

Background: The number of new biologics in treatment of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is rapidly increasing. It is important to assess timely their place in the treatment of axSpA, especially with regard to retention on therapy.
Objectives: To compare retention on therapy with different biologics in patients with axSpA.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data of axSpA patients receiving biologics from the MUAR register. Predictors of retention on therapy were selected by forward stepwise variable selection within Cox regression proportional hazard model. These predictors were considered as confounders when comparing the risks of biologics withdrawal.
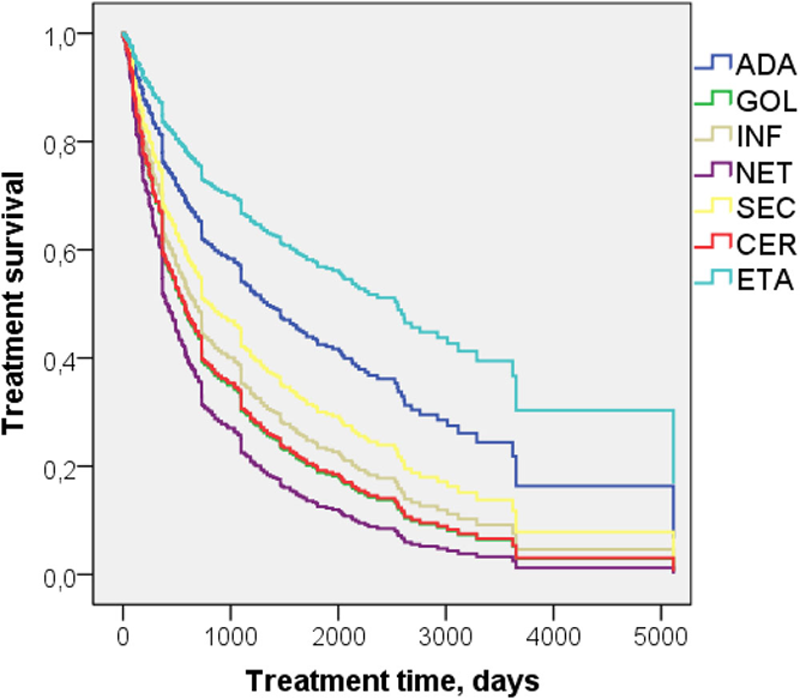
Results: 990 treatment episodes in 640 patients with axSpA were analyzed (non-radiographic axSpA – 4.1%, ankylosing spondylitis - 95.9%). The duration of episodes was 824±920 days. Men were 66,6%, mean age 46,4±11,4.The patients were treated with Adalimumab (ADA) (n= 252 treatment episodes), Golimumab (GOL) (n=82), Infliximab (INF) (n=167), Netakimab (NET) (n=9), Secukinumab (SEC) (n=75), Certolizumab pegol (CER) (n=66), Etanercept (ETA) (n=339).
The following predictors of withdrawal risk were identified –
1.The total duration of the disease
2.The duration of the disease before the onset of biologic treatment
3.Gender
4.Family history of non-inflammatory spondylopathy (degenerative spinal disease)
5.The line of biologic treatment
6.The level of education
The severity of radiographic sacroiliitis and HLA B-27 positivity were not associated with the risk of discontinuation of biologics.
The identified predictors were further considered as confounders. Adjusted for confounders, ETA had the lowest treatment withdrawal risk (
Conclusion: Our analysis detected predictors associated with risk of biologics withdrawal in axSpA patients in real clinical practice. There are significant differences between biologics regarding retention on treatment.
Hazard ratio for treatment withdrawal
| Drug | Hazard ratio (Exp B) | p |
| ADA | 1.52 * | 0.004 |
| GOL | 2.95 * | 0.000 |
| INF | 2.574 * | 0.000 |
| NET | 3.680* | 0.073 |
| SEC | 2.133* | 0.005 |
| CER | 2.922* | 0.000 |
* - withdrawal risk relative to ETA
Picture 1. Treatment withdrawal risk
Disclosure of Interests: None declared