

Background: Guselkumab (GUS), a selective IL-23 inhibitor dosed every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W or Q8W), demonstrated efficacy for joint and skin symptoms, inhibition of structural damage progression (Q4W), and safety vs. placebo (PBO) through Week 24 (W24) of the Ph3, double-blind, PBO-controlled trial in biologic-naïve pts with PsA (DISCOVER-2). 1 Favorable benefit-risk was also seen through 1 year. 2
Objectives: To assess GUS efficacy and safety through 2 years.
Methods: Biologic-naïve adults with active PsA (≥5 swollen joint count [SJC] + ≥5 tender joint count [TJC]; CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) were randomized (1:1:1) to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, Q8W; or PBO with crossover to GUS 100 mg Q4W (PBO→Q4W) at W24. Clinical efficacy (ACR/PASI/IGA/HAQ-DI) was assessed in the modified intention to treat (mITT) population through W100 with missing data imputation (nonresponse for categorical endpoints; no change/multiple imputation for continuous endpoints). Observed PsA-modified van der Heijde Sharp (vdH-S) scores derived from blinded radiographic images collected at W0, W24, W52, W100 (or at discontinuation [d/c]) and adverse events (AEs) through W112 were collected.
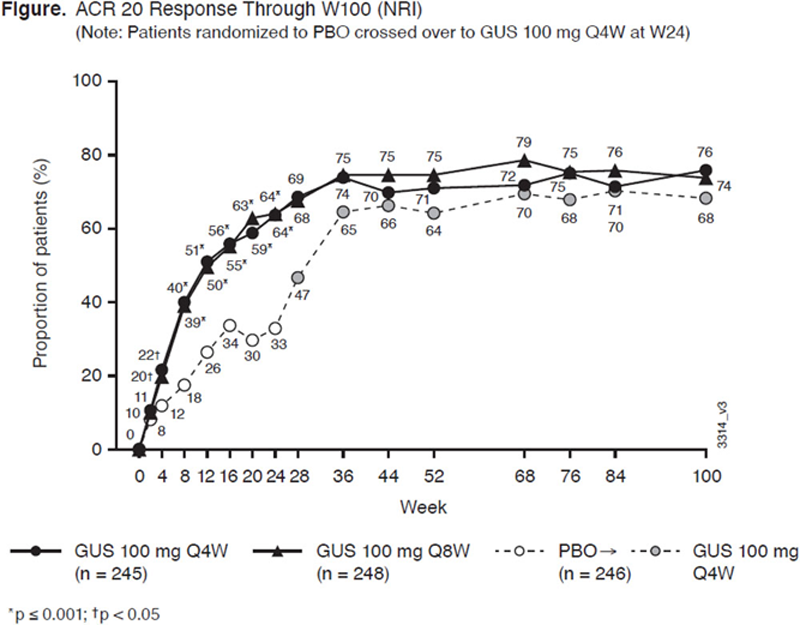
Results: 712/739 (96%) randomized pts continued study agent at W24; 687/739 (93%) continued at W52; 652/739 (88%) completed W100. ACR20 response rates in the mITT population continued to increase after W24, and at W100 were 76% for Q4W and 74% for Q8W (
Conclusion: In biologic-naïve PsA pts, GUS improvements in joint and skin symptoms, physical function, and low rates of radiographic progression persisted through 2 years. GUS safety in PsA through 2 years was comparable with safety at 6 months and 1 year, similar between Q4W and Q8W, and consistent with GUS safety in psoriasis.
REFERENCES:
[1]Mease PJ. Lancet . 2020 Apr 4;395(10230):1126-1136. [2] McInnes IB. Arthritis Rheumatol . 2020 Oct 11. doi: 10.1002/art.41553.
Efficacy Through W100 (NRI)
| Data are % | GUS Q4W | GUS Q8W | PBO→GUS Q4W | ||||||
| W24 | W52 | W100 | W24 | W52 | W100 | W24 | W52 | W100 | |
| Analysis set, n | 245 | 248 | 246 | ||||||
| ACR 50 | 33 | 46 | 56 | 32 | 48 | 55 | 14 | 41 | 48 |
| ACR 70 | 13 | 26 | 35 | 19 | 28 | 36 | 4 | 18 | 30 |
| BL HAQ-DI ≥0.35, n | 228 | 228 | 236 | ||||||
| Improvement ≥0.35 a | 56 | 59 | 63 | 50 | 58 | 64 | 31 | 48 | 56 |
| BL ≥3% BSA psoriasis + IGA ≥2, n | 184 | 176 | 183 | ||||||
| IGA0/1 | 69 | 63 | 62 | 71 | 58 | 55 | 19 | 63 | 67 |
| PASI75 | 78 | 87 | 83 | 79 | 86 | 82 | 23 | 83 | 80 |
| PASI90 | 61 | 77 | 74 | 69 | 74 | 70 | 10 | 72 | 77 |
| PASI100 | 45 | 58 | 59 | 45 | 53 | 53 | 3 | 52 | 61 |
BL, Baseline; BSA, Body surface area; HAQ-DI, Health assessment questionnaire disability index; IGA, Investigator global assessment; NRI, nonresponder imputation; PASI, Psoriasis area and severity index. a ≥0.35 improvement among pts with HAQ-DI ≥0.35 at BL.
Disclosure of Interests: Iain McInnes Consultant of: AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, and UCB, Proton Rahman Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Janssen and Novartis, Alice B Gottlieb Consultant of: Avotres Therapeutics, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb Co, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Inc, UCB, and Xbiotech, Grant/research support from: Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries Inc, UCB, and Xbiotech, Elizabeth C Hsia Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research and Development, LLC, Alexa Kollmeier Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Xie L Xu Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Shihong Sheng Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Yusang Jiang Employee of: Cytel, Inc. providing statistical support (funded by Janssen), May Shawi Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Soumya D Chakravarty Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Désirée van der Heijde Paid instructor for: Director of Imaging and Rheumatology BV, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Cyxone, Daiichi, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and UCB, Philip J Mease Speakers bureau: Boehringer Ingelheim and GlaxoSmithKline, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN, and UCB.