

Background: Guselkumab (GUS), a novel monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the p19-subunit of IL-23, demonstrated efficacy in the Ph 3 DISCOVER-1 (D1) & DISCOVER-2 (D2) trials of pts with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). 1,2 Dactylitis & enthesitis, key PsA clinical manifestations, can be difficult to treat and may portend more significant disease burden. 3,4
Objectives: In pts with dactylitis or enthesitis at baseline, assess: 1) changes in symptoms over time and 2) relationships between improvements in dactylitis or enthesitis and other PsA domains.
Methods: Adults with active PsA despite standard therapies were eligible for D1 & D2. Approx. 30% of D1 pts previously received 1-2 TNF inhibitors; D2 pts were biologic-naïve. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100mg Q4W; GUS 100mg at W0, W4, Q8W; or PBO. Independent assessors evaluated dactylitis (total score: 0-60) & enthesitis (Leeds Enthesitis Index [LEI]; total score 0-6). Dactylitis and enthesitis findings through W24 were prespecified to be pooled across D1 & D2. P-values are unadjusted. We assessed changes in dactylitis and LEI scores over time (ANCOVA); associations between dactylitis or enthesitis resolution and ACR/PASI responses at W24 (Chi-square); and correlations between dactylitis or LEI and HAQ-DI/SF-36 change scores at W24 (Spearman’s correlation). AEs through W24 were reported. 1,2
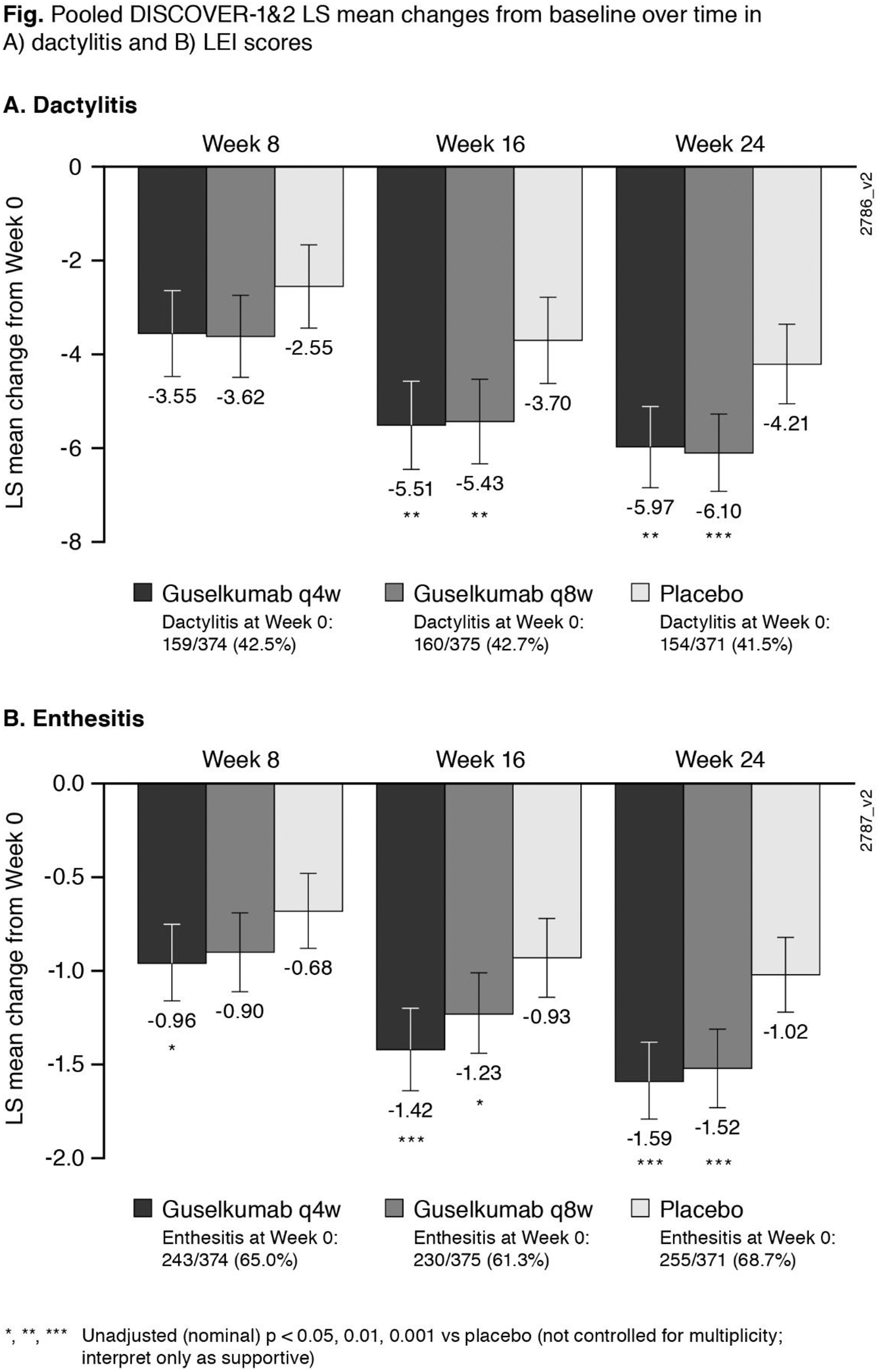
Results: At W0, 42% of pooled D1+D2 pts had dactylitis; 65% had enthesitis. GUS improved dactylitis and LEI scores vs PBO at W8, W16, W24. GUS vs PBO differences were significant for dactylitis changes at W16 & W24 and LEI changes at W8 (Q4W only), W16 & W24; no dose response was observed ( Fig ). Rates of dactylitis or enthesitis resolution by W24 were consistently significantly (p<0.001) associated with ACR20/50/70 and PASI75/90 response ( Table ). In GUS-treated pts at W24, significant correlations were observed between dactylitis change scores and PASI (p<0.001 Q4W; p=0.006 Q8W) and SF-36 MCS (p=0.038 Q4W; p=0.003 Q8W) changes, and between LEI and HAQ-DI change scores (p<0.001 Q4W; p=0.005 Q8W). No consistent correlations/associations were observed between dactylitis or LEI scores and other clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: In PsA pts with dactylitis or enthesitis at W0, GUS improved dactylitis or LEI scores vs PBO by W8; treatment differences were significant at W16 & W24. Resolution of dactylitis or enthesitis was significantly associated with clinically meaningful improvements in PsA joint & skin symptoms. Improved dactylitis scores correlated with improved skin symptoms and mental health; improved LEI scores correlated with improved physical function.
REFERENCES:
[1]Deodhar A (A#807),
[2]Mease P (A#L13), Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71(suppl 10);
