

Background: Riociguat is a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator approved for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease. Through its vasodilatory and anti-remodeling properties, it was predicted that riociguat might relieve Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) attacks and reduce net digital ulcer (DU) burden in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc).
Objectives: We present exploratory endpoints from the RISE-SSc study (NCT02283762) on the effects of riociguat on RP and DUs in early dcSSc patients.
Methods: RISE-SSc was a Phase IIb, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Inclusion criteria were: SSc fulfilling ACR/EULAR criteria, diffuse cutaneous involvement, disease duration ≤18 months, and modified Rodnan skin score 10−22 units. Patients were assigned to placebo or riociguat individually adjusted from 0.5 mg up to 2.5 mg, 3 times daily. Exploratory efficacy endpoints included 1) change in Raynaud’s attacks from baseline to Week 14, assessed by: Raynaud’s condition score; patient/physician assessment of RP; attack symptoms, attack duration, and average number of attacks per day; and 2) change in net DU burden from baseline to Week 52, assessed by ulcer count, ulcer burden, and visual analog score for patient-reported severity. Blood samples for exploratory evaluation of biomarkers were taken on Day 0, Week 14 and for discontinuation before Week 14.
Results: 60 patients were treated with riociguat and 61 with placebo. None of the effects of riociguat on RP or DUs were statistically significant vs placebo. However, there was a greater relative reduction in attack duration, attack frequency, pain, numbness, tingling, and patient/physician global assessment in the riociguat group vs placebo, from baseline to Week 14. Reductions in net DU burden were –0.09±0.50 for riociguat and –0.08±1.47 for placebo (estimated treatment difference: –0.11 [95% CI: –0.38, 0.17; p=0.44]) at Week 52. At Week 14, 2 patients in the riociguat group and 6 in the placebo group had developed new DUs. At Week 52, 5 and 12 patients, respectively, had developed new DUs. The total numbers of new DUs were 4 and 6 with riociguat and placebo, respectively, at Week 14, and 12 and 65, respectively, at Week 52 (Figure). Riociguat was associated with reductions vs placebo in serum sPECAM-1 (p=0.004) and CXCL-4 (p=0.008), potentially indicating anti-vasculopathy properties of riociguat.
Conclusion: Riociguat did not produce statistically significant changes in DUs. Riociguat may reduce the development of new DUs in patients with early dcSSc and may favourably improve cytokine vasculopathy.
Figure. Development of new digital ulcers
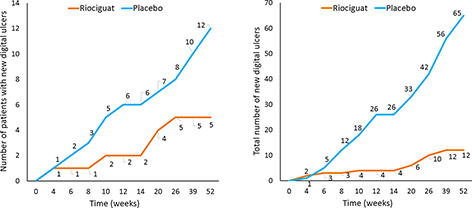
Left: Number of patients with new digital ulcers
Right: Total number of new digital ulcers
New digital ulcers are defined as ulcers not existing at baseline.
Acknowledgement: Adelphi Communications Ltd, Bollington, UK provided medical writing support.
Disclosure of Interests: Dinesh Khanna Shareholder of: Eicos Sciences, Inc, Grant/research support from: Bayer, BMS, Pfizer, Horizon, Consultant for: Actelion Acceleron, Arena, Bayer, BI, BMS, CSL Behring, Corbus, Cytori, GSK, Genentech/Roche, Galapagos, Employee of: Elcos Sciences, Inc, Yannick Allanore Grant/research support from: Inventiva, F Hoffman La-Roche, Sanofi, BMS, Pfizer, Consultant for: Actelion, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer, Roche, Sanofi, Christopher Denton Grant/research support from: GlaxoSmithKline, Inventiva, CSF Behring, Consultant for: Roche-Genentech, Actelion, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi Aventis, Inventiva, CSL Behring, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Masataka Kuwana Grant/research support from: Actelion, Consultant for: Chugai, Reata, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corpus, CSL-Berling, Mochida, Speakers bureau: Actelion, Pfizer, Bayer, Nippon Shinyaku, Chugai, Marco Matucci-Cerinic Grant/research support from: Actelion, MSD, Pfizer, BMS, Chemomab, Sanipedia, Speakers bureau: Actelion, BMS; MSD, Janssen, Janet Pope Consultant for: Eli Lilly and Company, Janethe de Oliveria Pena Employee of: Bayer, Kaisa Laapas Employee of: StatFinn Oy, partly insourced to Bayer, Zhen Yao Employee of: Bayer, Melanie Hemmrich Employee of: Bayer AG, Oliver Distler Grant/research support from: Prof. Distler received research funding from Actelion, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim and Mitsubishi Tanabe to investigate potential treatments of scleroderma and its complications, Consultant for: Prof. Distler has/had consultancy relationship within the last 3 years with Actelion, AnaMar, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, ChemomAb, espeRare foundation, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Inventiva, Italfarmaco, iQvia, Lilly, medac, MedImmune, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Pharmacyclics, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Serodapharm and UCB in the area of potential treatments of scleroderma and its complications. In addition, he had/has consultancy relationship within the last 3 years with A. Menarini, Amgen, Abbvie, GSK, Mepha, MSD, Pfizer and UCB in the field of arthritides and related disorders
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.5755