

Background: The Phase 3b/4 study ORAL Shift (NCT02831855) demonstrated sustained efficacy/safety of tofacitinib modified-release 11 mg QD following MTX withdrawal, that was non-inferior to continued tofacitinib + MTX use, in patients (pts) with moderate to severe RA who achieved LDA with tofacitinib + MTX at Week (W)24. 1
Objectives: To assess differences and similarities in clinical/functional responses in pts receiving tofacitinib ± MTX in ORAL Shift.
Methods: In ORAL Shift, pts received open-label tofacitinib + MTX to W24; at W24, pts who achieved CDAI LDA were randomised to receive tofacitinib + MTX or tofacitinib + placebo (PBO) from W24–48. In this post hoc analysis, clinical efficacy endpoints were ACR-N (minimum % change from baseline [BL; Δ] at W48 achieved by each pt in 3 efficacy measures), ΔDAS28-4(ESR), and DAS28-4(ESR) remission/LDA (scores ≤3.2) and moderate/high disease activity (scores >3.2). Functional efficacy endpoints were ΔHAQ-DI and HAQ-DI clinically relevant functional progression (CRFP) status at W48, defined as failure to achieve improvement in HAQ-DI ≥ minimum clinically important difference (MCID; ≥0.22 decrease from BL in HAQ-DI). Thus, CRFP was defined as <0.22 decrease, no change or increase from BL in HAQ-DI at W48. All efficacy endpoints were summarised descriptively. Cumulative probability plots of ACR-N and ΔHAQ-DI were produced. Median of mean CRP values from BL–W24 and >W24–48 were assessed by response subgroups.
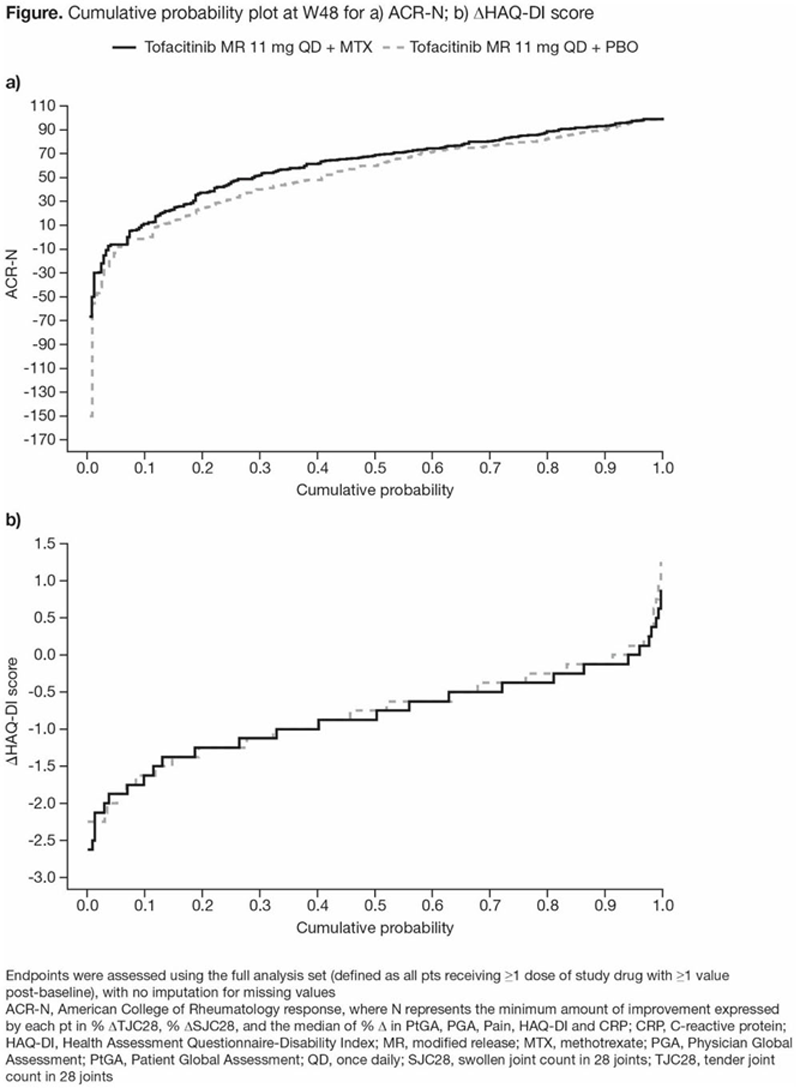
Results: 266 pts receiving tofacitinib + MTX and 264 pts receiving tofacitinib + PBO in W24–48 were included. At W48: mean ACR-N was numerically greater with tofacitinib + MTX vs tofacitinib + PBO (60.8 vs 53.1); mean decrease in HAQ-DI was generally similar between groups (-0.71 vs -0.67); mean decrease in DAS28-4(ESR) was numerically greater with tofacitinib + MTX vs tofacitinib + PBO (-2.95 vs -2.68). The differences/similarities between groups in ACR-N and ΔHAQ-DI were also seen in cumulative probability plots (
Median of mean CRP a up to W48 by response subgroups
| Tofacitinib 11 mg QD + MTX | Tofacitinib 11 mg QD + PBO | |||
| Mean CRP, a median (IQR) [n] | >BL–W24 | >W24–48 | >BL–W24 | >W24–48 |
| HAQ-DI CRFP | 2.84 (1.15–7.30) | 2.30 (0.82–4.75) | 1.45 (0.77–4.42) | 2.28 (0.53–7.28) |
| [45] | [46] | [56] | [56] | |
| HAQ-DI non-CRFP | 2.81 (1.09–6.19) | 2.91 (1.19–5.84) | 2.26 (0.98–4.63) | 2.47 (1.13–5.53) |
| [195] | [195] | [176] | [178] | |
| DAS28-4(ESR) remission/LDA | 2.48 (1.05–4.95) | 2.46 (1.07–4.76) | 1.70 (0.89–4.14) | 1.95 (0.81–3.82) |
| [126] | [127] | [115] | [117] | |
| DAS28-4(ESR) moderate/high disease activity | 3.56 (1.17–7.13) | 3.58 (1.36–8.33) | 2.60 (0.87–5.16) | 2.68 (1.34–8.23) |
| [107] | [107] | [115] | [115] | |
a Mean CRP was calculated as the average CRP value during each time period (>BL–W24 or >W24–48)
CRP, C-reactive protein; DAS28-4(ESR), Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; IQR, interquartile range; LDA, low disease activity; MTX, methotrexate; n, number of pts meeting assessment criteria; QD, once daily
Conclusion: Although clinical/functional responses were generally similar between treatment groups, numerical improvements were seen for some efficacy endpoints with tofacitinib + MTX vs tofacitinib + PBO. A numerically higher CRFP rate may be associated with higher DAS28-4(ESR) disease activity. CRP changes up to W48 may not trend with CRFP status.
REFERENCES:
[1]Cohen et al. Lancet Rheumatol 2019; 1: E23-34.
Acknowledgements: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Anthony G McCluskey, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer Inc.
Disclosure of Interests: Stanley B. Cohen Consultant of: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer Inc, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer Inc, Yi-Hsing Chen Grant/research support from: Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer Inc, Naonobu Sugiyama Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Jose Luis Rivas Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Annette Diehl Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Tatjana Lukic Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Jerome Paulissen Consultant of: Pfizer Inc, Haiyun Fan Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Tomohiro Hirose Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Edward Keystone Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, F. Hoffman-La Roche, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi Genzyme, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, F. Hoffman-La Roche, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck, Myriad Autoimmune, Pfizer Inc, Sandoz, Sanofi Genzyme, Samsung Bioepsis, Grant/research support from: Amgen, Merck, Pfizer Inc, PuraPharm