

Background: We recently reported that the inhibitor of hyaluronan (HA) biosynthesis, 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU) blocked IL-1β activation of MMP13 mRNA and protein expression in human osteoarthritic (OA), bovine as well as bovine or OA cartilage explants [1]. This was a somewhat counterintuitive observation because we have also demonstrated that the overexpression of HAS2 (HAS2-OE) exerted the same chondroprotective effects on human and bovine chondrocytes. Others [2] have reported that HAS2-OE in tumor cells generates a flux in intracellular UDP-sugar pools that resulted in changes in cell metabolism; switching from a dependence on glycolysis to aerobic respiration. HAS2-OE and 4-MU likely also cause dramatic fluxes in intracellular UDP-GlcUA pools. From these results, we hypothesized that the effect of HAS2-OE and 4-MU relate to changing metabolism and the possibility of inhibition of glycolysis induce chondroprotective effect. To determine that, we used the glycolysis inhibitor, 2-Deoxyglucose (2DG) as an alternative agent to change metabolism in chondrocytes.
Objectives: The objective of this study was to investigate the mechanism of chondroprotective effects of 2DG
Methods: Bovine and human chondrocyte were stimulated with IL-1β (2ng/ml) in the presence or absence of 4MU (1.0 mM), 2DG (0.2-20 mM). Bovine chondrocytes were tested using Seahorse Flux Analyzer (Agilent Tech) to determine rate changes in medium accumulation of +H protons (indicative of lactic acid accumulation: ECAR) and for O2 consumption (indicative of mitochondrial respiration: OCR). Accumulation of MMP13 and phosphor AMPK (pAMPK) protein was quantified with Western blotting. Human and Bovine cartilage explants were cultured with L-1β in the presence or absence of 2DG (20 mM) and d 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide 1-β-D-ribofuranoside (AICAR) to pharmacologically induce AMPK for 7 days and stained with Safranin O.
Results: Reduced mitochondrial potential and enhanced dependence on glycolysis was observed in IL-1β stimulated chondrocytes. Co-treatment with 4-MU and 2DG returned the cell metabolism to levels at or below baseline (
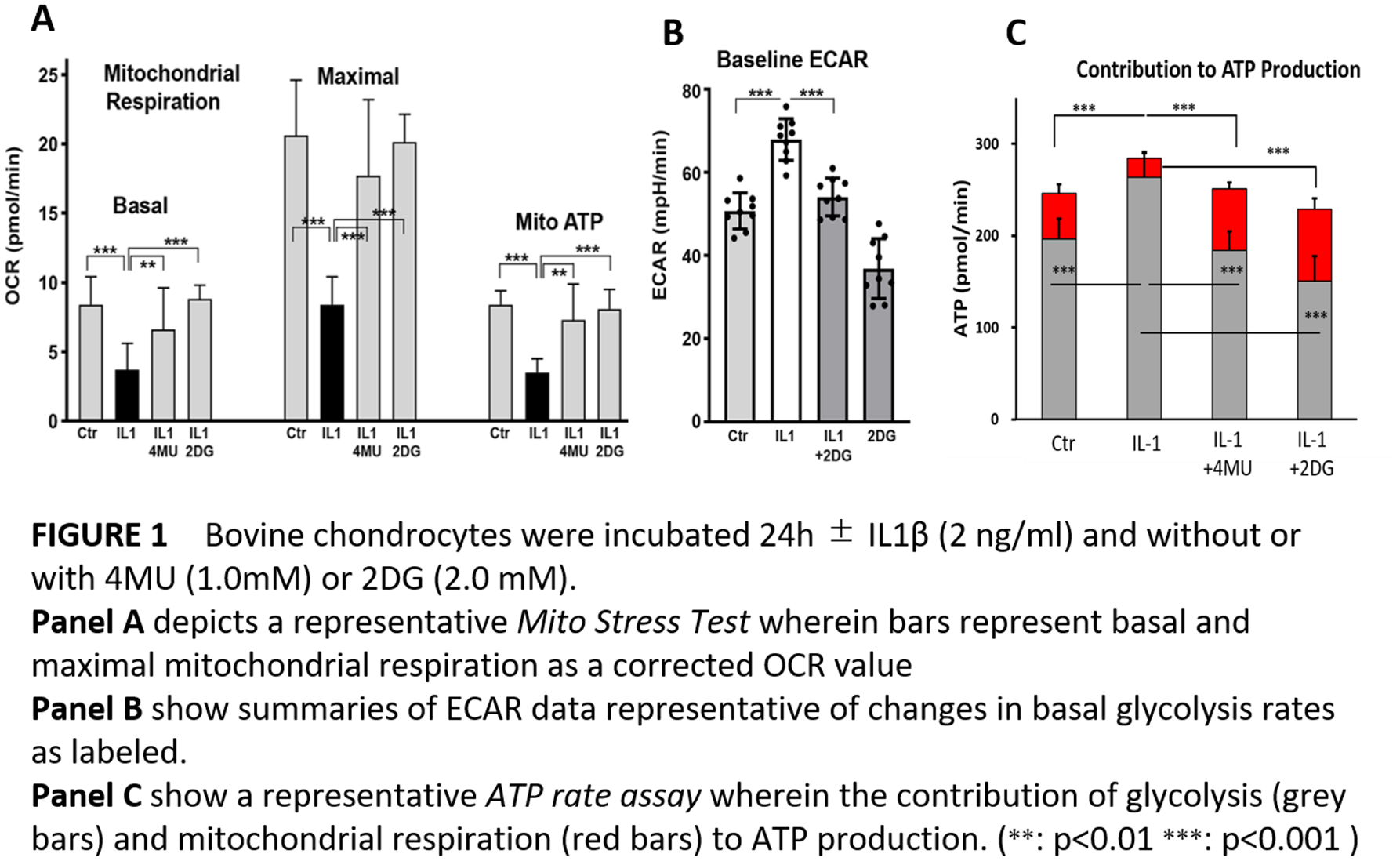
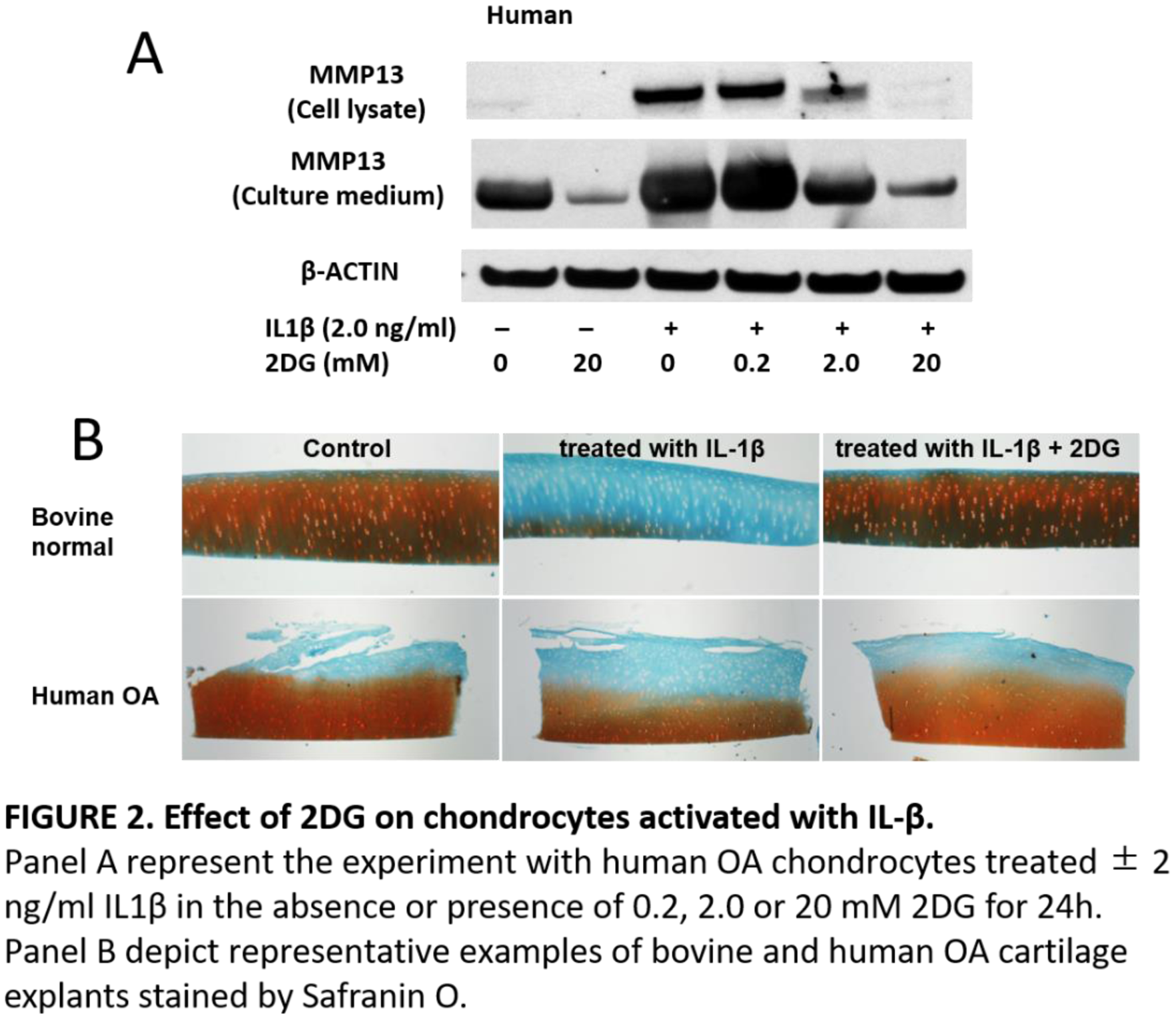
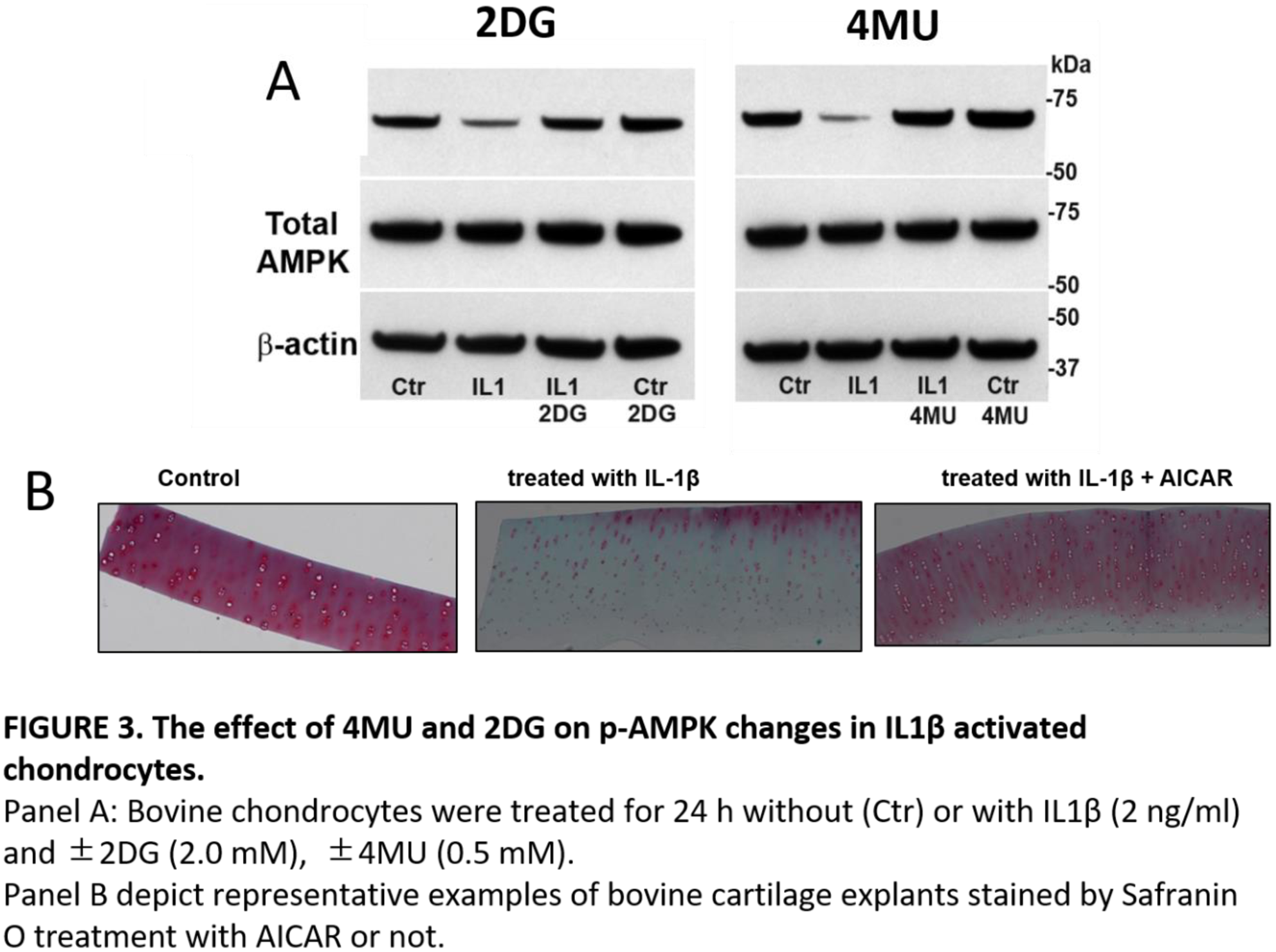
Conclusion: 4-MU and 2DG have chondroprotective effect by changing metabolism and upregulate AMPK. We propose that 4MU and 2DG become useful when these endogenous responses are not enough to rescue cells from a pro-catabolic phenotype.
REFERENCES:
[1]J. Biol. Chem. 291:12087, 2016; [2] J. Biol. Chem. 291:24105, 2016
Disclosure of Interests: KENYA TERABE: None declared, Nobunori Takahashi Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Ono, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB Japan, Ohashi Yoshifumi: None declared, Maeda Masataka: None declared, Warren Knudson: None declared, Cheryl Knudson: None declared, Toshihisa Kojima Grant/research support from: Chugai, Eli Lilly, Astellas, Abbvie, and Novartis, Consultant of: AbbVie, Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer, and Takeda, Naoki Ishiguro Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Asahi Kasei, Astellas, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Kaken, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Otsuka, Pfizer, Takeda, and Zimmer Biomet, Consultant of: Ono, Speakers bureau: Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Taisho Toyama