

Background: Autoimmunity to citrullinated autoantigens forms a critical component of disease pathogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Presence of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) in patients has high diagnostic value. Recently, several citrullinated antigen specific CD4+T cells have been described. However, detailed studies of their T-cell receptor usage and in-vivo profile suffer from the disadvantage that these cells are present at very low frequencies. In this context, we here present a pipeline for TCR repertoire analysis of antigen-specific CD4+T cells from RA patients, including both citrulline and influenza (control) specificities using in-vitro peptide challenge induced-cell expansion.
Objectives: To enable studies of the T cell repertoire of citrullinated antigen-specific CD4+T cells in rheumatoid arthritis
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (n=7) and synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs) (n=5) from HLA-DR*0401-postive RA patients were cultured in the presence of citrullinated Tenascin C peptide cocktails or influenza peptides (positive control). Citrulline reactive cells were further supplemented with recombinant human IL-15 and IL-7 on day 2. All cultures were replenished with fresh medium on day 6 and rIL-2 was added every 2 days from then. Assessment of proportion of peptide-HLA-tetramer positive cells was performed using flow cytometry whereby individual antigen-specific CD4+T cells were sorted into 96-well plates containing cell lysis buffer, followed by PCR-based alpha/beta TCR sequencing. TCR sequencing data was demultiplexed and aligned for TCR gene usage using MiXCR. Some tetramer positive cells were sorted into complete medium containing human IL-2 and PHA for expansion of antigen-specific cells. Cells were supplemented with irradiated allogenic PBMCs (30 times number of antigen specific cells). Clones of antigen specific CD4+T cells were further subjected to tetramer staining to confirm expansion of cells.
Results: As evidenced by increase in frequency of tetramer positive CD4+T cells, in vitro peptide stimulation resulted in expansion of both influenza specific (
In-vitro expansion of antigen specific CD4+T cells:
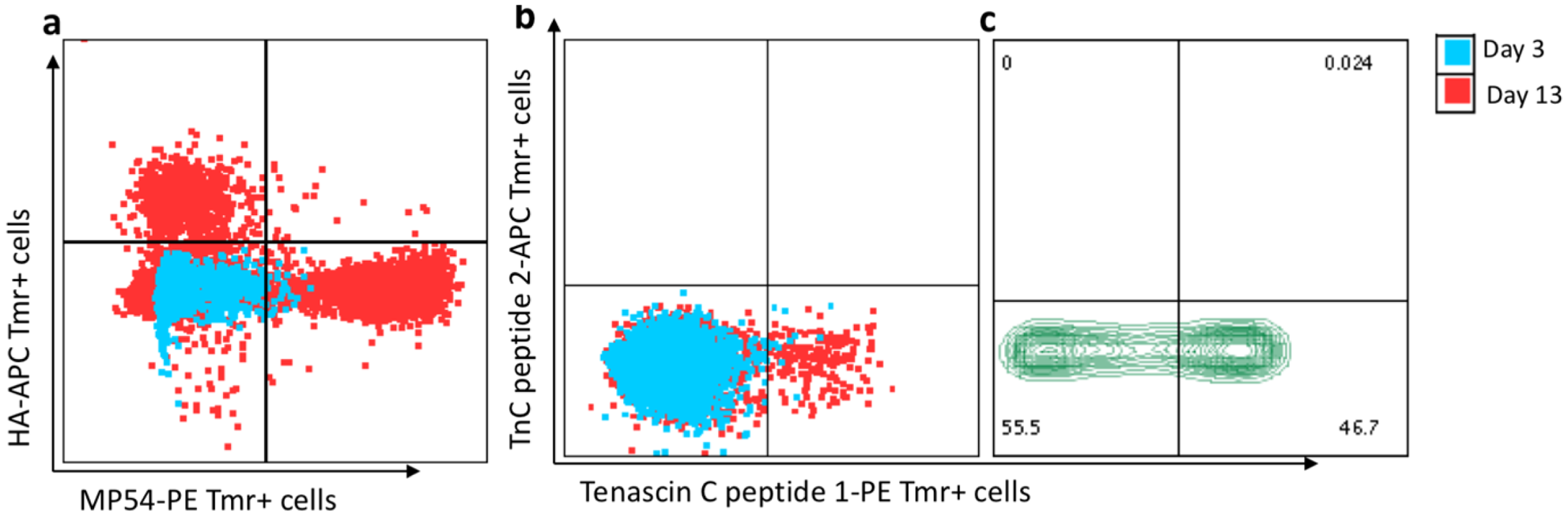
Conclusion: This method provides a highly suitable approach for investigating TCR specificities of antigen specific CD4+T cells under conditions of low cell yields. Building on this dataset will allow us to assess specific features of TCR usage of autoreactive T cells in RA.
PBMCs were cultured in presence of (a) influenza (HA, MP54) and (b) citrullinated tenascin peptides. The proportion of antigen specific CD4+T cells was assessed using HLA-class II tetramer staining. We observed an increase in frequency of (a) Infleunza specific cells (red dots in upper left and lower right quadrants) and (b) citrullinated tenascin C specific cells (red dots in lower right quadrant), at day 13 post culture as compared to day 3. (c) Sorting of citrullinated tenascin specific CD4+T cells, followed by PHA expansion resulted in visible increase in proportion of citrullinated tenascin specific CD4+T cells.
Disclosure of Interests: Ravi kumar: None declared, Niyaz Yoosuf: None declared, Christina Gerstner: None declared, Sara Turcinov: None declared, Karine Chemin: None declared, Vivianne Malmström Grant/research support from: VM has had research grants from Janssen Pharmaceutica