

Background: Mechanistic differences between protein biologics are poorly understood. HLA-DRB1 alleles containing the shared epitope (SE), which are strongly associated with RA, are present in 70–80% of anti-citrullinated protein antibody+ patients (pts) with RA. 1 Numerically higher efficacy responses with abatacept (ABA) vs adalimumab (ADA) were reported after 24 wks of treatment (Tx) in pts with early seropositive RA, specifically in SE+ pts. 2
Objectives: To prospectively explore the relationship between HLA-DRB1 SE genotype and the effects on disease activity after switching from ADA to ABA after completing 24 wks of initial Tx in biologic-naïve pts with early active RA.
Methods: This head-to-head exploratory trial (NCT02557100) enrolled seropositive (anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide 2+ and RF+) adults with early (≤12 mos of symptoms), moderate-to-severe RA (ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria). Pts were randomised 1:1 to SC ABA 125 mg/wk or SC ADA 40 mg every 2 wks (both with stable, oral MTX wkly) for 24 wks (single-blind period). At Wk 28, ADA-treated pts were switched to open-label (OL) ABA, following a 6-wk washout period (switch arm); ABA-treated pts continued treatment with ABA in an OL manner (non-switch arm). Pts were grouped by SE status based on HLA-DRB1 genotype (−, no SE allele; +, ≥1 SE allele). Clinical efficacy was assessed to Wk 48 to determine the proportion of ACR20/50/70 responders and DAS28 (CRP) remitters in each arm. Safety was analysed throughout the trial and up to 8 wks post last dose.
Results: All 40 ABA-treated and 36/40 ADA-treated pts entered the OL ABA period; 3 (lost to follow up n=2, other n=1) and 1 (pt request to discontinue) pts, respectively, discontinued during the OL period. Baseline characteristics were balanced
