

Background: Obinutuzumab, a type II anti-CD20 mAb, resulted in rapid and complete B-cell depletion and improved renal responses in proliferative lupus nephritis (LN) in the Phase 2 NOBILITY trial and will be further evaluated in the Phase 3 REGENCY trial. Recent analyses suggest alternative urinary sediment, serum creatinine (SCr), and urine protein/creatinine ratio (UPCR) requirements may be better measures of response in LN than those used in NOBILITY [1,2].
Objectives: To evaluate the NOBILITY response definitions and to report the results of NOBILITY using alternative definitions of renal response.
Methods: 126 patients with active Class III/IV LN were randomized to obinutuzumab or placebo in combination with mycophenolate and glucocorticoids. NOBILITY complete renal response (CRR) required UPCR < 0.5, SCr ≤ the upper limit of normal (ULN) of the reference laboratory and not increased > 15% from baseline SCr, and inactive urinary sediment. Exploratory analyses were conducted, and alternative response definitions were evaluated post hoc.
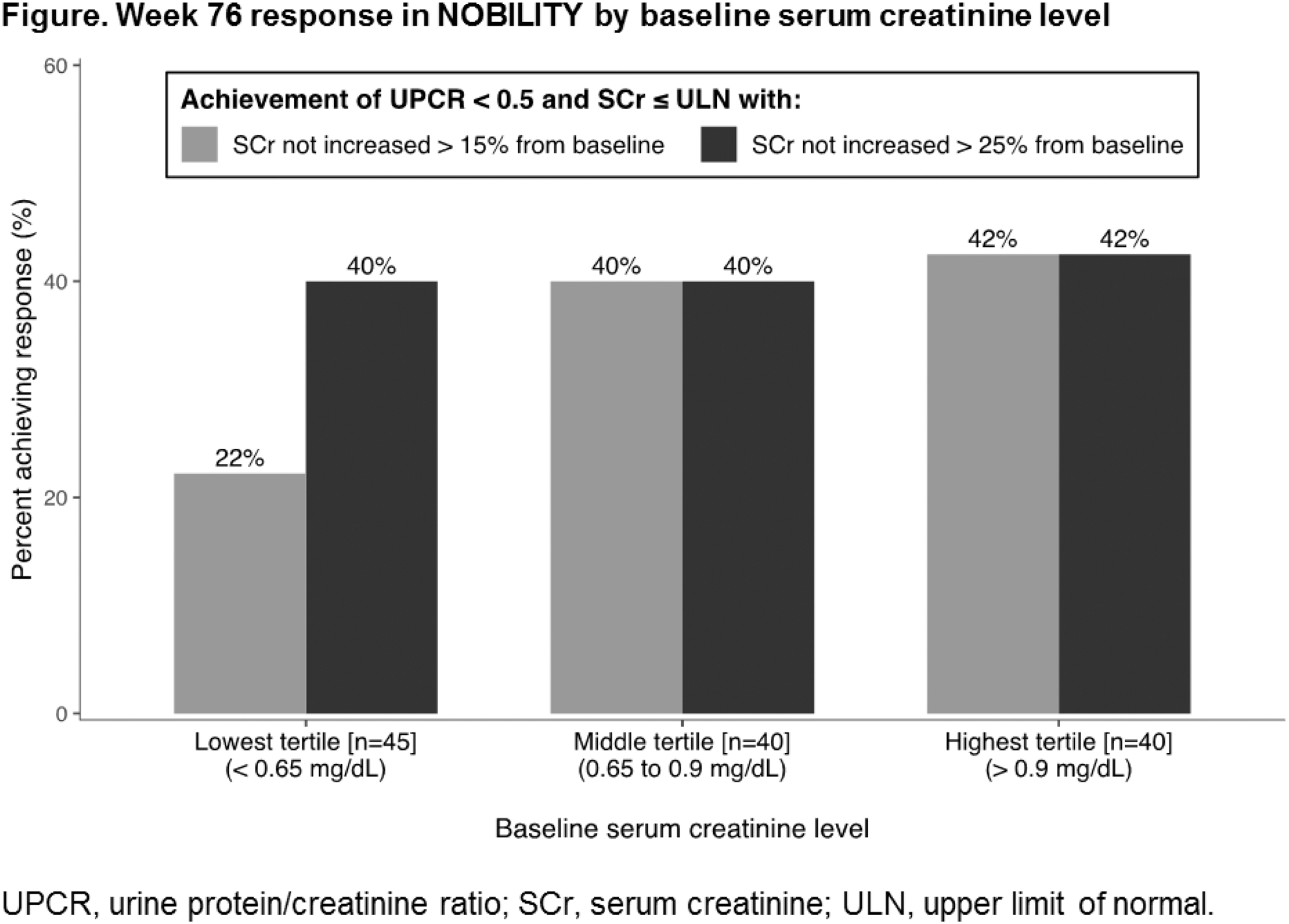
Results: NOBILITY CRR was increased with obinutuzumab over placebo at Week 52 (35% vs. 23%, P = 0.11) and Week 76 (40% vs. 18%, P = 0.007). Response rates were low among patients with baseline SCr < 0.65 mg/dL (n = 45) due to the requirement that SCr not increase > 15% from baseline; increasing this threshold to 25% increased the response rate to a level similar to other groups (Figure). Alternative response definitions demonstrated increased rates of response in both treatment groups and similar benefits of obinutuzumab over placebo at Weeks 52 and 76 (Table).
Conclusion: Obinutuzumab resulted in consistent treatment benefits across a range of renal response definitions in NOBILITY and will be further evaluated in REGENCY. A requirement that SCr not increase > 15% from baseline may be overly restrictive in patients with low baseline SCr (< 0.65 mg/dL), where a change of 15% represents < 0.1 mg/dL and is of questionable clinical relevance. These findings may inform LN clinical trial design and more accurately reflect clinical practice.
