

Background: The pathogenesis of primary sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) is multifactorial. Self-antigen-driven responses perform a vital function in the development of autoimmune diseases [1]. B cells, only 20-25% of total infiltrating cells in labial glands, are the cellular basis for spontaneous antibody production [2].Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified Blimp-1 as a susceptibility gene for autoimmune diseases and played an important role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases [3].
Objectives: To investigate the expression and effect of B lymphocyte induced maturation protein 1 (Blimp-1) in pSS and the correlation of Blimp-1 with B cell subsets and clinical features.
Methods: The PRDM1 mRNA expression in B lymphocyte and labial gland were examined by RT-PCR. The levels of B cell subsets were examined by flow cytometry. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were used to examine the invasion degree of lymph cell and Blimp-1 distribution, respectively. The correlation of PRDM1 mRNA with B cell subsets and clinical indicators were also analyzed.
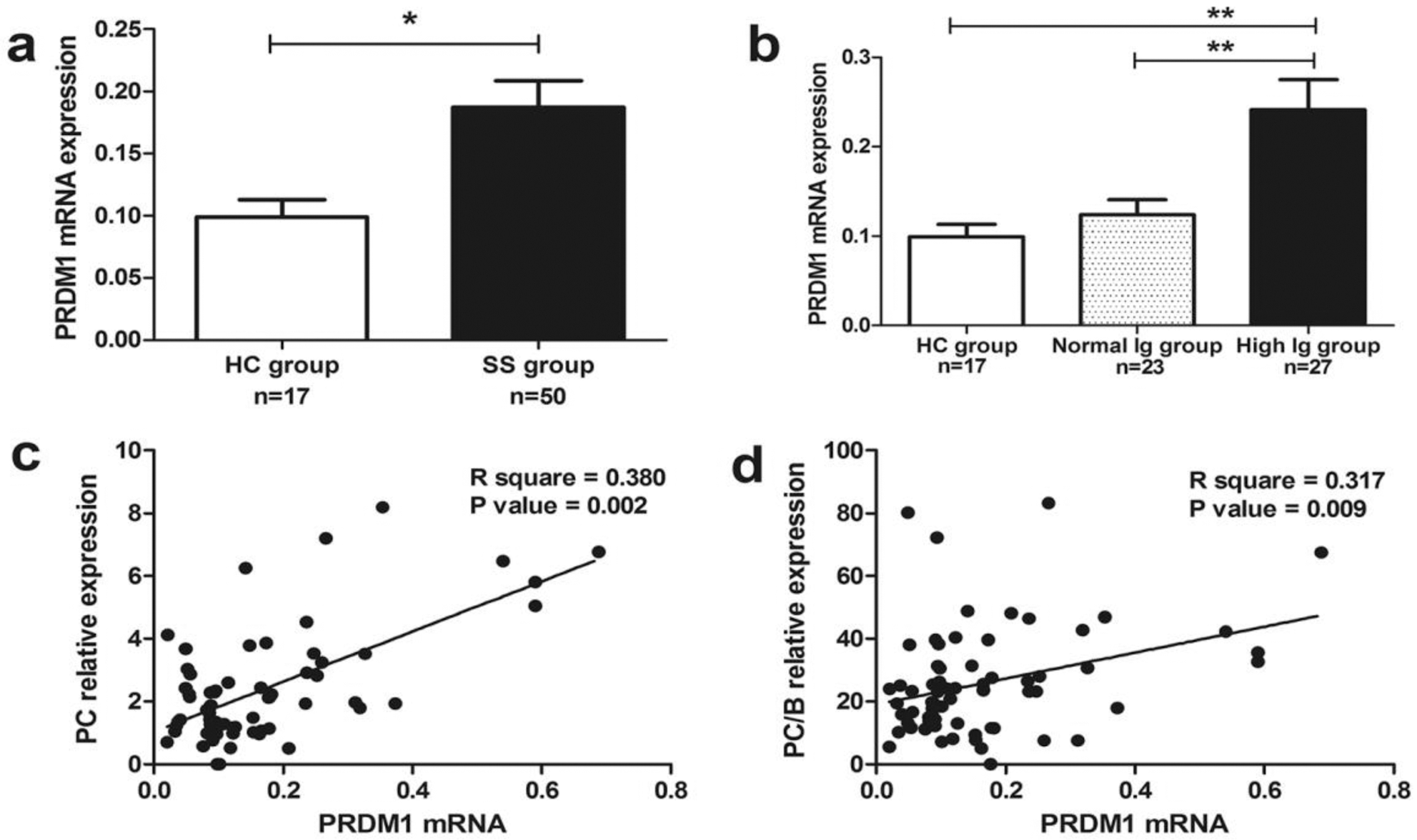
Results: The levels of PRDM1 mRNA expression of B cells were significantly higher in SS than in healthy controls (HC) and which were also significantly higher in the high immunoglobulin (Ig) group than that in normal Ig group (
P
<0.02,
(a-b) RT-PCR showed that PRDM1 mRNA expression in SS patients and HC. (c-d) Correlation between PRDM1 mRNA expression and PC and PC/B.
