

Background: Obesity could be a risk factor for response to treatment and disease severity in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) because of potential pro-inflammatory effects of cytokines produced by adipose tissue (1).
Objectives: This study aimed to assess association of demographic, clinical and disease activity indices with obesity in patients using biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) treatment in HUR-BIO cohort.
Methods: HUR-BIO (Hacettepe University Rheumatology Biologic Registry) is a prospective, single center database of biological treatments since 2005. Until January 2020, HUR-BIO PsA registry enrolled 469 patients. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, therapeutic data were collected from this database which including tender/swollen joint counts, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), Disease Activity Score - 28 joint (DAS28), Disease Activity index for Psoriatic Arthritis - 28 joint score (DAPSA-28), Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease 12-item questionnaire (PSAID-12). BMI≥30 was defined as obesity.
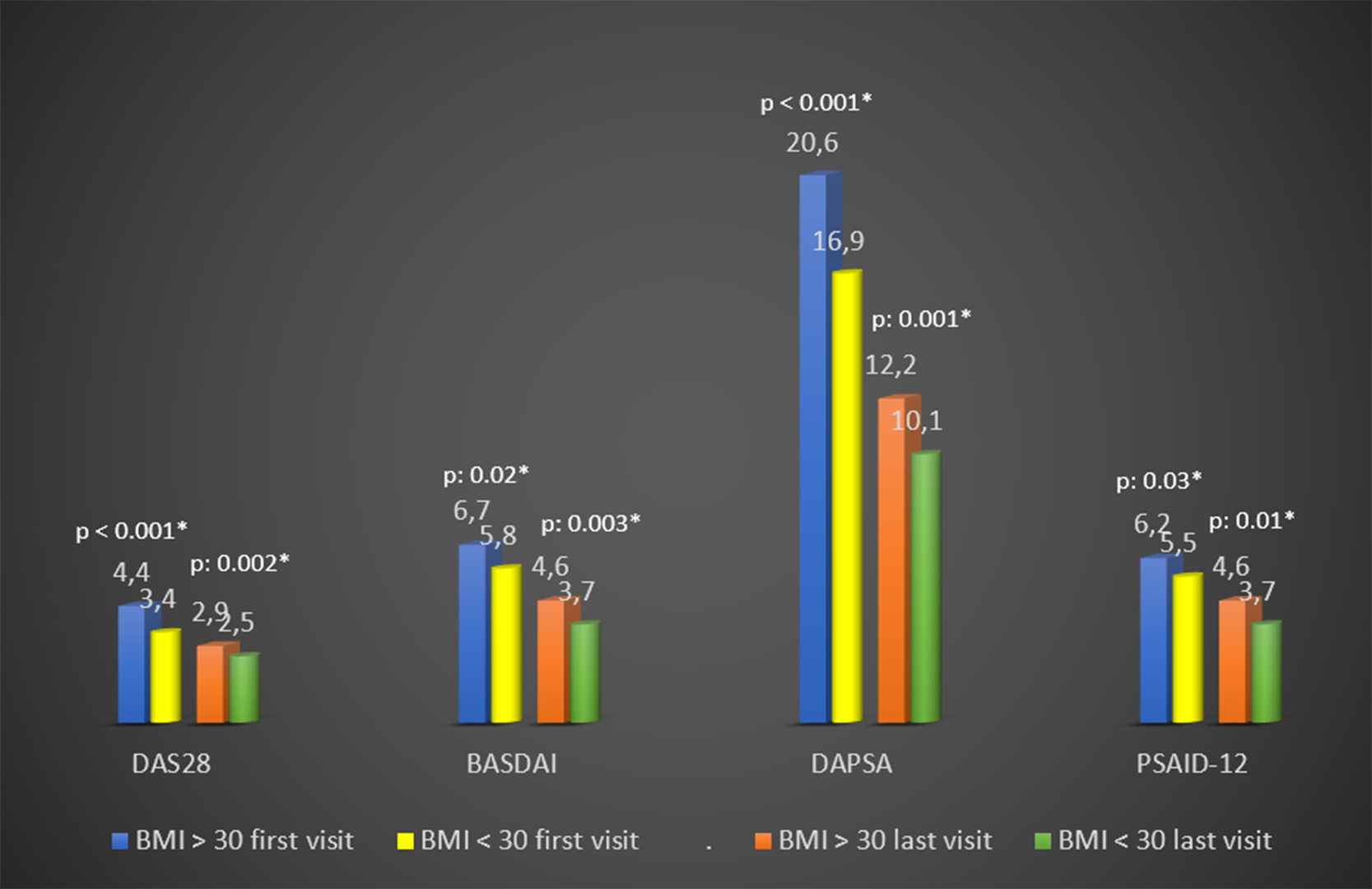
Results: HUR-BIO PsA had 469 PsA patients and 441 patients with available BMI data were enrolled. Overall, 187/441 patients (42%) had obesity. The median follow-up period of obese and non-obese PsA patients was 7 (3-12) and 8 (4-12) years, respectively (p: 0.31). Obese patients