

Background: Whilst anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP) positivity in associated with poor outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), it is unclear whether titre level over time is associated with outcome.
Objectives: Whilst anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP) positivity in associated with poor outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), it is unclear whether titre level over time is associated with outcome.
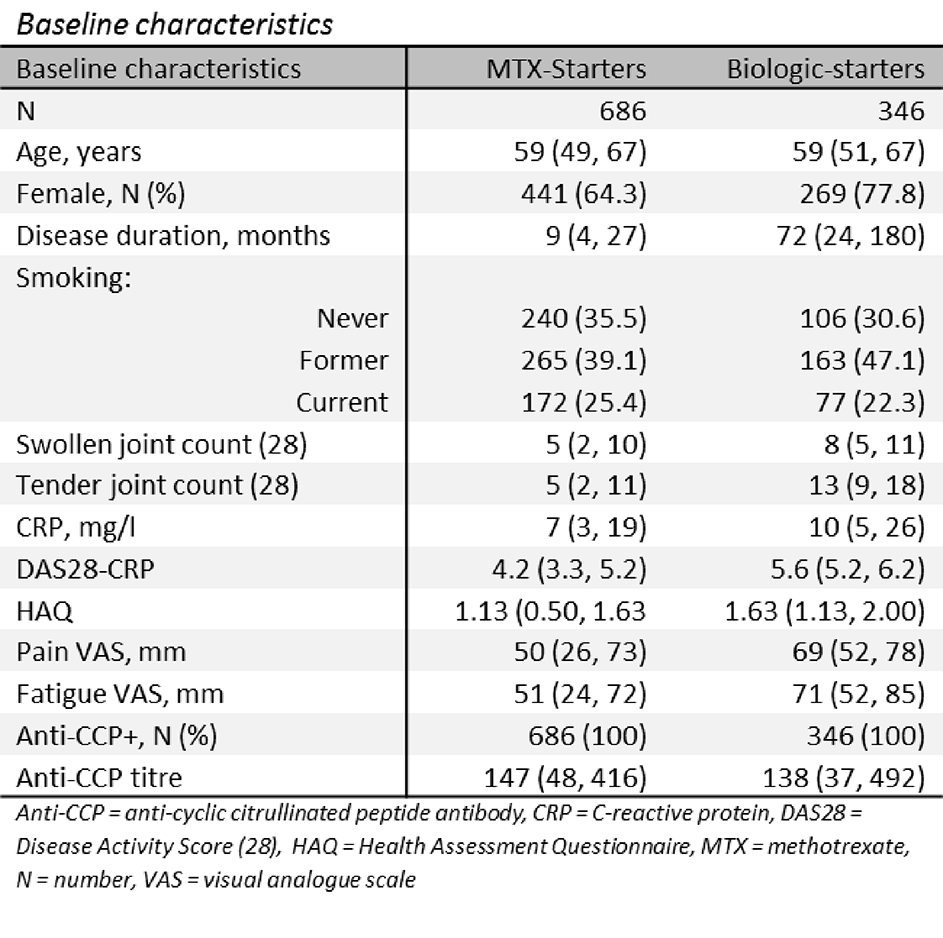
Methods: Patients were recruited to one of two, UK-based, multi-centre prospective cohort studies: MTX-starters = Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication Study (RAMS); biologic-starters = Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate (BRAGGSS). Anti-CCP titre (Axis-Shield Anti-CCP test; U/ml; anti-CCP titre >5 U/ml = anti-CCP+) was measured at the co-ordinating centre from blood samples taken at baseline, 6 months and 12 months. Patients who were anti-CCP+ at baseline and had titre measured at one other assessment were included in the analysis. Patients completed the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) and the Disease Activity Score (DAS28) was calculated at each assessment. The association between anti-CCP titre and DAS28 and HAQ was assessed using linear random effects models, controlling for age, gender and disease duration (months). Anti-CCP titre was natural log-transformed. Missing data resulting from anti-CCP assay failure were imputed using multiple imputation.
Results: In total, 686 MTX-starters and 346 biologic-starters were included. Biologic-starters had worse disease at baseline compared to MTX-starter (Table). Median [IQR] titre decreased slightly over follow-up for MTX-starters (baseline = 147 [48, 416]; 6 months = 133 [47, 454]; 12 months = 124 [44, 421]; p=0.63) and biologic-starters (baseline = 138 [37, 492]; 6 months = 112 [30, 468]; 12 months = 103 [30, 451]; p=0.36) but this was non-significant. For MTX-starters, anti-CCP titre was statistically significantly associated with DAS28 and HAQ, but the effect sizes were small (mean difference [95% CI] per unit increase in log anti-CCP: DAS28 = 0.07 [0.02, 0.11]; HAQ = 0.06 [0.03, 0.08]). There was no significant association between anti-CCP titre and DAS28 and HAQ for biologic-starters (mean difference [95% CI] per unit increase in log anti-CCP: DAS28 = 0.03 [-0.05, 0.10]; HAQ = 0.02 [-0.01, 0.05]).
Conclusion: Time-varying anti-CCP titre level was not strongly associated with disease activity or disability over one year in either MTX-starters or biologic-starters who were anti-CCP+ at baseline, indicating repeat testing of anti-CCP level may not be necessary.
Disclosure of Interests: James Gwinnutt: None declared, Kimme Hyrich Grant/research support from: Grants to institution: BMS, Pfizer, UCB, Mark Lunt: None declared, Darren Plant: None declared, Nisha Nair: None declared, Anne Barton: None declared, Suzanne Verstappen: None declared
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.4724