

Background: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by peripheral arthritis, axial inflammation, dactylitis, enthesitis, & skin/nail psoriasis. Patients (pts) with PsA often experience reduced health-related quality of life (HRQoL) due to these features.
Objectives: Using EuroQoL-5 dimension-5 level (EQ-5D-5L) questionnaire index & visual analog scale (EQ-VAS) scores, we assessed HRQoL in pts with PsA & its association with pt characteristics & clinical features of PsA, including fatigue.
Methods: The Phase 3 DISCOVER-2 trial evaluated guselkumab (GUS), a human monoclonal antibody targeting the IL-23p19-subunit, in bio-naïve adults with active PsA (swollen joint count [SJC] ≥5, tender joint count [TJC] ≥5, C-reactive protein [CRP] ≥0.6 mg/dL) despite standard therapies.
1
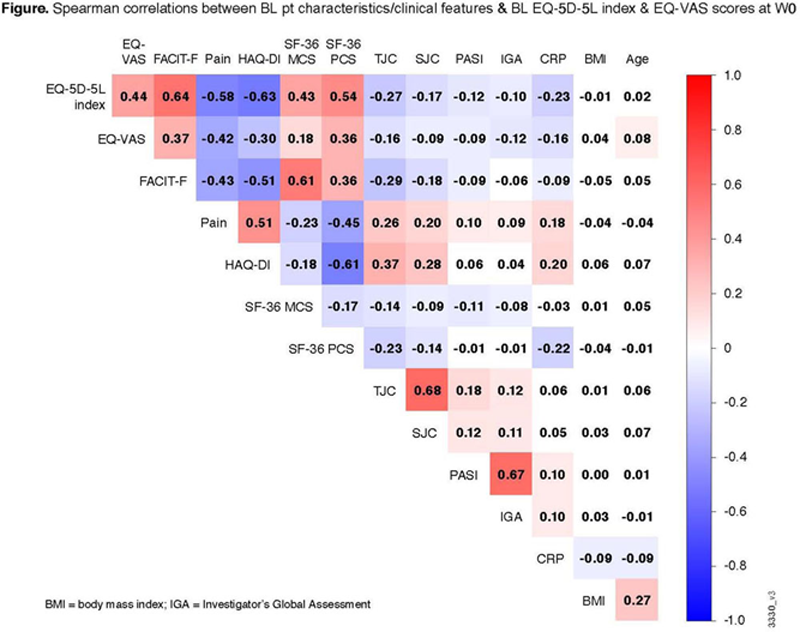
Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at Week 0 (W0), W4, then Q8W; or placebo (PBO). EQ-5D-5L index assesses mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, & anxiety/depression. EQ-VAS assesses pt health state. Spearman correlation testing was used to evaluate relationships between baseline (BL) pt characteristics & PsA clinical features & BL EQ-5D-5L index & EQ-VAS scores (
Results: Among 738 pts, BL EQ-5D-5L index & EQ-VAS scores were moderately to strongly correlated (ie, ≥0.4) with BL pt-reported pain (0-10 VAS), physical function (Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index [HAQ-DI]), fatigue (Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue [FACIT-F] scale), & 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) physical & mental component summary (PCS & MCS) scores & weakly correlated with other variables (
Conclusion: Joint & skin symptoms, dactylitis, fatigue, pain, & elevated levels of CRP were significantly associated with reduced HRQoL (measured by EQ-5D-5L index & EQ-VAS) in bio-naïve pts with active PsA. Treatment of multiple PsA domains may help optimize HRQoL. Improvement across clinical domains 1 & in HRQoL has been observed in GUS-treated pts with PsA.
REFERENCES:
[1]Mease P, et al. Lancet 2020;395:1126-36.
Multivariate analysis of pt characteristics/clinical features & EQ-5D-5L index & EQ-VAS scores at W0 & W24
| Parameter | EQ-5D-5L Index | EQ-VAS | ||
| Estimate | p value | Estimate | p value | |
| Age (y) | -0.0001 | 0.69 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| Female | -0.003 | 0.53 | 1.11 | 0.20 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | -0.005 | <0.001 | -0.51 | 0.007 |
| FACIT-F (0-52) | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.57 | <0.001 |
| Pain (0-10) | -0.02 | <0.001 | -3.47 | <0.001 |
| PASI (0-72) | -0.001 | 0.03 | -0.17 | <0.001 |
| SJC (0-66) | -0.001 | 0.21 | -0.17 | 0.02 |
| TJC (0-68) | -0.001 | 0.04 | -0.04 | 0.41 |
| Dactylitis (Y/N) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.74 | 0.49 |
| Enthesitis (Y/N) | -0.004 | 0.33 | -0.98 | 0.22 |
Disclosure of Interests: Jeffrey Curtis Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corrona, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corrona, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, and UCB, Iain McInnes Consultant of: AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, and UCB, Dafna D Gladman Consultant of: Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, Feifei Yang Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Global Services, LLC, Steve Peterson Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Global Services, LLC, Prasheen Agarwal Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Alexa Kollmeier Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Elizabeth C Hsia Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Chenglong Han Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, May Shawi Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Global Services, LLC, William Tillett Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, MSD, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Philip J Mease Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN, and UCB, Proton Rahman Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Janssen and Novartis.