

Background: DISCOVER 1 and 2 are phase-3 trials of guselkumab (GUS, a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds the p19-subunit of IL-23) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In both trials, treatment with GUS led to significantly more improvement than placebo (PBO) in the primary endpoint (ACR20) as well as in other measures of arthritis and psoriasis at week (W) 24. 1,2
Objectives: To evaluate the effect of GUS on fatigue in DISC 1 & 2 using the patient reported outcome (PRO) FACIT-Fatigue, which has demonstrated content validity and strong psychometric properties in clinical trials. 3
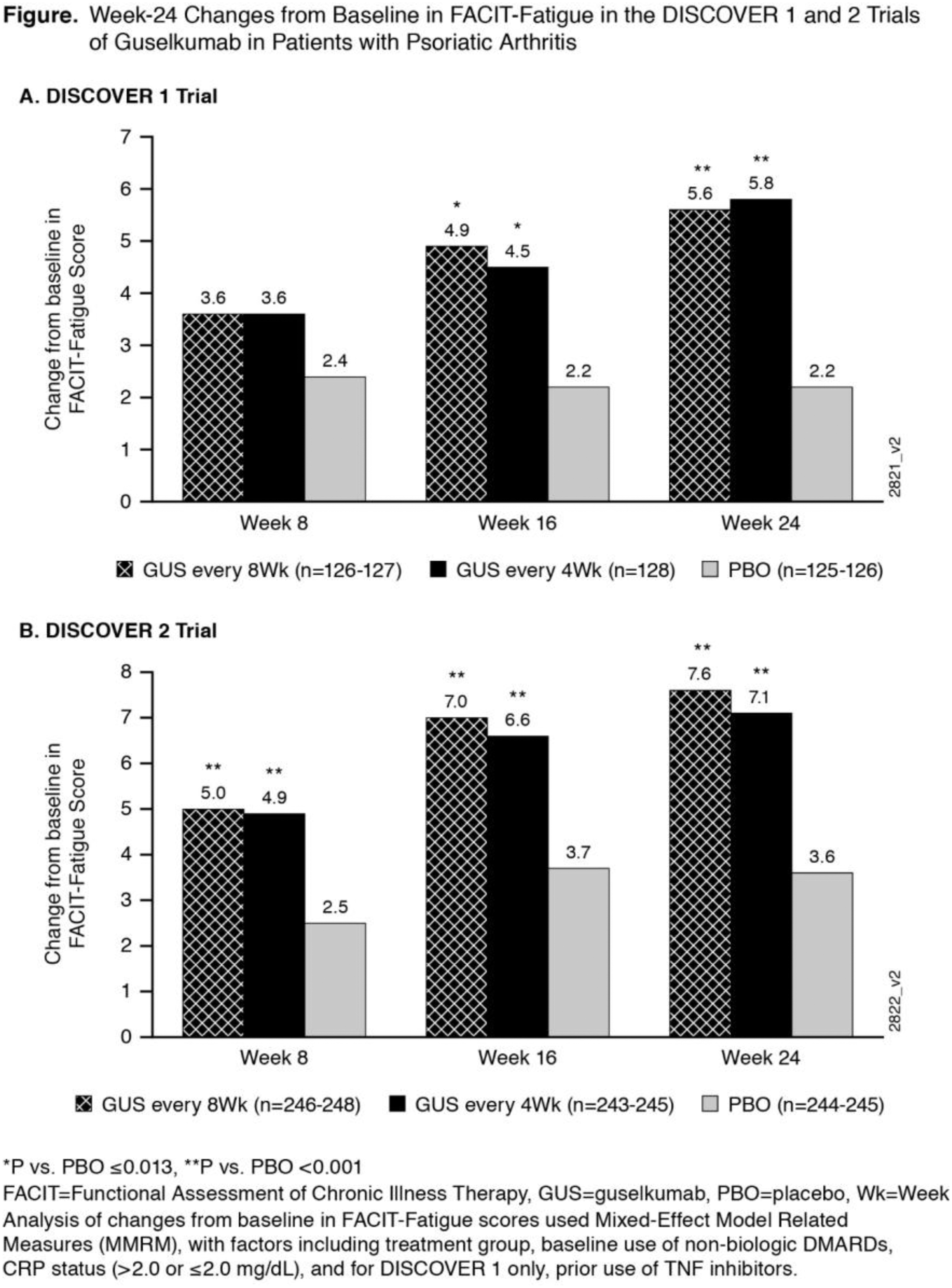
Methods: DISC 1 & 2 enrolled patients with active PsA, despite nonbiologic DMARDS and/or NSAIDS, who were mostly biologic naïve except for ~30% of patients in DISC 1 who had received 1-2 TNFi. Patients were randomized (1:1:1) in a blinded fashion to subcutaneous GUS 100 mg at W0 and W4 then every (q) 8W, to GUS 100 mg q4W, or to matching PBO. Concomitant treatment with select non-biologic DMARDS, oral corticosteroids, and NSAIDs was allowed. The FACIT-Fatigue is a 13-item PRO instrument assessing fatigue and its impact on daily activities and function over the past seven days, with a total score ranging from 0 to 52, higher score denoting less fatigue. A change of ≥4 points is identified as clinically meaningful. 3 Change from baseline in FACIT-Fatigue was analyzed using MMRM (Figure). Independence of treatment effect on FACIT-Fatigue from effect on ACR20 was assessed using Mediation Analysis 4 (Table) to estimate the natural direct effect (NDE) and natural indirect effect (NIE) mediated by ACR20 response.
