

Background: The presence of axial involvement significantly impacts on psoriatic arthritis (PsA) activity, outcomes and patients (pts) quality of life. IL-17A inhibitors were previously shown to improve axial disease in PsA. Netakimab (NTK) is a humanized anti-interleukin 17A antibody approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of NTK on axial symptoms in patients with PsA, based on data of 24-week (wk) observation from an ongoing phase 3 PATERA study (NCT03598751).
Methods: PATERA is a phase 3 international double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. After completion of screening 194 eligible adult patients with PsA fulfilling the CASPAR criteria, with inadequate response to csDMARD or one TNFi, were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive NTK 120 mg or placebo (PBO) at Wks 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14, 18 and 22. 84 patients from PBO arm, failed to achieve ACR20 (20% improvement the American College of Rheumatology criteria) by Wk 16, were switched to NTK. A subset of pts with axial involvement (defined by presence of inflammatory back pain (IBP) according to ASAS IBP criteria, 2009) was evaluated with spondylitis-specific assessments: spinal pain (10-item numerical rating scale), nocturnal back pain (10-item numerical rating scale), BASDAI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index), ASDAS-CRP (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with C-reactive protein.
Results: 104 PsA patients (NTK N=54, PBO N=50) with IBP at baseline (BL) were included in the analysis. Demographic and BL disease characteristics were comparable across the groups (
Baseline demographics and mean composite endpoint scores
| Arm | NTK (N=54) | PBO (N=50) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 43.5 (12.16) | 42.7 (10.76) |
| Male, n (%) | 27 (50) | 26 (52) |
| PsA duration, mo * | 70.0 (78.78) | 79.0 (81.62) |
| BASDAI score * | 5.58 (1.80) | 5.79 (1.94) |
| ASDAS-CRP score * | 3.38 (1.16) | 3.38 (1.28) |
| nocturnal pain * | 4.2 (2.42) | 5.1 (2.29) |
| spinal pain * | 4.4 (2.41) | 5.3 (2.40) |
* mean (standard deviation) BASDAI=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index, ASDAS-CRP=Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with C-reactive protein
Changes in BASDAI and ASDAS-CRP vs baseline
| BASDAI | ASDAS-CRP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTK (N=54) | PBO (N=50) | NTK (N=54) | PBO (N=50) | |