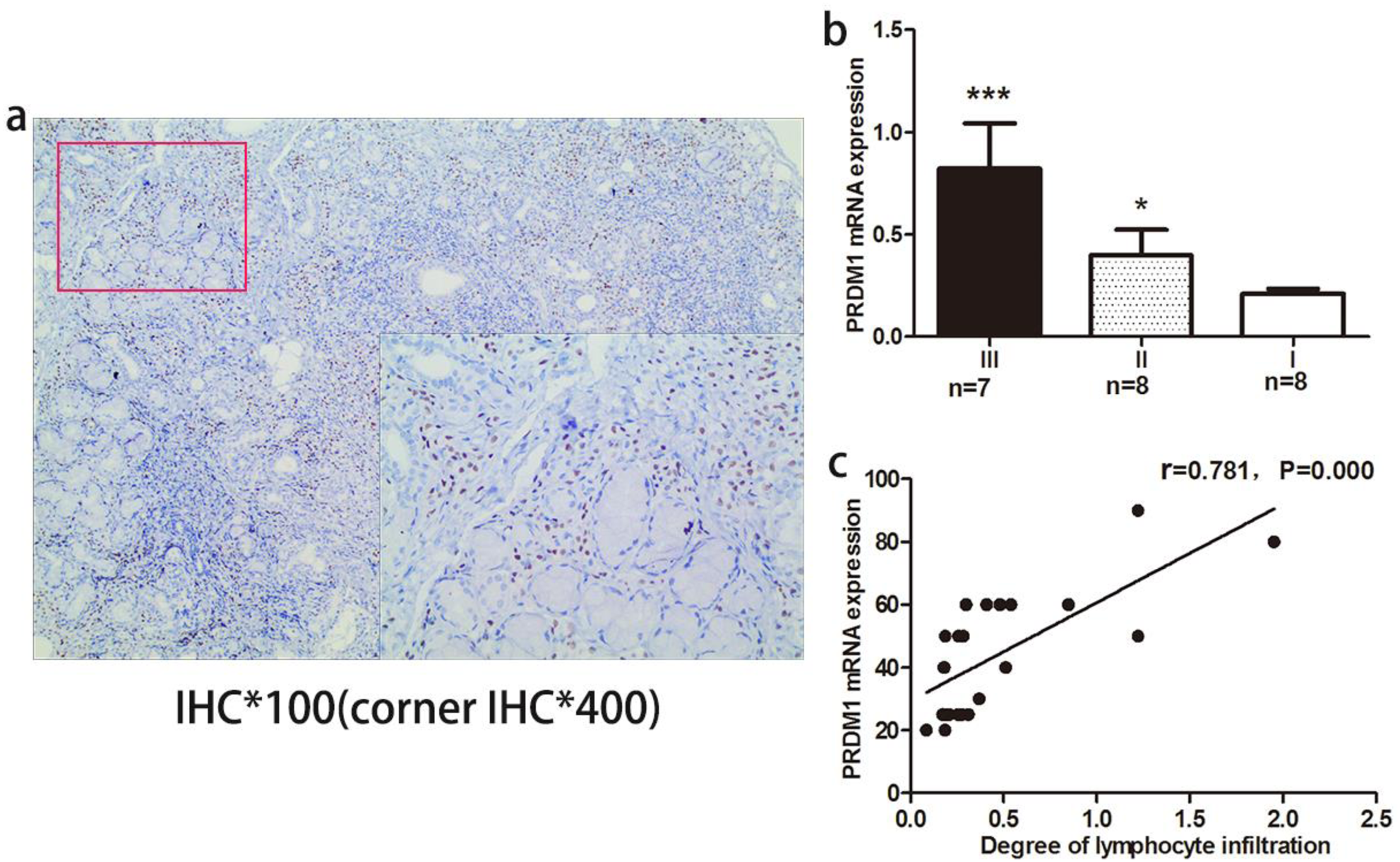
(a) Expression of Blimp-1 in labial glands of sjögren’s syndrome. (b) PRDM1 mRNA levels in different invasion degree of lymph cell group. (c) Correlation between PRDM1 mRNA expression and invasion degree of lymph cell. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.
