

Background: In patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), fatigue is a major driver of perceived impact of disease and has been identified as an important domain to be assessed in clinical trials. 1,2 The association between fatigue and other PsA domains (eg, physical function) or clinical response is not well understood.
Objectives: Fatigue was measured with the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue questionnaire in the pivotal DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 Phase 3 studies of guselkumab (GUS) vs placebo (PBO). This post hoc analysis explores the correlation between FACIT-Fatigue and physical function and clinical response in the DISCOVER program.
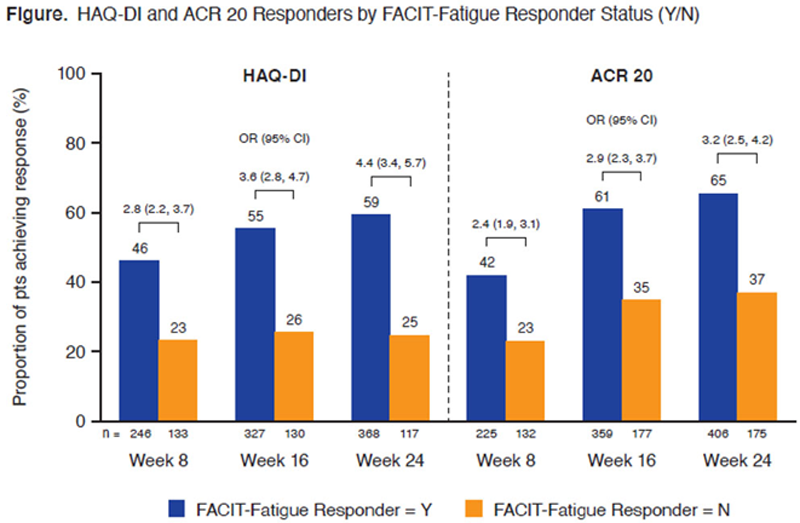
Methods: This analysis used pooled data from pts (N=1120) treated with GUS or PBO. In DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, 381 pts with active PsA (swollen joint count [SJC] ≥3, tender joint count [TJC] ≥3, C-reactive protein [CRP] ≥0.3 mg/dL) and 739 pts with active PsA (SJC ≥5, TJC ≥5, CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) and inadequate response to standard therapies, respectively, were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or PBO. PBO pts switched to GUS 100 mg Q4W at W24. The FACIT-Fatigue questionnaire has 13 items that assess self-reported fatigue/tiredness over the last 7 days. Items are scored from 0 (very much fatigued) to 4 (not at all fatigued). FACIT-Fatigue response was defined as an increase of ≥4 points from baseline. Physical function was evaluated with the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). HAQ-DI response was defined as a decrease of ≥0.35 points from baseline. Clinical response was defined as achievement of ≥20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR 20) criteria. Relationships between FACIT-Fatigue and HAQ-DI at W8/16/24 were assessed by Pearson correlation coefficients. Mean changes in HAQ-DI scores at W8/16/24 were summarized in FACIT-Fatigue responders and nonresponders. A logistic regression model was applied to estimate odds ratios (ORs) for achievement of HAQ-DI and ACR 20 response by FACIT-Fatigue response status at each visit. A multiple linear regression model was used to evaluate the association between FACIT-Fatigue and HAQ-DI at W24 after adjusting for SJC, TJC, CRP, and pt assessment of pain.
Results: FACIT-Fatigue and HAQ-DI scores and changes from baseline were negatively correlated at W8, W16, and W24 (
Conclusion: In pts with PsA, fatigue response is a clinically meaningful predictor of improvements in physical function and achievement of ACR 20 response, reinforcing the importance of assessing fatigue in PsA disease management.
REFERENCES:
[1]Leung YY et al. J Rheumatol. 2020;96:46-9.
[2]Gudu T et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2016;83:439-43.
Correlation* of FACIT-Fatigue and HAQ-DI
| Visit | HAQ-DI and FACIT Fatigue Scores | Changes From Baseline in HAQ-DI and FACIT-Fatigue Scores |
| W8 | −0.61 (p<0.0001) | −0.42 (p<0.0001) |
| W16 | −0.60 (p<0.0001) | −0.47 (p<0.0001) |
| W24 | −0.62 (p<0.0001) | −0.50 (p<0.0001) |
*Determined by Pearson correlation coefficient; p-values derived from hypothesis tests of correlation ρ=0 (ie, no correlation).
Disclosure of Interests: Arthur Kavanaugh Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, Yan Liu Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Atul Deodhar Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Philip J Mease Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN, and UCB; and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and GlaxoSmithKline, Philip Helliwell Consultant of: Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Janssen, Pfizer, Laure Gossec Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Biogen, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi-Aventis, UCB, Grant/research support from: Amgen, Galapagos, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sanofi, Alexa Kollmeier Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Elizabeth C Hsia Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, May Shawi Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Global Services, LLC, Chenglong Han Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Proton Rahman Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Janssen and Novartis.