2
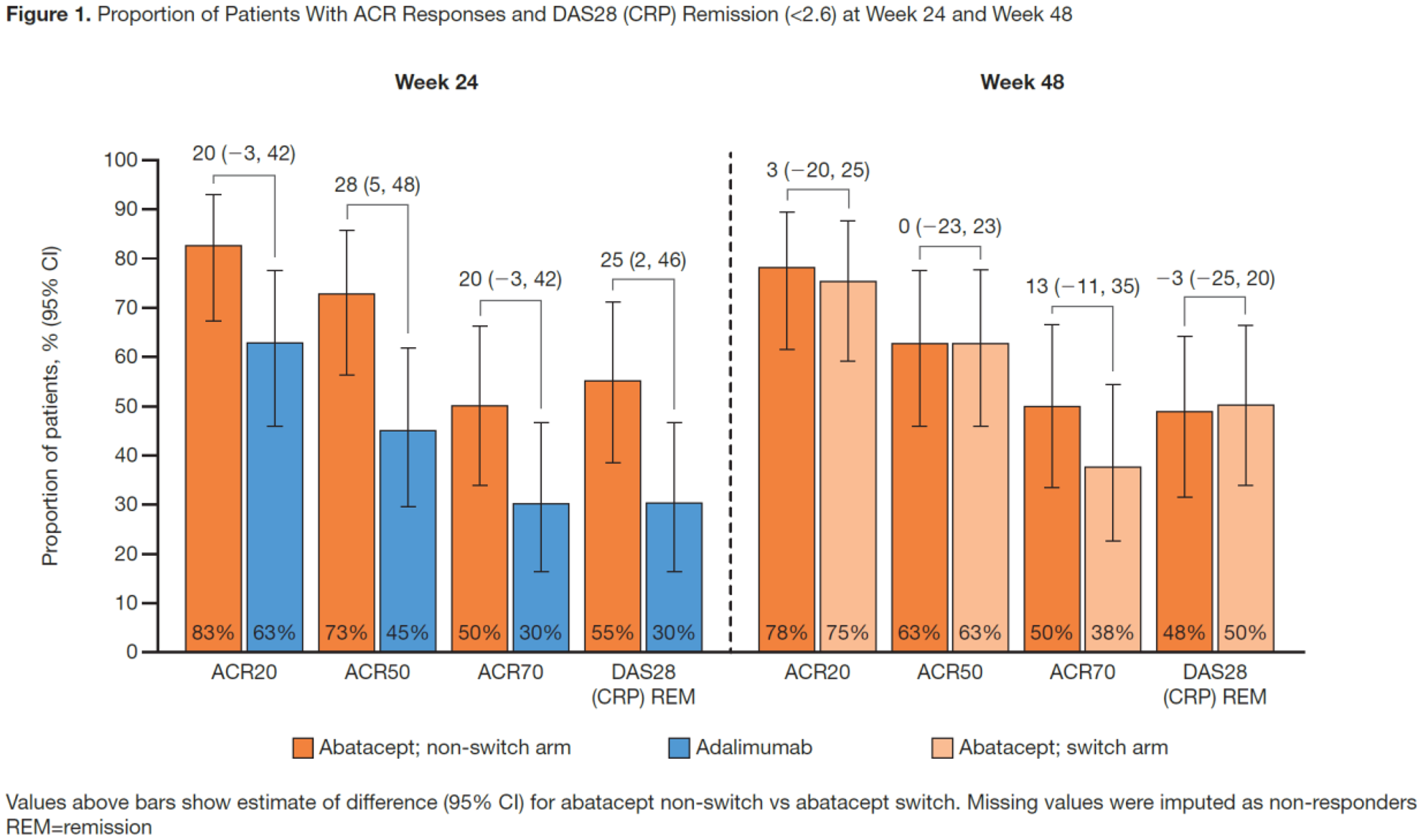
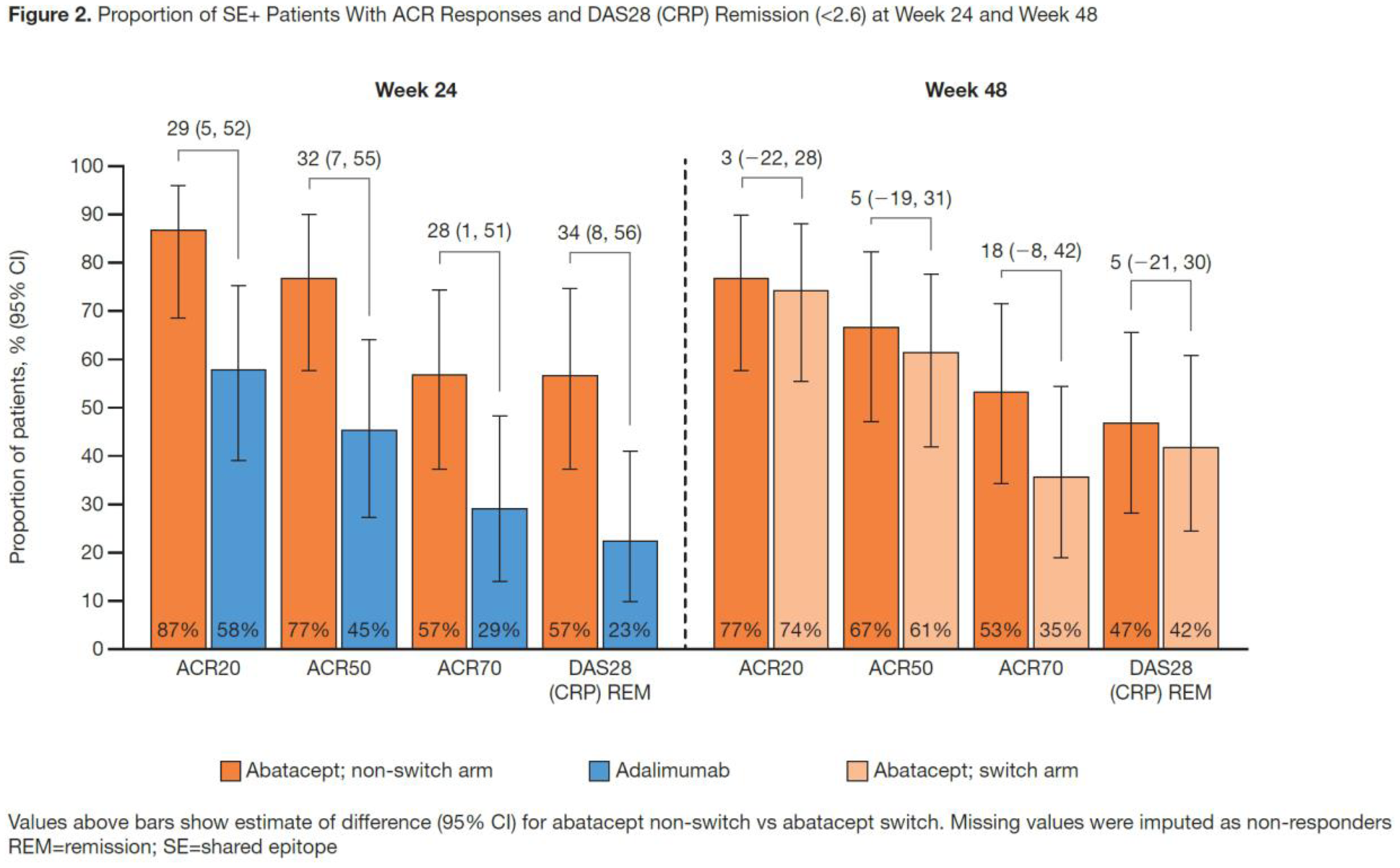
; mean (SD) RA duration was 5.5 (2.6) mos. The greater efficacy responses seen with ABA vs ADA to Wk 24
2
were sustained at Wk 48 in the non-switch arm; in the switch arm, the efficacy responses generally increased over the OL period to Wk 48. Specifically, in both the overall population (
Conclusion: In this seropositive early RA population, particularly in the SE+ subgroup, a trend towards numerically higher and sustained efficacy responses by stringent definitions was seen in the abatacept non-switch arm at Wk 48; trends towards further improvement were observed in the adalimumab-to-abatacept switch arm.
REFERENCES:
[1]Terao C, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015; 67 :1744–50.
[2]Rigby W, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019: 78 :abstract 263.
Acknowledgments: Marianne Peluso (protocol manager); medical writing: Lola Parfitt (Caudex; funding: BMS)
Disclosure of Interests: William Rigby Grant/research support from: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Consultant of: AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Pfizer, Jane Buckner Grant/research support from: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, S. Louis Bridges, Jr.: None declared, Marleen Nys Shareholder of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Sheng Gao Shareholder of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Martin Polinsky Shareholder of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Neelanjana Ray Shareholder of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Vivian Bykerk: None declared