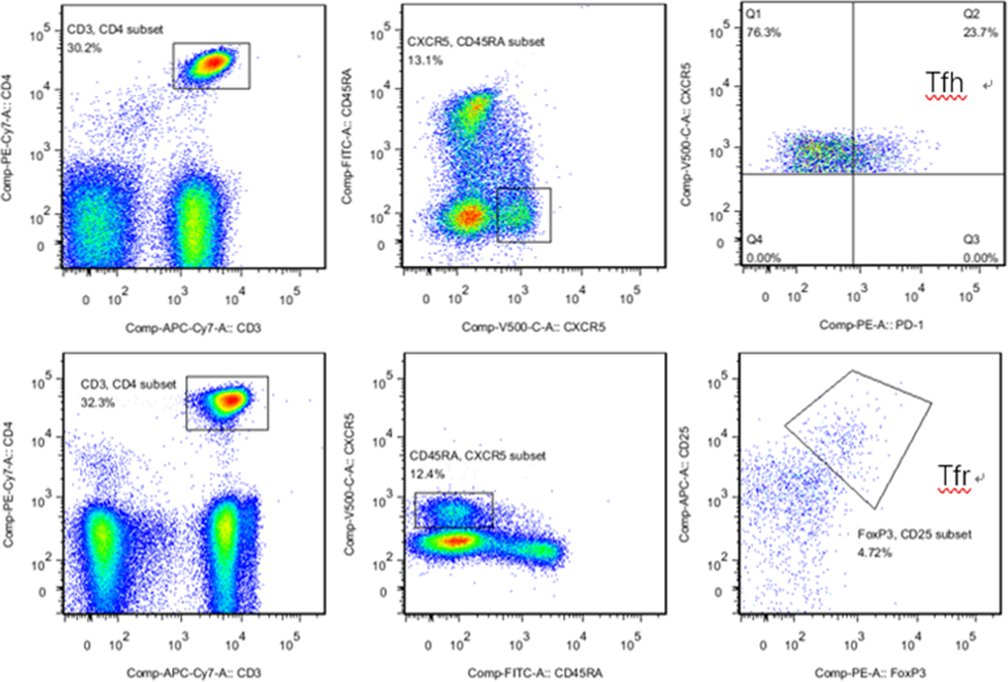
Methods: The study included 26 patients with a diagnosis of RA according to the 1987 revised criteria of the American College of Rheumatology and 17 healthy individuals as control group. All follicular T cell subsets from them were assessed by flow cytometry(
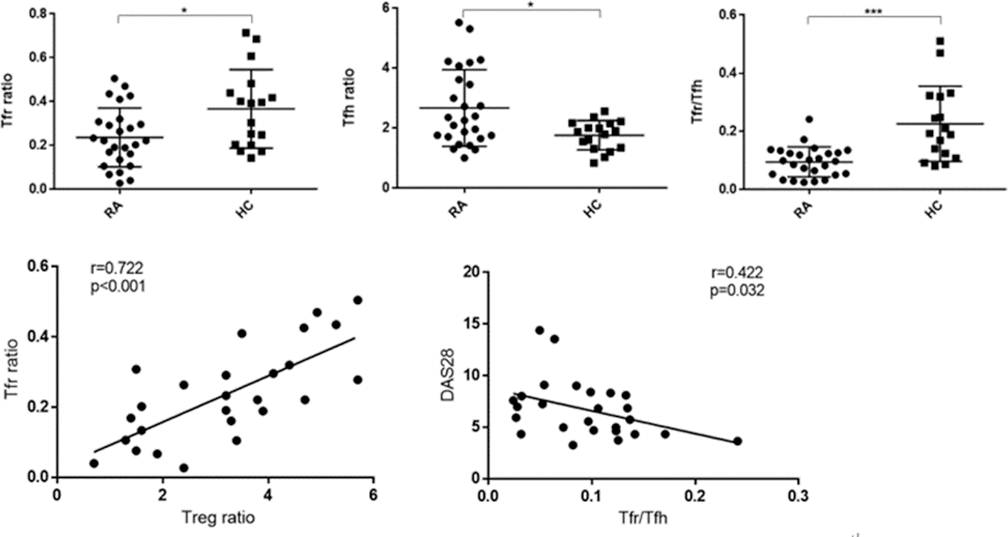
Results: (1)Compared with healthy controls, the proportions of CD4
+
CXCR5
+
PD-1
high
Tfh cells were higher in RA patients (P=0.029), In contrast, patients with RA had much lower level of CD25
+
CXCR5
+
FoxP3
+
Tfr cells (P=0.010). And there were significant differences of Tfr/Tfh between these two groups (P=0.000). (2)Among 26 RA patients, there was obvious correlation between Tfr/Tfh and the DAS28 value(r=0.422, P=0.032). But there was no correlation between Tfr/Tfh and ESR(P>0.05). Correlation between CD4
+
CD25
+
FoxP3
+
Treg cells and Tfr cells was also analyzed(r=0.722, P=0.000)(
Conclusion: Treg cells have a negative immunomodulatory effect on inflammatory response, the high correlation between Tfr cells and Treg cells indicates that Tfr cells may come from directional transformation of Treg. There is a Tfr/Tfh imbalance in RA patients, which suggests a potential mechanism of RA disease severity. However, more samples are needed to confirm whether it is related to the production of autoantibodies to affect disease activity.
REFERENCES:
[1] Wing J B, Tekgüc Murat, Shimon S. Control of germinal center responses by T-follicular regulatory cells[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2018, 9:1910-1922.
[2] Moschovakis G L, Bubke A, Friedrichsen M, et al. T cell specific CXCR5 deficiency prevents rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):8933-8946.
Follicular T lymphocytes from RA patients and healthy controls were analyzed through staining for CD3, CD4, CXCR5, CD45RA and PD-1 as Tfh cells, andCD3, CD4, CD25, CXCR5,CD45RAandFoxP3 as Tfr cells. Using isotypic control IgG1 to distinguish follicular T cell subsets that were not clearly clustered. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells of last gate.
The percentage of circulating follicular T lymphocyte subsets in patients with RA and healthy controls (*p<0.05, ***p<0.001). Correlation between Treg cells and Tfr cells, and correlation between Tfr/Tfh and the DAS28.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.3302