REFERENCES:
[1]Dall’era M et al. Arthritis Rheumatol . 2015;67:1305-13.
[2]Almaani S et al. J Am Soc Nephrol . 2019;30:669 [abstract].
Data from NOBILITY at weeks 52 and 76 using several response definitions
| Definition of response | Week 52 | Week 76 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBI (n = 63) | PBO (n = 62) | Diff. | OBI (n = 63) | PBO (n = 62) | Diff. | |
| NOBILITY complete response
| 35% | 23% | 12%* | 40% | 18% | 22%** |
| REGENCY complete response
| 43% | 29% | 14%* | 54% | 31% | 23%** |
| UPCR < 0.8 only | 64% | 48% | 15%* | 64% | 47% | 17%* |
| UPCR < 0.8 with SCr requirement
| 60% | 48% | 12%* | 64% | 45% | 18%** |
| NOBILITY overall response
| 56% | 36% | 20%** | 51% | 29% | 22%** |
| REGENCY overall response
| 68% | 45% | 23%** | 67% | 50% | 17%** |
OBI, obinutuzumab; PBO, placebo.
* P < 0.2 vs. placebo group. ** P < 0.05 vs. placebo group.
a ≥ 50% reduction in UPCR to a value < 1 (< 3 if the baseline UPCR was ≥ 3). All response definitions required no use of rescue medications or early withdrawal.
Acknowledgments: This study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche.
Disclosure of Interests: Zahir Amoura Grant/research support from: GSK, Roche, Consultant of: GSK, Astra Zeneca, Amgen, Philippe Rémy: None declared, Luis Fernando Quintana Porras: None declared, Laurent Chiche: None declared, Dominique Chauveau: None declared, Dario Roccatello: None declared, Richard Furie Grant/research support from: AstraZeneca, Biogen, Consultant of: AstraZeneca, Biogen, Thomas Schindler Employee of: F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Jay Garg Employee of: Genentech, Matthew D. Cascino Employee of: Genentech, Brad H Rovin Grant/research support from: GSK, Consultant of: GSK, Andrea Doria Consultant of: GSK, Pfizer, Abbvie, Novartis, Ely Lilly, Speakers bureau: UCB pharma, GSK, Pfizer, Janssen, Abbvie, Novartis, Ely Lilly, BMS