

Background: Patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have an increased susceptibility to seasonal influenza and its complications. 1 In light of the COVID-19 pandemic, there is a need to better understand acute respiratory viral RNA infections, such as influenza, in pts with RA.
Objectives: To present a comprehensive summary of data on influenza adverse events (AEs) occurring in the tofacitinib RA clinical programme.
Methods: Influenza AEs were evaluated in pts with RA from 21 Phase (P)1–3b/4 trials and two open-label, long-term extension (LTE) studies from 2005–2019. These were analysed as two cohorts: P2–3b/4 cohort (pts who received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily [BID] as monotherapy or with conventional synthetic [cs]DMARDs, adalimumab, methotrexate or placebo, in P2–3b/4 controlled studies) and Overall cohort (pts who received ≥1 tofacitinib dose, as monotherapy or with csDMARDs, in P1–3b/4 and LTE studies; data were summarised by average tofacitinib dose [average tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID based on average total daily dose of <15 or ≥15 mg, respectively]). Incidence rates (IRs; unique pts with events/100 pt-years of exposure; censored at day of first event or up to last dose +28 days) were evaluated for influenza AEs, influenza complication AEs, influenza-like illness (all composites of several MedDRA preferred/verbatim terms) and overall influenza AEs (composite of all preferred/verbatim terms included under influenza AEs, influenza complication AEs and influenza-like illness). In the Overall cohort, the incidence of serious non-influenza AEs within 28 days of the start of an overall influenza AE and time taken to resolution of overall influenza AEs by action taken were summarised descriptively.
Results: In total, 7964 pts were included; 517 (6.5%) pts reported overall influenza AEs, three of which occurred outside the risk period. In the P2–3b/4 cohort (N=6690), IRs for influenza AEs, influenza-like illness and overall influenza AEs generally appeared similar across treatment arms (
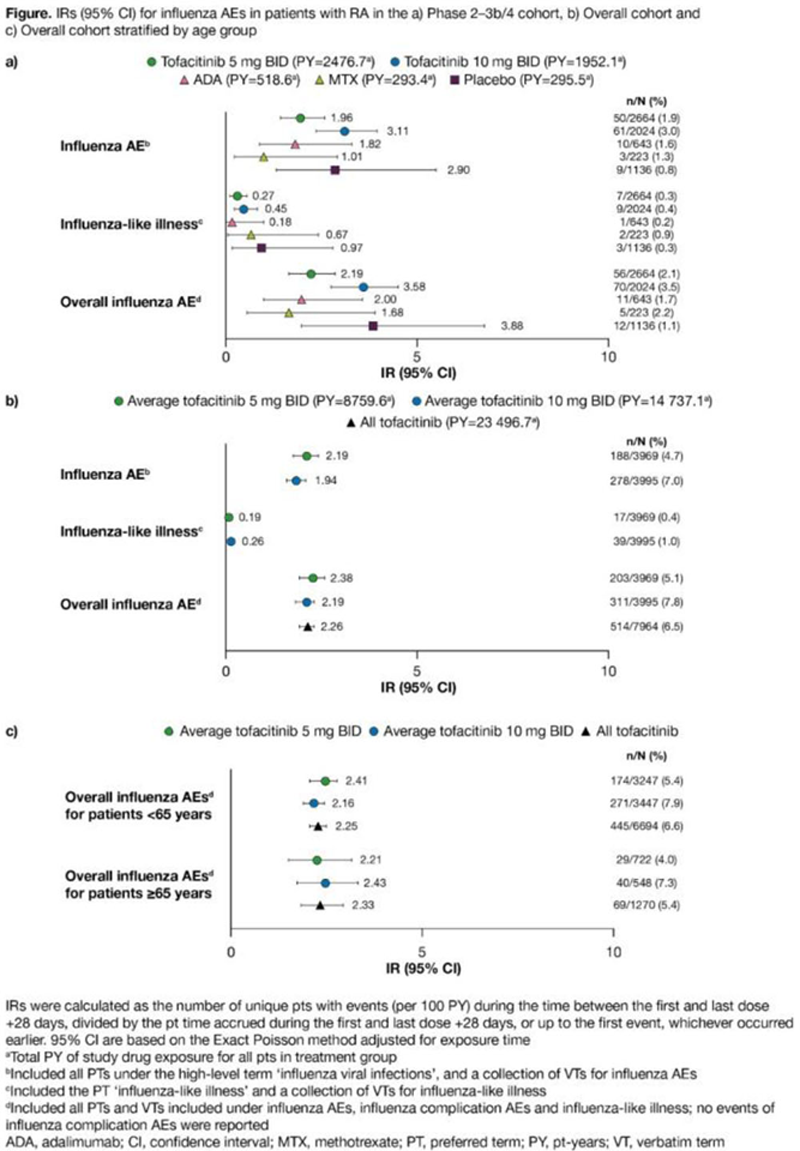
Conclusion: This post hoc analysis of influenza AEs across the tofacitinib RA clinical programme, over 14–15 influenza seasons, showed generally similar rates between treatment groups, and between tofacitinib doses and pt age groups. Limitations include varying exposure across treatment arms in the P2–3b/4 cohort. Most influenza AEs were non-serious (98.3%), and were not associated with changes to tofacitinib treatment.
REFERENCES:
[1]Blumentals et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2012; 13: 158.
Acknowledgements: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Kirsten Woollcott, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer Inc.
Disclosure of Interests: Kevin Winthrop Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer Inc, Roche, UCB, Arne Yndestad Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Dan Henrohn Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Hyejin Jo Consultant of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Syneos Health, Sara Marsal Shareholder of: IMIDomics, Consultant of: AbbVie, Celgene, Galapagos, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer Inc, Sandoz, Sanofi, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Jansen-Cilag, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, UCB, María Galindo-Izquierdo Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen-Cilag, Annette Diehl Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Andrea Shapiro Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Stanley B. Cohen Consultant of: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer Inc, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer Inc