[3]DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1399-5; 4 DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.02.002
Pooled DISCOVER-1&2: associations between dactylitis/enthesitis resolution and joint/skin response
| ACR20 | ACR50 | ACR70 | PASI75 a | PASI90 a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dactylitis resolution b | N | %pts | %pts | %pts | N | %pts | %pts |
| Q4W | 373 | 55* | 34* | 16* | 121 | 78* | 55* |
| Q8W | 375 | 53* | 31* | 16* | 116 | 80* | 65* |
| PBO | 372 | 26* | 12* | 5* | 115 | 19* | 10* |
| Enthesitis resolution c | |||||||
| Q4W | 243 | 34* | 31* | 11* | 187 | 82* | 63* |
| Q8W | 230 | 40* | 7* | 12* | 162 | 77* | 62* |
| PBO | 255 | 14* | 13* | 5* | 182 | 19* | 9* |
* p < 0.001 (Chi-square)
a In pts with ≥3% BSA psoriasis & IGA ≥2 at W0
b In pts with D at W0
c In pts with E at W0
Acknowledgments: None
Disclosure of Interests: Dennis McGonagle Grant/research support from: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Iain McInnes Grant/research support from: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Atul Deodhar Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myer Squibb (BMS), Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myer Squibb (BMS), Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Georg Schett Speakers bureau: AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roche and UCB, Philip J Mease Grant/research support from: Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB – grant/research support, Consultant of: Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB – consultant, Speakers bureau: Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB – speakers bureau, May Shawi Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Shelly Kafka Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Chetan Karyekar Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Consultant of: Janssen, Employee of: Janssen Global Services, LLC. Previously, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Abbott Labs., Alexa Kollmeier Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Elizabeth C Hsia Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Xie L Xu Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Shihong Sheng Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Prasheen Agarwal Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Bei Zhou Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Christopher T. Ritchlin Grant/research support from: UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Amgen, Consultant of: UCB Pharma, Amgen, AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Novartis, Gilead, Janssen, Proton Rahman Grant/research support from: Janssen and Novartis, Consultant of: Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer., Speakers bureau: Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer