

Background: Sarcopenia has been defined as a loss of muscle mass and consequently of muscle function. In patients affected by osteoarthritis (OA) a more likely and accelerated development of sarcopenia has been reported. The SARC-F is a simple sarcopenia screening tool includes five assessment items: strength, assistance walking, rising from a chair, climbing stairs, and falls. SARC-F ≥ 4 is defined as sarcopenia.
Objectives: The present study aimed to examine the utility of SARC-F in the patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Methods: Patients with radiographic and clinic evidence of tibiofemoral OA (Kellgren-Lawrence score ≥2) were included. Sarcopenia were identified using the SARC-F scale. Patients with a total score 4 and higher than 4 were classified as having sarcopenia. Patients were assessed by The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), four-meter walking test, hand grip test, shortened version of the falls efficacy scale-international (the short FES-I) and EuroQol- 5 Dimension (EQ-5D). A multiple linear regression model was used to identify independent predictors of SARC-F.
Results: A total 76 patients with median age 61 ranged 55 to 78 years old (72.4% female) were screened in this study (
Summary Table of Characteristics of sarcopenic vs non-sarcopenic patients with knee OA
| Measures |
Sarcopenic patients with knee OA (n:47
)
|
Non-Sarcopenic patients with knee OA (n:29
)
| p value φ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean(SD) | 62.7(6.9) | 59.3 (6.9) | 0.294 |
| BMI, mean(SD) | 27.84 (9.56) | 28.54 (8.38) | 0.327 |
| WOMAC, mean(SD) | 43.52 (10.83) | 28.06 (14.9) | 0.001* |
| GRADE (K-L ) med (min-max) | 3(2-4) | 2(2-4) | 0.008* |
| Hand Grip, mean(SD) | 20 33 (4.89) | 28.22 (7.13) | 0.001* |
| 4 m Walking Test , mean(SD) | 11.88 (4.24) | 9.55 (4.30) | 0.001* |
| EQ-5D, mean(SD) | 9.41 (1.52) | 7. 13 (1.75) | 0.001* |
| EQ-5D-VAS, mean(SD) | 44.31 (14.12) | 66.90 (16.25) | 0.001* |
| Short FES-I, mean(SD) | 18. 06 (9.45) | 9.04 (5.32) | 0.001* |
| Number of falls the past year, mean(SD) | 4.01 (1.24) | 3.14 (2.74) | 0.674 |
φ Mann Whitney U test; *p< 0.05; BMI, Body mass index; WOMAC, Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index EQ-5D, EuroQol-5 Dimension; FES-I, Falls Efficacy Scale-International
Multiple linear regression analysis for SARC-F
| β | t | P value |
95% Confidence Interval
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Walking Speed | 0.11 | 1.20 | 0.23 | -0.31/ 0.12 |
| Hand Grip | -0.35 | -1.73 | 0.04 | -0.20 / 0.01 |
| WOMAC-Function | 0.26 | 2.31 | 0.01 | 0.00 / 0.05 |
| Short FES-I | 0.18 | 1.96 | 0.01 | 0.04 / 0.01 |
| EQ-5D | 0.22 | 2.29 | 0.02 | 0.02 / 0.39 |
|
EQ-5D VAS
| -0.24 | -2.73 | 0.001 | -0.04 / -0.00 |
WOMAC, Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index, EQ-5D, EuroQol-5 Dimension; FES-I, Falls Efficacy Scale-International
Sarcopenic vs non-sarcopenic patients according to sex
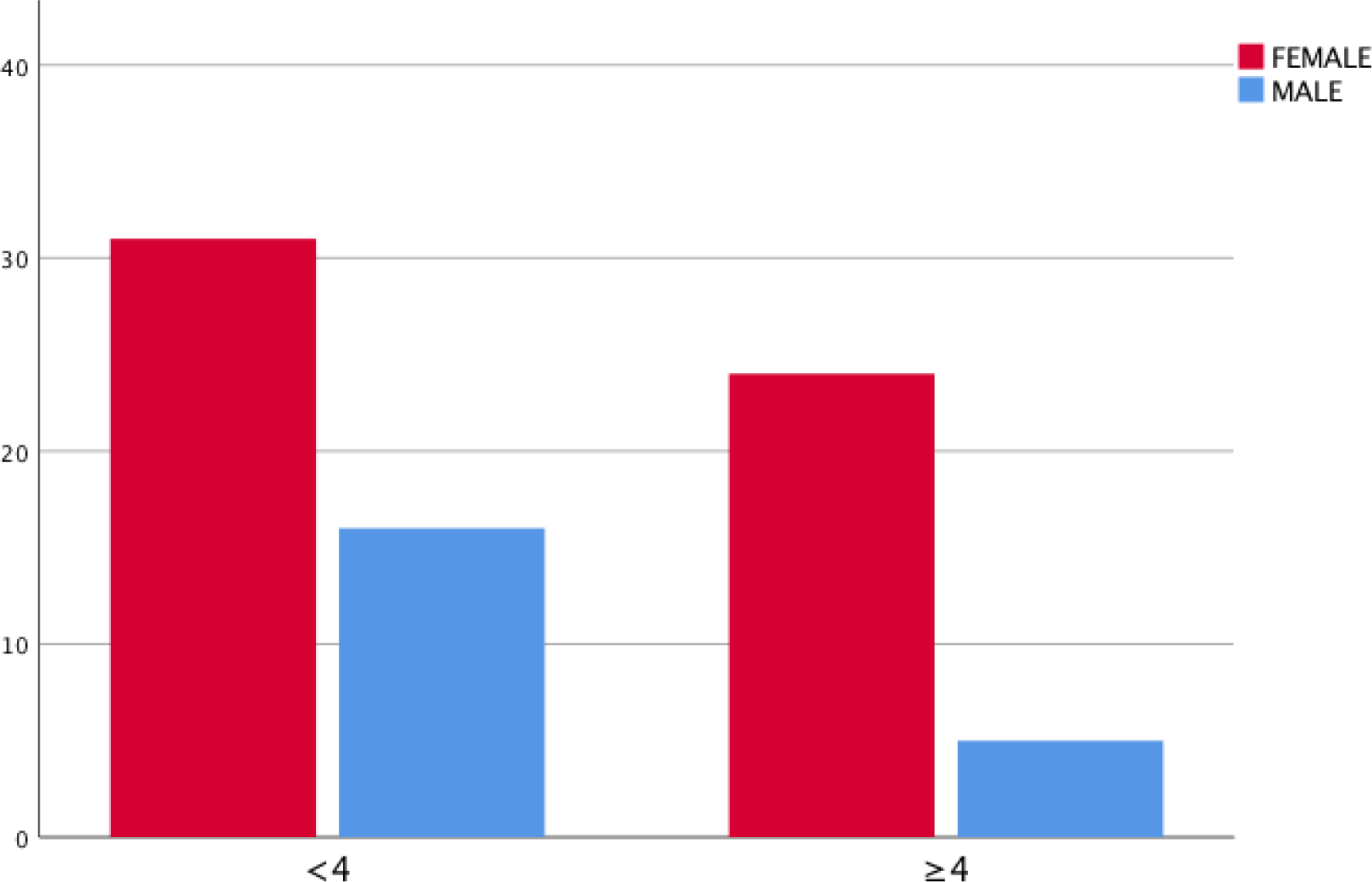
Conclusion: In this study, sarcopenia defined by the SARC-F questionnaire has a predictive value of clinical characteristics of patients to predict sarcopenia parameters and poor physical performance in patients with knee OA.
REFERENCES:
[1]Papalia, R., Zampogna, B., Torre, G., Lanotte, A., Vasta, S., Albo, E., ... & Denaro, V. (2014). Sarcopenia and its relationship with osteoarthritis: risk factor or direct consequence?. Musculoskeletal surgery , 98 (1), 9-14.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared