

Background: Meniscal injuries are the most common pathology of the knee and are associated with pain, stiffness, and localized swelling. Meniscal damage is a frequent finding on MRI images of knee osteoarthritis (OA). 1 Efforts to repair meniscal damage have been largely unsuccessful and do not prevent the progression of degenerative changes that lead to knee OA. 2 The Wnt signaling pathway has been shown to be regulated during meniscal development, 3 suggesting that manipulation of this pathway may influence the regenerative capacity of the meniscus. Lorecivivint (LOR; SM04690) is an intra-articular (IA), small-molecule CLK2/DYRK1A inhibitor that modulates the Wnt pathway. 4
Objectives: LOR was evaluated in preclinical studies to determine its protective and anabolic effects in ex vivo explants and in a rat model of chemically induced inflammatory meniscal degeneration.
Methods: Effects of LOR (30 nM) on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression in cultured rat menisci treated with IL-1B were measured by qRT-PCR. In vivo, LOR activity was evaluated in a rat model of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) injection-induced inflammatory meniscal degeneration. A single IA injection of MIA was immediately followed by a single IA injection of LOR (0.3 ug) or vehicle. Knees were harvested on Days 1, 4, and 11 and menisci were isolated. Anti-inflammatory effects were evaluated by qRT-PCR for TNFA and IL6 expression. Meniscal protection was evaluated by qRT-PCR for MMPs and aggrecanase. Anabolic effects were evaluated by qRT-PCR for collagens.
Results: In ex vivo meniscal explants, LOR inhibited expression of
MMP1
,
MMP3
, and
MMP13
compared with DMSO (
P
<0.01). In vivo, LOR significantly decreased expression of MMPs and aggrecanase (
P
<0.05) and reduced expression of inflammatory cytokines
TNFA
and
IL6
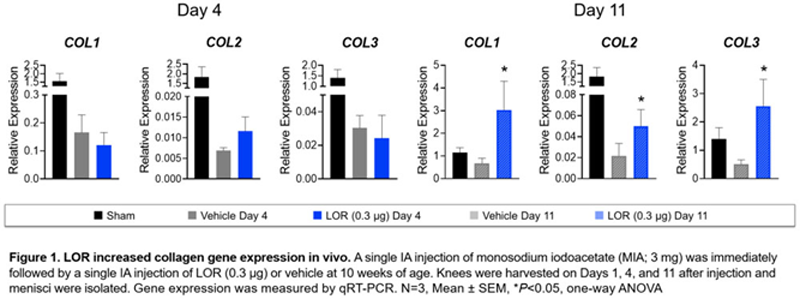
compared with vehicle in the rat model of inflammatory meniscal degeneration at Day 4 after MIA injection. Additionally, LOR increased expression of collagen types I, II, and III at Day 11 after MIA injection (
Conclusion: LOR exhibited protective effects in the meniscus ex vivo and in vivo by reducing catabolic enzyme expression compared with control. Anti-inflammatory effects of LOR were demonstrated by inhibition of inflammatory cytokine expression. Compared with vehicle, LOR increased collagen expression in vivo, indicating potential meniscal anabolic effects. These data support further investigation of LOR as a potential structure-modifying treatment for meniscal injuries.
REFERENCES:
[1]Englund M, et al. Rheum Dis Clin North Am . 2009.
[2]Collins JE, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken ). 2019.
[3]Pazin DE, et al. Dev Dyn . 2012.
[4]Deshmukh V, et al. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2019.
Disclosure of Interests: Tim Seo Shareholder of: Samumed, LLC, Employee of: Samumed, LLC, Vishal Deshmukh Shareholder of: Samumed, LLC, Employee of: Samumed, LLC, Yusuf Yazici Shareholder of: Samumed, LLC, Employee of: Samumed, LLC