

Background: Behçet’s disease (BD) is a chronic, multi-system vasculitic disease. It is characterized with relapsing episodes of oro-genital ulcers accompanied by cutaneous lesions, ocular symptoms, arthropathy, vascular thrombosis, central nervous system, gastrointestinal & cardiopulmonary involvements. Oral ulcers are frequently the first disease manifestationOral and genital ulcers cause pain and interfere with the quality of life. They may lead to difficulty in swallowing and walking. Most of them can be managed with topical glucocorticoids. Up till now there is no study discussed the effect of combined local therapy on oral ulcers in BD. 1,2
Objectives: To evaluate the effectiveness of combined local therapy (colchicine, steroid, antibiotic and anesthetic) on oral ulcers in BD
Methods: This study included 44 Patients who had Behçet’s disease (according to International Study Group criteria) with active oral ulcers (at least three times in the previous 12-month period) Patients were excluded if they had active major organ involvement in the last 6 months. Patients with depilating diseases also were excluded.
Patients were randomly divided into two equal groups; group I received combined local therapy (lidocaine HCL 2.0% gel mixed with grinded tablet of 5 mg prednisone and grinded tablet of 0.6 mg colchicine). Group II received combine local therapy (lidocaine HCL 2.0% gel mixed with grinded tablet of 5 mg prednisone). Local treatments were applied to the lesions 3 times per day until healing of the ulcer (advised not to eat or drink for 30 minutes after application). All other topical medications were stopped during this study.
All patients were assessed with Oral ulcer severity score (OUSS), Behçet’s Disease Quality of Life score (BD-QoL), Medical Outcomes Study Questionnaire Short Form 36 Health Survey (SF-36) at baseline and after 24 weeks.
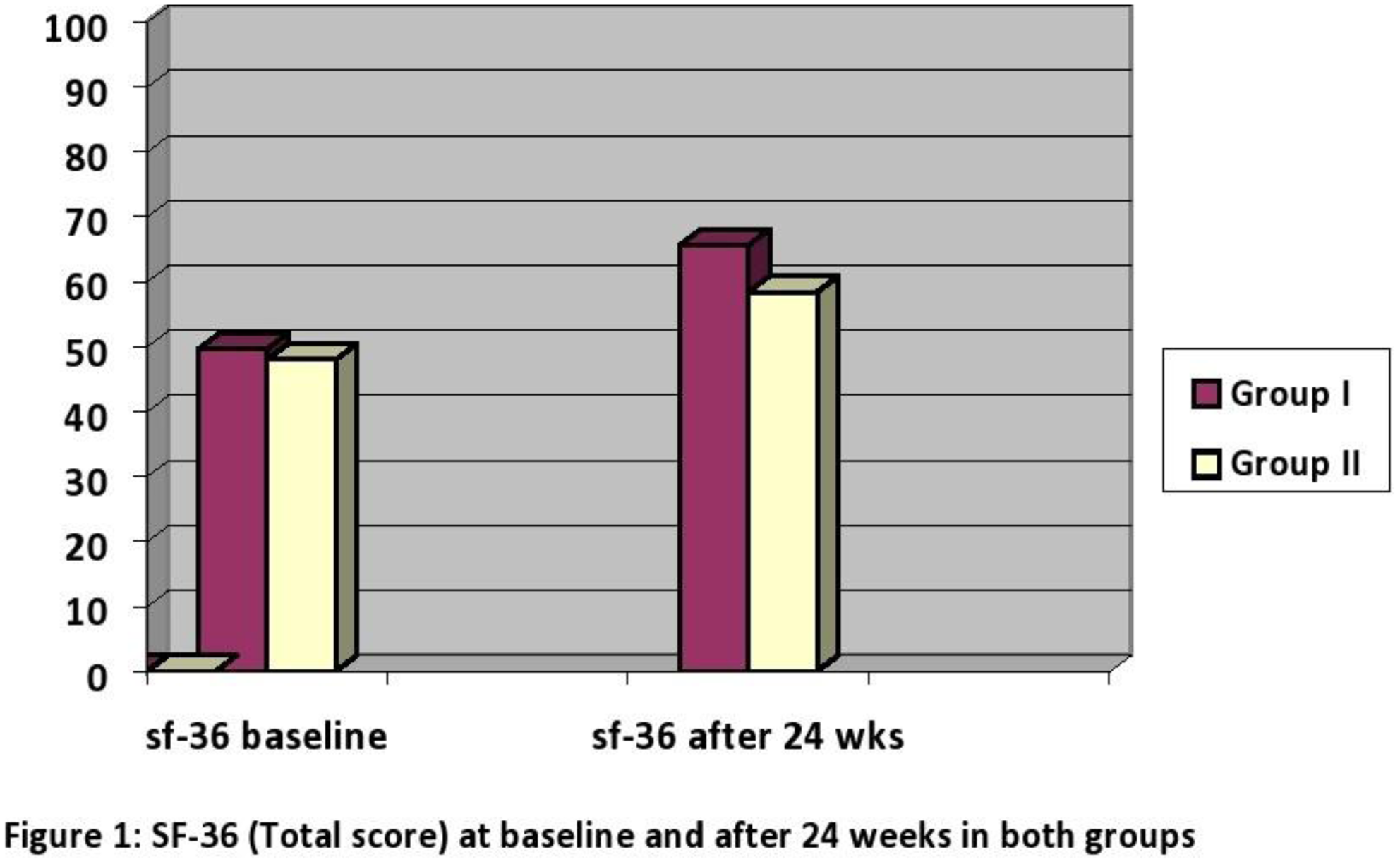
Results: Thirty eight patients had completed this study; (20 in Group I & 18 in Group II). There were no significant differences between the 2 groups in both demographic data &educational status. At baseline there was no significant difference between both groups regarding all assessment measures. There was significant improvement (P<0.05) in both groups regarding OUSS, BD-QoL, SF-36 after 24 weeks. There was significant better improvement (P<0.05) in group I than in group II in all assessment measures (except ulcer free periods and sites). The results of the study are summarized in
A comparison of the individual ulcer characteristics in both groups at baseline and after 24 weeks
|
Ulcer
| Group I baseline | Group II baseline | Group I after 24 weeks | Group II after 24 weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 13.6 ±3.5 | 12.9 ±2.3 | 8.2 ±1.5* ¶ | 10.3 ±1.7* |
| Size | 11.8 ±3.3 | 12.5 ±2.4 | 7.6 ±1.8* ¶ | 9.6 ±1.2* |
| Duration | 6.7 ±1.1 | 6.6 ±1.7 | 4.5 ±1.9* ¶ | 5.5 ±1.3* |
| Ulcer-free period | 4.7 ±0.9 | 5.1 ±1.5 | 5.7 ±1.1* | 5.9 ±0.7* |
| Pain | 8.7 ±1.2 | 8.6 ±1.4 | 5.3 ±1.5* ¶ | 6.7 ±1.1* |
| Site | 4.9 ±0.8 | 5.1 ±1.2 | 3.8 ±0.6* | 4.2 ±0.9* |
*Significant improvement after 24 weeks of the study
¶ Significant difference between the two studied groups
Conclusion: Combined local therapy (colchicine, steroid, antibiotic and anesthetic) is an effective method in management of oral ulcers in BD.
REFERENCES:
[1]Taylor J, Glenny AM, Walsh T, et al. Interventions for the management of oral ulcers in Behçet’s disease (Review). 2014;(9):CD011018.
[2]Hatemi G, Mahr A, Ishigatsubo Y et al. Trial of Apremilast for Oral Ulcers in Behçet’s Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381(20):1918-1928.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared