

Background: Tofacitinib is a potent and selective oral inhibitor prevalently of JAK1 and JAK3and is currently included in the international recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Nonetheless, the mechanisms of the immune response to the treatment remain unclear, particularly regarding the effects on overlooked immune cell subpopulations specifically involved in the pathogenesis of PsA, i.e. mucosal-associated invariant T cells (MAIT), innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), both relevant sources of IL-17, and T lymphocytes producing interleukin 9 (Th9). We thus investigated the effect of tofacitinib on these cell population function and compared with glucocorticoids.
Objectives: To investigate the effect of tofacitinib and dexamethasone on MAIT cells, ILCs, and Th9 cells in PsA.
Methods: We investigated synovial fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with PsA that were cultured with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin in the presence or absence of 100 or 300nM Tofacitinib or 1000uM Dexamethasone for 24 hours and the addition of brefeldin in the last 2 hours. FACS analysis allowed to identify MAIT cells by CD3+CD161+Valpha7.2TCR; ILCs by CD3+CD45+CD127+, from this population ILC1 were arrayed as cKit- CRTH2-; ILC2 as cKit +/- and CRTH2+, and ILC3 as cKit+ and CRTH2-; Th9: CD3+CD4+IL-9+.
Results: A significant decrease in IL-17 production was observed in CD8+ MAIT cells treated with tofacitinib 300 nM compared to untreated conditions, with a magnitude similar to what observed with dexamethasone [mean fluorescence intensity-MFI median 1920 (interquartile range-IQR 1597-2761), 18.6% (3.9-31.4) in untreated cultures; 1481 (1325-3163), 13.4% (4.5-9.3) in tofacitinib-treated cultures; 1511 (1147-2882); 11.5% (2.5-49) in Dexamethasone-treated cultures;
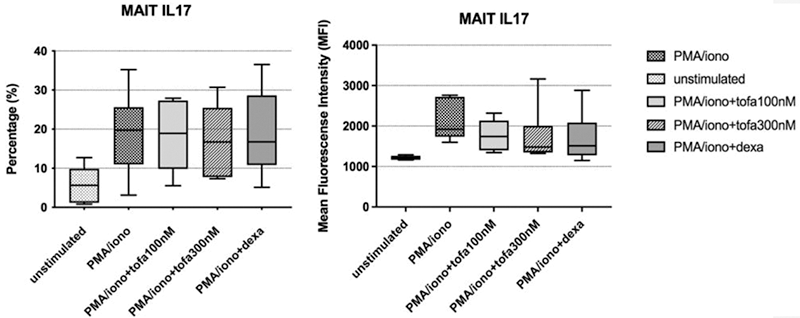
Conclusion: In PsA, tofacitinib is superior to dexamethasone in reducing the production of IL-17 by synovial fluid MAIT cells and ILC3 cells and of IL-9 by peripheral blood T cells.
Disclosure of Interests: Maria De Santis Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Alfa-Wassermann, Biogen, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme, Actelion, Boehringer, Italfarmaco, Grunenthal, Roche, Natasa Isailovic: None declared, Angela Ceribelli Speakers bureau: Amgen, Paid instructor for: SPA Farmaceutici, Grant/research support from: Eli-Lilly, Grunenthal, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, Francesca Motta Consultant of: Thermo-Fisher, Matteo Vecellio: None declared, Marta Caprioli: None declared, Giacomo Maria Guidelli Speakers bureau: Amgen, UCB, Galapagos, Eli-Lilly, Consultant of: Amgen, UCB, Galapagos, Eli-Lilly, Nicoletta Luciano Speakers bureau: Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Consultant of: Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Carlo Selmi Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Alfa-Wassermann, Biogen, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme), Paid instructor for: AbbVie, Amgen, Alfa-Wassermann, Biogen, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme), Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Alfa-Wassermann, Biogen, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme), Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Pfizer