were older at the age of PsA diagnosis (43 (33 - 53) vs 36 (28 – 45) years, p<0.001), higher female gender (76% vs 64%, p: 0.008), higher comorbidities (53% vs 27%, p<0.001). While there was no difference between the two groups in uveitis, IBD, family history and smoking; HLA-B27 was higher in non-obese patients (table). DAS28, BASDAI, DAPSA-28 joints, PSAID-12 were higher in the obese group than in the non-obese group, both before the biological DMARD and at the last visit (p <0.05) (
Conclusion: Obesity was associated with higher disease activity and poorer effect of bDMARD treatment in patients with PsA. In obese PsA patients with high disease activity despite bDMARD therapy, intentional weight loss may be recommended as an adjunctive therapy.
REFERENCES:
[1] Klingberg E, Bilberg A, Björkman S et al. Weight loss improves disease activity in patients with psoriatic arthritis and obesity: an interventional study. Arthritis research & therapy , 2019, 21.1: 17.
Baseline and last visit demographic, clinical and disease activity by BMI categories
| BMI > 30 | BMI < 30 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at PsA, years, median (Q1-Q3) | 43 (33-53.5) | 36 (28-45) | 0.000* |
| Disease duration, years, median (Q1-Q3) | 7 (3-12) | 8 (4-12) | 0.31 |
| Gender (male/female, %) | 24/76 | 36/64 | 0.008* |
| Smoking Ever n, % | 102 (54.8) | 159 (62.8) | 0.091 |
| HLA B-27 (+) n, (%) | 7 (14) | 32 (35) | 0.006* |