(a-b) RT-PCR showed that PRDM1 mRNA expression in different usage of glucocorticoids. (c) Correlation between PRDM1 mRNA expression and different glucocorticoid usage. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
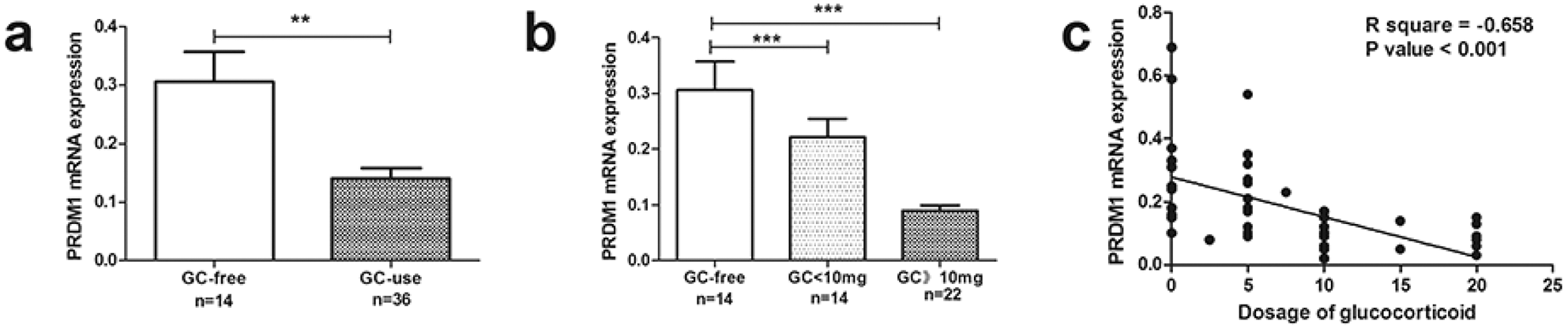
Conclusion: Blimp-1 displayed high expression in SS, which could affect pSS disease activity. SS activity is suppressed by glucocorticoid which might be through inhibition of Blimp-1.
REFERENCES:
[1]Kapsogeorgou EK, Abu-Helu RF, Moutsopoulos HM, Manoussakis MN (2005) Salivary gland epithelial cell exosomes: A source of autoantigenic ribonucleoproteins. Arthritis Rheum 52(5):1517-21.
[2]Arneth BM (2019) Impact of B cells to the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):128.
[3]Bönelt P, Wöhner M, Minnich M et al (2019) Precocious expression of Blimp-1 in B cells causes autoimmune disease with increased self-reactive plasma cells. EMBO J 38(2). pii:e100010.
Clinical characteristics of pSS and HC.
| HC(n=17 ) | pSS(n=50 ) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (Male/Female) | 0/17 | 0/50 |
| Age(x± s ) | 45.24±18.55 | 46.8±11.05 |
| Xerostomia(positive/negative) | 0/17 | 43/7 |
| Keratoconjunctivitis sicca | 0/17 | 35/15 |
| Arthralgia | 0/17 | 32/18 |
| Fatigue | 0/17 | 18/32 |
| ESSDAI(x± s ) | - | 2.78±1.61 (0~7) |
| ESSPRI(x± s ) | - | 3.3±1.39 (1~6) |
| ANA(positive/negative) | - | 49/1 |
| SSA | - | 49/1 |
| SSB | - | 18/32 |
pSS: primary sjögren ‘s syndrome; HC: Healthy controls; ESSDAI: The European League Against Rheumatism Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index; ESSPRI: EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index.** P<0.01,*** P<0.001.
Acknowledgments : This study was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81871271).
Disclosure of Interests : None declared