

Background: According to different international registries, the frequency of use of biological agents in monotherapy in RA ranges from 12 to 39%. Targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs-Jaki) have shown great efficacy when used as monotherapy. The rationale for this study is based on the fact that the frequency has increased with the appearance of the Jaki.
Objectives: To estimate the frequency and reason of the use of biological drugs (bDMARDs) or tsDMARDs in monotherapy since 2013 (Year the Jaki were available in Argentina). To describe the frequency of monotherapy by treatment class and analyze the differential characteristics.
Methods: Retrospective and cross-sectional multicenter study (10 reference centers from Argentina). Consecutive patients, ≥18 years, diagnosis of RA (ACR / EULAR 2010), who were under treatment with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs, started after 2013. Socio-demographic, disease and therapeutic data were collected.
Statistical analysis: descriptive statistics, Chi2 test, Fisher’s exact test, Student’s T test and Mann Whitney were performed, according to the nature of the variables. A p <0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Total 505 patients were included, 87.7% women, with a mean age 58 years (SD ± 13.5) and disease duration of 13 years (SD ± 7.8). Treatment: TNF blocker 42.1%, JAKi 30.3%, IL-6 blocker 10.9% and other treatments 16.8%.
Since 2013, the frequency of monotherapy was 49% (95% CI: 45-53), in the last visit the current frequency was 41% (95% CI 37-45),of this 40% received JAKi. JAKi and IL-6 blocker were the treatments that were used more frequently in monotherapy vs combination modality (
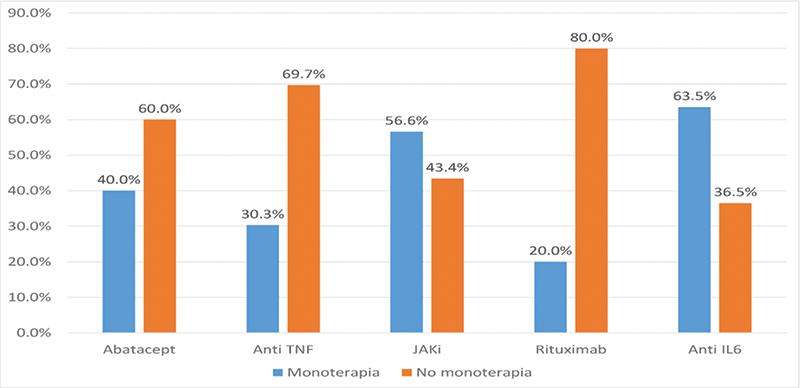
The main causes of monotherapy were intolerance (39.9%), adverse event (22%), physician’s decision (20.2%) and lack of adherence (17.7%) to DMARDs. Patients who were active workers (64% vs 55%, p <0.05), with higher socioeconomic status (31.4% vs 17.2% p <0.01), better mean HAQ at diagnosis (1.1 vs 1.3, p <0.05) an association was observed with monotherapy. In addition, an association was observed with the use of monotherapy in patients in the 2nd biological line or higher vs 1st line (53% vs 33%, p <0.01), lower polypharmacy (45.6% vs 60%, p <0.02) and a shorter mean time of biological treatment (47 months vs 39 months, p <0.01). These variables were entered in a logistic regression model, the results of the independently associated variables are shown in
| Variable | p | OR | CI 95% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employment status (active). | 0,191 | 1,327 | 0,868 | 2,029 |
| Socioeconomic level (medium-high stratum ) | 0,002 | 2,15 | 1,323 | 3,494 |
| HAQ at diagnosis, M (SD ) | 0,019 | 0,704 | 0,524 | 0,944 |
| First Line of biological treatment or Jaki (yes ) | 0,02 | 0,459 | 0,3 | 0,7 |
| Polypharmacy (>4 drugs) (yes ) | 0,018 | 0,603 | 0,395 | 0,918 |
| bDMARDs or tsDMARDs exposure time (months) | 0,054 | 0,994 | 0,987 | 1 |
Conclusion: The frequency of monotherapy, since the Jaki’s emergence, was 49% (all follow-up) and 41% (current-last visit). Intolerance to cDMARDs doctor and the patient decision were the main cause. The monotherapy use pattern was greater in those who received JAKi and anti IL6. The use of monotherapy was associated with work activity, socioeconomic status, and functional capacity at diagnosis. An association was also observed with less polypharmacy.
REFERENCES:
[1]Smolen JS, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:685–699.
[2]Emery P, Sebba A, Huizinga TW. Ann Rheum Dis.2013;72(12):1897–904.
[3]F. Sommerfleck et al. Rev Arg Reumatol. 2013;24(4): 30-36
[4]Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ,et al. Arthritis Rheum 2010. 2010;62(9):2569–81.
Disclosure of Interests: Rodrigo Garcia Salinas Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Lilly, BMS, Jassen, Novartis, boehringer ingelheim, Consultant of: Lilly, Jassen, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Fernando Sommerfleck Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Alfredo Vargas Caselles: None declared, Luis Palomino Romero: None declared, Javier Rosa: None declared, Mariana Benegas: None declared, Etel Saturansky: None declared, Pamela Giorgis: None declared, Florencia Martinez: None declared, Marcelo Abdala: None declared, Jimena Sanchez Alcover: None declared, Emma Estela Civit De Garignani: None declared, Gabriela Vanesa Espasa: None declared, Verónica Inés Bellomio: None declared, Juan Manuel Bande: None declared, Silvia Papasidero: None declared, Veronica Saurit: None declared, Leticia Ibañez Zurlo: None declared, Emilio Buschiazzo: None declared