

Background: Digital diagnostic decision support tools promise to accelerate diagnosis and increase health care efficiency in rheumatology. Rheumatic? is an online tool developed by specialists in rheumatology and general medicine together with patients and patient organizations for individuals suspecting a rheumatic disease. 1,2 The tool can be used by people suspicious for rheumatic diseases resulting in individual advise on eventually seeking further health care.
Objectives: We tested Rheumatic? for its ability to differentiate symptoms from immune-mediated diseases from other rheumatic and musculoskeletal complaints and disorders in patients visiting rheumatology clinics.
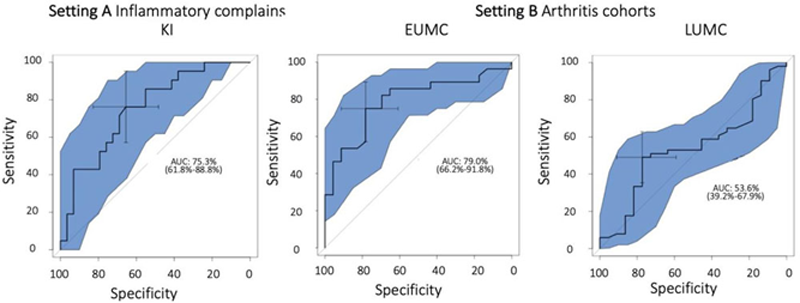
Methods: The performance of Rheumatic? was tested using data from 175 patients from three university rheumatology centers covering two different settings:
A.Risk-RA phase setting. Here, we tested whether Rheumatic? could predict the development of arthritis in 50 at risk-individuals with musculoskeletal complaints and anti-citrullinated protein antibody positivity from the KI (Karolinska Institutet)
B.Early arthritis setting. Here, we tested whether Rheumatic? could predict the development of an immune-mediated rheumatic disease in i) EUMC (Erlangen) n=52 patients and ii) LUMC (Leiden) n=73 patients.
In each setting, we examined the discriminative power of the total score with the Wilcoxon rank test and the area-under-the-receiver-operating-characteristic curve (AUC-ROC).
Results: In setting A, the total test score clearly differentiated between individuals developing arthritis or not, median 245 versus 163,
P < 0.0001,
AUC-ROC = 75.3 (
(Area under) the receiver operating curve for the total Rheumatic? score
Conclusion: Rheumatic? is a web-based patient-centered multilingual diagnostic tool capable of differentiating immune-mediated rheumatic conditions from other musculoskeletal problems. A following subject of research is how the tool performs in a population-wide setting.
REFERENCES:
[1]Knitza J. et al. Mobile Health in Rheumatology: A Patient Survey Study Exploring Usage, Preferences, Barriers and eHealth Literacy. JMIR mHealth and uHealth. 2020.
[2]
Acknowledgements: This project has received funding from EIT Health. EIT Health is supported by the European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT), a body of the European Union that receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program.
This project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement No 777357, RTCure.
Disclosure of Interests: Rachel Knevel: None declared, Johannes Knitza: None declared, Aase Hensvold: None declared, Alexandra Circiumaru: None declared, Tor Bruce Employee of: Ocean Observations, Sebastian Evans Employee of: Elsa Science, Tjardo Maarseveen: None declared, Marc Maurits: None declared, Liesbeth Beaart- van de Voorde: None declared, David Simon: None declared, Arnd Kleyer: None declared, Martina Johannesson: None declared, Georg Schett: None declared, Thomas Huizinga: None declared, Sofia Svanteson Employee of: Elsa Science, Alexandra Lindfors Employee of: Ocean Observations, Lars Klareskog: None declared, Anca Catrina: None declared