

Background: Anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) antibody is associated with interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM). Although the mechanisms leading to pulmonary involvements remain uncertain, both inflammatory cytokines and autoimmune response between MDA5 and anti-MDA5 antibody could been inferred. The present study examined the roles of MDA5 in an inducible form of lung involvement that develops in autoimmune mice treated with the pristane.
Objectives: MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice and wild type controls (+/+) at 5 weeks of age. They received 0.5ml of pristane or an equal volume of PBS IP at the age 7 week (day 1). And 1.2μg of recombinant human MDA5 protein (rMDA5) was instilled IP or PBS at day2 and Day9. The mice were sacrificed on 8 weeks after the intraperitoneal injection. Lung tissue was harvested for histological assessment.
Methods: MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice and wild type controls (+/+) at 5 weeks of age. They received 0.5ml of pristane or an equal volume of PBS IP at the age 7 week (day 1). And 1.2μg of recombinant human MDA5 protein (rMDA5) was instilled IP or PBS at day2 and Day9. The mice were sacrificed on 8 weeks after the intraperitoneal injection. Lung tissue was harvested for histological assessment.
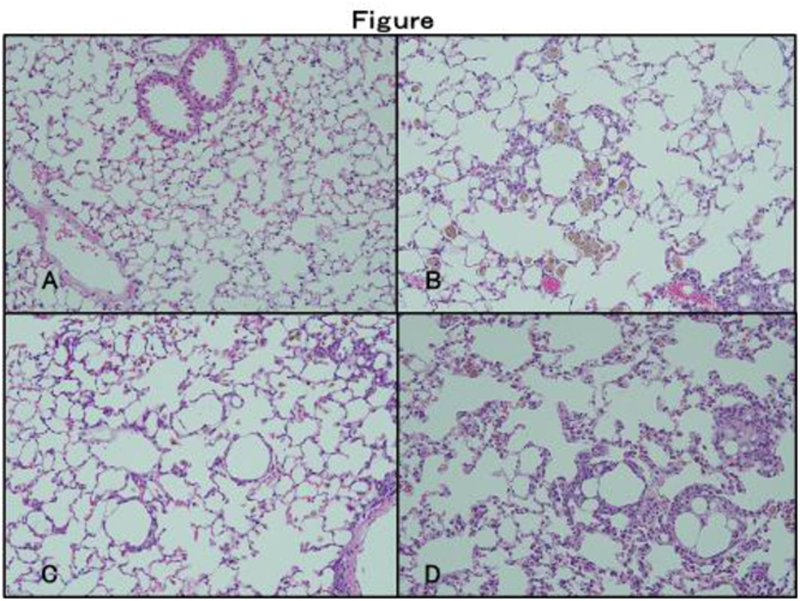
Results: Lung involvements did not develop in PBS-treated MRL/ lpr mice and WT mice. And Lung involvements did not develop in rMDA5 protein-treated WT mice. H&E staining of lung tissue from MRL/ lpr mice and WT mouse with pristane that showed induced bland alveolar hemorrhage. H&E staining of lung from WT mouse compared with lung from a MRL/ lpr mouse treated with pristane + rMDA5 protein showing mild thickening of the alveolar septa despite the alveolar hemorrhage. And perivascular lymphocytes infiltrate in a MRL/ lpr mouse rather than a WT mouse treated with pristane + rMDA5 protein. CD163 staining of alveolar macrophages were present in the alveolar spaces was more intense in mouse treated with pristane + rMDA5 protein than in mouuse treated with only pristane. The Lymphocyte infiltrations around alveolar macrophages was more prominent in MRL/ lpr mouse treated with pristane + rMDA5 protein than other mouse.
Conclusion: These results suggest that lung involvements such as the alveolar hemorrhage, are caused by pristeine and rMDA5 prtotein in the pathogenesis of interstitial pneumonia. MRL/ lpr mouse treated with pristane + rMDA5 protein showed more alveolar macrophages that had lymphocyte infiltrations. After the alveolar hemorrhage by pritane, the antigen exposure of MDA5 might induce continuously inflammatory response to lymphocytes and macrophages in the alveolar lesions.
REFERENCES:
[1]Sunderrajan VE, McKenzie NW, Lieske RT, et al. Pulmonary inflammation in autoimmune MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. Histopathology and bronchoalveolar lavage evaluation. Am J Pathol. 1986;124: 353–362.
[2]Tolga Barker T, Lee YP, Scumpia KK, et al. Pathogenic role of B-cells in the development of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage induced by pristane. Lab Invest. 2011; 91: 1540–1550.
Lung disease (A-D). Light microscopy. Lung tissue from mice 8 weeks after treatment were stained with H&E. (A) Pristeine -treated WT mice with almost no alveolar lesions. (B) Pristane + rMDA5 protein -treated WT mice with alveolar hemorrhage and slight lymphocyte infiltrations. (C) Pristeine -treated MRL/ lpr mouse with almost no alveolar lesions and slight lymphocyte infiltrations. (D) Pristeine -treated MRL/ lpr mouse with alveolar hemorrhage and lymphocyte infiltrations, thickening of the alveolar septa.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared