

Background: The primary therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is remission, assessed using validated composited measures. Currently, index-based remission frequently used in clinical practice are disease activity (CDAI) and disease activity score for 28 joints (DAS28). Generally, CDAI is believed more stringent than DAS28 in assessing clinical remission, however, this confirmation was mainly derived from trial results.
Objectives: To investigate the real-world performance of CDAI and DAS28 -erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in RA.
Methods: We reviewed consecutive RA patients who are receiving any disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARDs) in Keio University Hospital between 2016 and 2017 and collected medical information. We focused on the patients in CDAI remission and/or DAS28-ESR remission at the time of last visit, and analyzed their clinical characteristics.
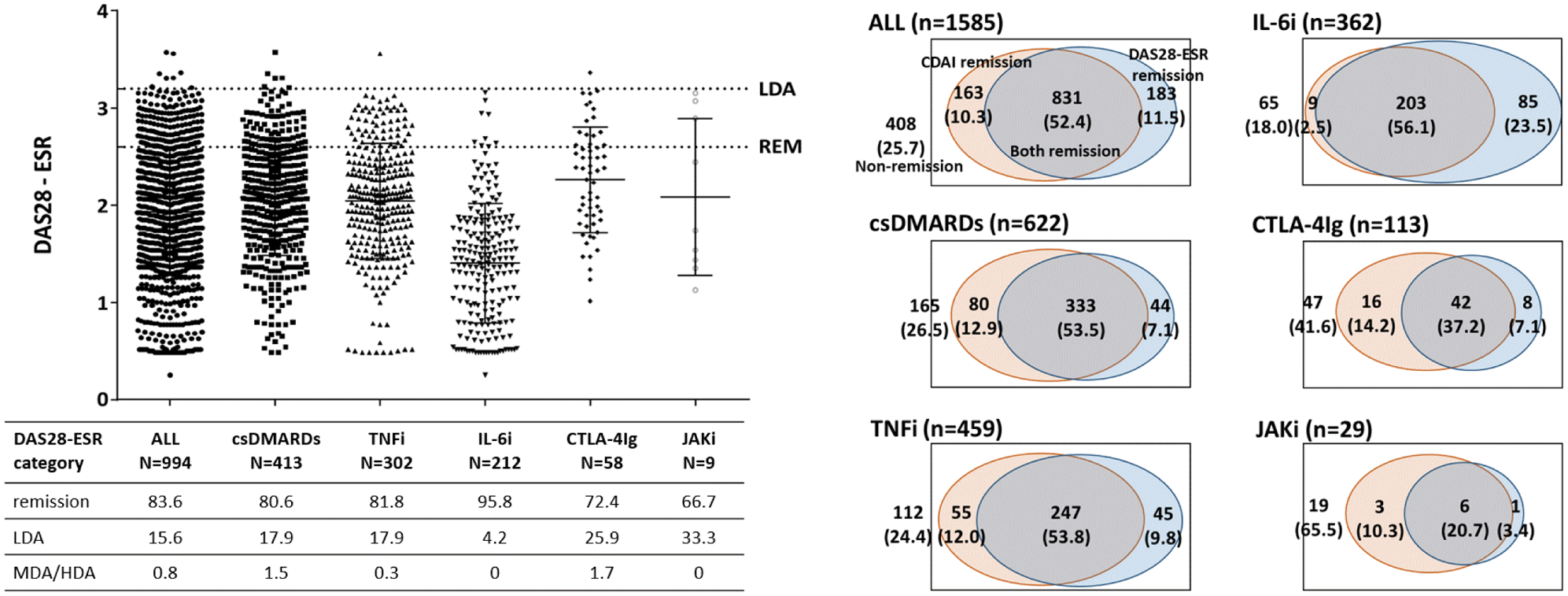
Results: A total of 1585 patients with RA were reviewed. Their characteristics were mean age of 64 years old, female of 84% and mean disease duration of 12.0 years. Current treatments were conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs alone, TNF inhibitors (TNFi), IL-6 receptor inhibitors (IL-6i), CTLA-4Ig, and JAK inhibitors (JAKi) in 39.2%, 29.0%, 22.8%, 7.1%, and 1.8% patients, respectively. Of them, 62.7% were in CDAI remission and 64% were in DAS28-ESR remission. Among patients in CDAI remission, the proportion of DAS28-ESR non-remission was 19.4% in those treated with csDMARDs, 18.2% treated with TNFi, 4.2% treated with IL-6i, 27.6% treated with CTLA-4Ig, and 33.3% treated with JAKi (Figure). In contrast, among patients in DAS28 remission, the proportion of CDAI non-remission was 11.7% in those treated with csDMARDs, 15.4% treated with TNFi, 29.5% treated with IL-6i, 16.0% treated with CTLA-4Ig, and 14.3% treated with JAKi. Venn diagrams of CDAI remission and DAS28-ESR remission demonstrated that more patients satisfied the CDAI remission criteria without satisfying the DAS28-ESR remission criteria than vice versa, except for those treated with IL-6i (Figure). Patients in CDAI remission and DAS28-ESR non-remission had higher C-reactive protein, ESR and comorbidity rates (0.37 vs 0.07 mg/dL, p<0.001; 45.7 vs 8.0 mm/h, p<0.001; 26.4 vs 18.0%, p=0.07, respectively), and those in CDAI non-remission and DAS28-ESR remission had worse patient-reported outcomes including patient global assessment and health assessment questionnaire-disability index (31.1 vs 9.5 mm, p<0.001; 0.82 vs 0.41, p<0.001, respectively). Patients in both CDAI and DAS28-ESR remission were apparently in better disease activity than those who met either criteria.
Conclusion: Assessing patients with two composite measures simultaneously is important to evaluate patients’ condition from view points of RA itself and comorbidities and adjust treatment appropriately.
REFERENCES:
[1] Smolen JS et al. T2T Expert Committee. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(4):631-7.
Disclosure of Interests: Satoshi Takanashi: None declared, Yuko Kaneko Speakers bureau: Dr. Kaneko reports personal fees from AbbVie, personal fees from Astellas, personal fees from Ayumi, personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Chugai, personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Eli Lilly, personal fees from Hisamitsu, personal fees from Jansen, personal fees from Kissei, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from Tanabe-Mitsubishi, personal fees from UCB, Tsutomu Takeuchi Grant/research support from: Eisai Co., Ltd, Astellas Pharma Inc., AbbVie GK, Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd, UCB Pharma, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma Corp., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Consultant of: Chugai Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Astellas Pharma Inc., Eli Lilly Japan KK, Speakers bureau: AbbVie GK, Eisai Co., Ltd, Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, AYUMI Pharmaceutical Corp., Eisai Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Gilead Sciences, Inc., Novartis Pharma K.K., Pfizer Japan Inc., Sanofi K.K., Dainippon Sumitomo Co., Ltd.