

Background: Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID) may have a global increased risk of infections due to the disease itself, and/or immunosuppressive therapy. The severity and characteristics of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic IMID (R-IMID) remain unknown.
Objectives: To analyze the severity of COVID-19 infection in R-IMID.
Methods: Cross-sectional study in a single University Hospital. We included all consecutive patients with a diagnosis of a R-IMID and a positive test for COVID-19 up to November 6th, 2020. Confirmed infection was defined if the patient had a positive nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2.
Medical records of 11,199 patients with COVID-19 in our region, and 6891 with R-IMID from our hospital were reviewed.
COVID-19 case severity was divided into mild, moderate, severe and critical according to the United States National Institute of Health (NIH) COVID-19 guidelines (1 ). Mild/moderate COVID19 was compared with critical.
Results: We included 147 patients (96 women/51 men), mean age 60±18 years. Most cases were mild to moderate (n=123, 83.7%), 30 of them (20.4%) were asymptomatic. The remaining patients presented severe (n=5, 3.4%) or critical (n=19, 12.9%) disease (
More frequent underlying R-IMID were Rheumatoid Arthritis (n=36; 24.5%), Psoriatic Arthritis (n=30; 20.4%), axial spondyloarthritis (n=24; 16.3%), conectivopathies (n=19; 12.9%), polymyalgia rheumatica (n=16; 10.9%) and vasculitis (n=9; 6.1%) (
Main comorbidities were hypertension (n=65, 44.2%), dyslipidemia (n=64, 43.5%), age higher than 65 years old (n=55, 37.4%), obesity (n=35, 23.8%), coronary vascular disease (CVD) (n=27, 18.4%) and diabetes mellitus (n=22, 15%).
Comorbidities and R-IMID associated with critical disease (p<0.05) were hypertension, age higher than 65 years,CVD and Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Critical compared with mild/moderate disease showed significantly higher levels of creatinine and D-dimer, and lower level of lymphocytes and platelets (
Conclusion: Although most cases are mild, COVID-19 can be a severe life threatening disease in patients with R-IMID. Hypertension, older age, CVD and polymyalgia rheumatica were associated with critical disease.
REFERENCES:
[1]COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Available at
Clinical severity of 147 with R-IMID diagnosed with COVID-19, (analytical findings and Immunosuppressants are at COVID diagnosis)
|
Overall
|
Mild/Moderate
|
Severe
|
Critical
|
Mild/moderate vs critical;
|
|
| Analytical findings (mean±SD) | |||||
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.04±1.14 | 1.27±0.65 | 1.18±0.47 | 1.35±0.61 | 0.001 * |
| Platelets (x10 3 /µL) | 206 ±93 | 226 ± 95 | 154 ±87 | 159 ±62 | 0.01* |
| Lymphocytes (x10 3 /µL) | 1.11±0.65 | 1.27±0.65 | 0.8±0.29 | 0.71±0.5 | 0.001* |
| D-Dimer (ng/mL) | 1162±1356 | 915±986 | 782±483 | 1947±2024 | 0.026* |
| Immunosuppressants, n(%) | |||||
| Oral GC | 38 (25.9) | 32 (26) | 0 | 5 (26.3) | 0.8 |
| HCQ | 25 (17) | 23 (18.7) | 0 | 2 (10.5) | 0.58 |
| MTX/ Other cDMARDs | 27 (18.4)/19 (13) | 26 (21.1)/18 (14.6) | 0/ 0) | 1 (5.3/1 (5.3) | 0.18/0.45 |
| TNF inhibitors | 13 (8.8) | 12 (9.8) | 1 (20) | 0 | 0.33 |
| RTX | 5 (3.4) | 2 (1.6) | 1 (20) | 2 (10.5) | 0.15 |
| Other bDMARDs | 13 (8.8) | 10 (8.1) | 1 (20) | 2 (10.5) | 0.28 |
| JAKINIB | 3 (2) | 3 (2.4) | 0 | 0 | 0.87 |
| COVID-19 therapy, n (%) | |||||
| No treatment | 94 (64) | 88 (71.5) | 1 (20) | 5 (26.3) | 0.0003* |
| HCQ | 37 (25.2) | 25 (20.3) | 4 (80) | 8 (42.1) | 0.07 |
| Systemic GC | 17 (11.6) | 8 (6.5) | 1 (20) | 8 (42.1) | 0.00001* |
| Antivirals | 20 (13.6) | 13 (10.6) | 0 | 7 (36.8) | 0.07 |
| Anti IL1/IL6 agents | 4 (2.7) | 0 | 0 | 4 (21.1) | 0.00001* |
GC: Glucocorticoids, HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine, MTX: Methotrexate, RTX: Rituximab
* P < 0.05
Severity of COVID-19 according to underlying R-IMID. Data are number of cases
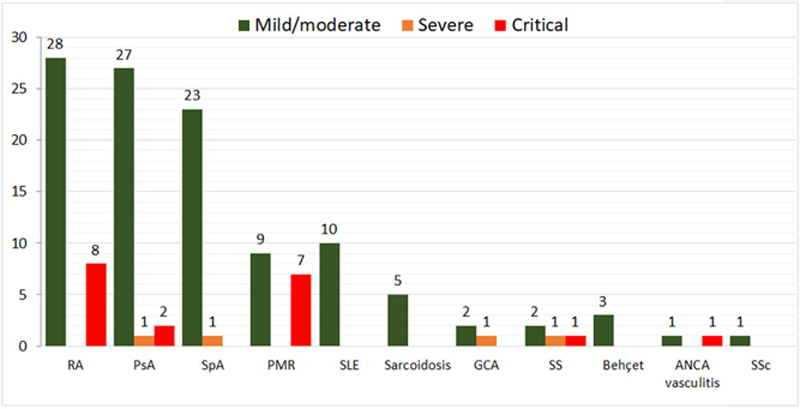
GCA: Giant cell arteritis, PsA: Psoriatic arthritis, RA: Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE: Systemic lupus erythematosus, SpA: Axial spondyloarthritis, SSc: Systemic scleroderma.
Disclosure of Interests: David Martínez-López: None declared, Diana Prieto-Peña Grant/research support from: UCB Pharma, Roche, Sanofi, Pfizer, Abbvie and Lilly, Lara Sanchez-Bilbao: None declared, Alba Herrero-Morant: None declared, Carmen Álvarez-Reguera: None declared, Martin Trigueros-Vazquez: None declared, Miguel A González-Gay Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, MSD, Consultant of: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, MSD, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, MSD, Janssen and Roche., Ricardo Blanco Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Janssen, Lilly and MSD, Consultant of: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Janssen, Lilly and MSD, Grant/research support from: Abvie, MSD and Roche