Results: At baseline in DISC 1 & 2, the mean FACIT-fatigue scores (SD) were 30.4 (10.4) and 29.7 (9.7), respectively, indicating moderate to severe fatigue. In both DISCOVER 1 & 2 trials, treatment with GUS led to improvements in FACIT-Fatigue scores compared with PBO as early as W8 (Figure). 54%-63% of GUS patients compared with 35%-46% of PBO patients achieved clinically meaningful improvement (≥4 points) in FACIT-Fatigue (P≤0.003). Mediation analysis revealed that the independent treatment effects on fatigue after adjustment for ACR20 response (Natural Direct Effect [NDE], Table) were 12-36% in the q8W GUS dosing group and 69% -70% in the q4W GUS group.
Conclusion: In 2 phase-3 trials, treatment with GUS of patients with active PsA led to significant improvements compared to PBO in fatigue, including substantial effects on FACIT-Fatigue that were independent of the effects on ACR 20, especially for the q4W dosing group.
REFERENCES:
[1]Deodhar et al. ACR 2019. Abstract #807. Arthr Rheumatol. 2019;71 S10: 1386
[2]Mease et al. ACR 2019. Abstract # L13. Arthr Rheumatol. 2019;71 S10:5247
[3]Cella et al. Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes. 2019;3:30
[4]Valeri et al. Psychologic Meth. 2013;18:137
Mediation Analysis of the Effect of ACR 20 Response on Change from Baseline in FACIT-Fatigue Score at Week 24
| Effect |
GUS 100 mg q8W vs. PBO
|
GUS 100 mg q4W vs. PBO
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| DISCOVER 1 | NDE | 0.36 (-1.7, 2.4) | 2.60 (0.6, 4.5)* |
| NIE | 2.75 (1.4, 4.3)* | 1.20 (0.3, 2.3)* | |
| Total Effect | 3.12 (1.0, 5.2)* | 3.79 (1.9, 5.4)* | |
| Proportion Independent | 11.7% | 68.5% | |
| Proportion Mediated | 88.3% | 31.5% | |
| DISCOVER 2 | NDE | 1.44 (-0.1, 3.0) | 2.49 (1.0, 4.1)* |
| NIE | 2.53 (1.6, 3.6)* | 1.09 (0.4, 1.9)* | |
| Total Effect | 3.97 (2.4, 5.5)* | 3.58 (2.1, 5.0)* | |
| Proportion Independent | 36.3% | 69.7% | |
| Proportion Mediated | 63.7% | 30.3% |
*P vs placebo<0.02
NDE=Natural Direct Effect (effect on FACIT-F beyond effect on ACR20), NIE=Natural Indirect Effect (effect on FACIT-F mediated by ACR20)
Mediation analysis 4 used linear and logistics regression models with Bootstrapping method
Acknowledgments: None
Disclosure of Interests: Philip Helliwell: None declared, Proton Rahman Grant/research support from: Janssen and Novartis, Consultant of: Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer., Speakers bureau: Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Atul Deodhar Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myer Squibb (BMS), Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myer Squibb (BMS), Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Alexa Kollmeier Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Elizabeth C Hsia Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Bei Zhou Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Xiwu Lin Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Chenglong Han Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Philip J Mease Grant/research support from: Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB – grant/research support, Consultant of: Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB – consultant, Speakers bureau: Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, BMS, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB – speakers bureau