| Uveitis n, % | 4 (2.2) | 6 (2.4) | 0.571 |
| IBD n, % | 4 (2.1) | 6 (2.4) | 0.567 |
| PsA/Pso Family history n, % | 74 (39.6) | 84 (33.2) | 0.169 |
| Taking steroids before biological drugs n, % | 115 (61.5) | 156 (61.7) | 0.972 |
| BASDAI50% response n, % | 35 (31.8) | 61 (41) | 0.13 |
| Last HAQ score < 0.5 n, % | 91 (52.3) | 160 (68.1) | 0.001* |
Baseline and last visit disease activity by BMI categories p: 0.03* p: 0.01* p: 0.001* p: 0.002* *p < 0.05 BMI: Body mass index, DAS: Disease Activity Score, BASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, DAPSA: Disease Activity index for Psoriatic Arthritis, PSAID: Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease
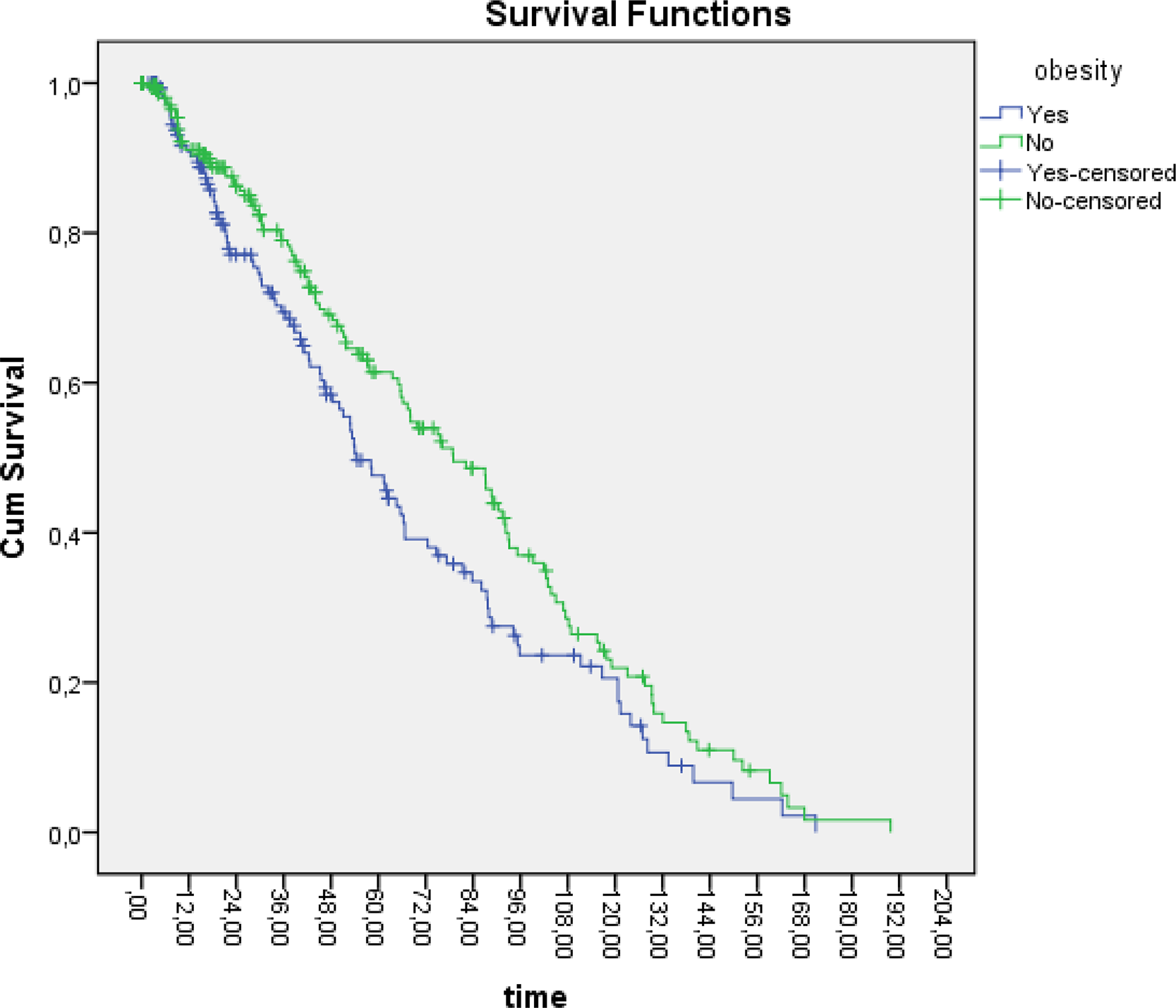
Retention rate for biological DMARD by BMI categories Median of retention rate of first bDMARD: BMI > 30 kg/m 2 and < 30 kg/m 2 54.2 and 79, respectively. Log rank p-value between BMI > 30 kg/m 2 and <30 kg/m 2 : 0.03*
Disclosure of Interests: Bayram Farisoğullari: None declared, Gözde Kübra Yardimci: None declared, Ertugrul Cagri Bolek: None declared, Emre Bilgin: None declared, Emine Duran: None declared, Gizem Ayan: None declared, Levent Kiliç: None declared, Omer Karadag: None declared, Ali Akdoğan: None declared, Şule Apraş Bilgen: None declared, Ali İhsan Ertenli: None declared, Sedat Kiraz: None declared, Umut Kalyoncu Consultant of: Abbvie, Amgen, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, UCB