| Wk 4 | -2.45 (1.94) | -0.51 (1.26) | -1.44 (1.06) | -0.19 (0.60) |
| Wk 8 | -2.77 (2.22) | -0.38 (1.55) | -1.53 (1.07) | -0.21 (0.74) |
| Wk 16 | -2.77 (1.83) | -0.17 (1.67) | -1.52 (0.98) | -0.10 (0.97) |
| Wk 24 | -2.83 (2.15) | -0.19 (1.70) | -1.57 (1.06) | -0.11 (0.95) |
mean (standard deviation)
Mean change in BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP, spinal pain, and nocturnal pain at Wk 24
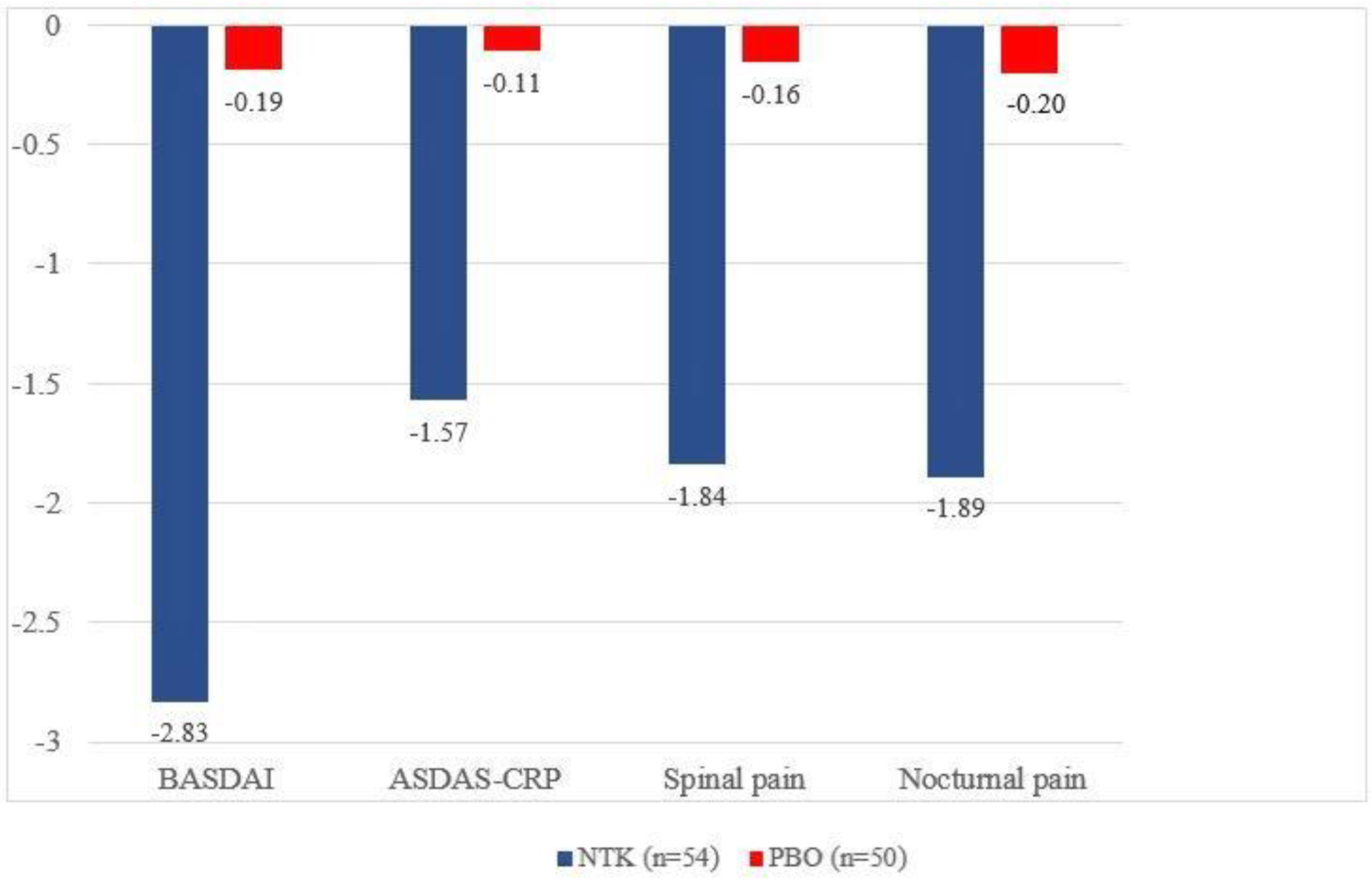
Conclusion: About 50% of subjects, randomized to PATERA study, had IBP at baseline. NTK leads to rapid and sustained improvement in axial disease in patients with active PsA.
Acknowledgments: This study was sponsored by JSC BIOCAD.
Disclosure of Interests: Tatiana Korotaeva Grant/research support from: Pfizer, Consultant of: Abbvie, BIOCAD, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novartis-Sandoz, Pfizer, UCB, Speakers bureau: Abbvie, BIOCAD, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novartis-Sandoz, Pfizer, UCB, Inna Gaydukova Grant/research support from: JSC BIOCAD, Speakers bureau: Pfizer, Novartis, AbbVie, JSC BIOCAD, Сelgene, MSD, Sanofi, V Mazurov: None declared, Aleksey Samtsov Grant/research support from: JSC BIOCAD, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Johnson&Johnson, Celgene, Glenmark, Galderma, Sanofi, Vladislav Khayrutdinov Grant/research support from: Akrikhin, Alkoy, Belupo, JSC BIOCAD, Bosnaliejk, Verteks, Glenmark, Elfa, Leo Pharma, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, Celgene, Pharmtec, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Jadran, Janssen, Andrey Bakulev Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, UCB, MSD, Novartis, Galderma, Celgene, Leo Pharma and Johnson&Johnson, JSC BIOCAD, Consultant of: Novartis, Celgene and Johnson&Johnson, Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galderma, UCB, Novartis, Celgene and Johnson&Johnson, Muza Kokhan Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, UCB, MSD, Novartis, Galderma, Celgene, Leo Pharma and Johnson&Johnson, JSC BIOCAD, Consultant of: Novartis, Celgene and Johnson&Johnson, Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galderma, UCB, Novartis, Celgene and Johnson&Johnson, Alena Kundzer: None declared, Nikolaj Soroka Grant/research support from: JSC BIOCAD, Ekaterina Dokukina Employee of: JSC BIOCAD, Anna Eremeeva Employee of: JSC BIOCAD