

Background: Active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite methotrexate monotherapy is seen in about 43% of patients 1 . The current American College of Rheumatology (ACR) guidelines recommend adding a biologic or targeted synthetic Disease Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drug (DMARD) to methotrexate (MTX) therapy in such cases. The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) guidelines recommend combination DMARDs but the most commonly used combination is that of MTX with sulphasalazine and hydroxychloroquine. In a resource limited country like ours, it is not always possible to give a biological or a targeted synthetic DMARD, and a more cost effective method needs to be implemented. Often, leflunomide (LEF) is added in such cases and is effective.
Objectives: We aimed to study if LEF with MTX combination is non inferior to rituximab (RTX) and MTX combination in patients with active RA despite MTX.
Methods: This open label, randomised controlled trial, carried out on patients with moderate to high disease activity despite MTX therapy for atleast 3 months (Clinical Trials Registry- India - REF/2021/04/042755) was conducted in a tertiary care centre in India. Patients were randomised to receive either LEF (10-20mg/day) or RTX (2 doses of 1gm, 2 weeks apart) along with background MTX (10-25mg/week) and followed up at 12, 18 and 24 weeks. The primary outcome ACR20 response at 24 weeks and secondary outcomes were ACR50 and 70 responses at 24 weeks.
Results: There were 21 patients in each arm. At baseline, all patients in both groups had seropositive RA and had high disease activity according to Disease Activity Score (DAS)28 scores. The ACR20 response at 24 weeks was achieved by 14 (66.6%) and 16 (76.19%) patients respectively in the LEF and RTX arms. The ACR50 response was achieved by 11 (52.38%) patients in both groups and ACR70 response by 4 (19%) and 7 (33.3%) in the LEF and RTX arms respectively (
Responses in both groups at week 24 (p= Not significant for all)
| Leflunomide, n=21 | Rituximab, n=21 | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean ±SD reduction in SJC | -4.57 ± 3.4 | -5.43 ± 4.6 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in TJC | -6.2 ± 3.9 | -7.1 ± 6.1 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in PhGA | -3.42 ± 1.8 | -4.04 ± 2.5 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in PGA | -3.05 ± 1.8 | -3.42 ± 2.4 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in pain VAS | -33.57 ± 23.2 | -38.57 ± 24.4 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in DAS28-ESR | -1.95 ± 1.2 | -2.08 ± 1.4 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in DAS28-CRP | -1.81 ± 1.2 | -2.07 ± 1.4 |
| Mean ±SD reduction in HAQ-DI | -0.65 ± 0.5 | -0.82 ± 0.6 |
| EULAR good response (%) | 1 (4.76%) | 1 (4.76%) |
| EULAR moderate response (%) | 15 (71.43%) | 14 (66.6%) |
| EULAR non-responders (%) | 5 (23.81%) | 6 (28.57%) |
CRP, C- Reactive Protein; DAS, Disease Activity Score; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; HAQ-DI, Healthy Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; PGA, Patient’s global assessment of disease activity; PhGA, Physician’s global assessment of disease activity; SJC, Swollen Joint Count; TJC, Tender Joint Count; VAS, Visual analogue scale.
Number of patients achieving ACR20, 50 and 70 responses at week 24
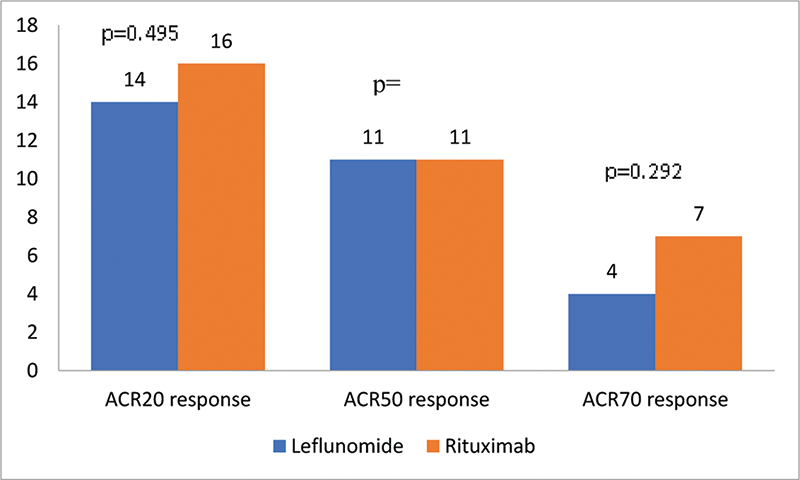
Conclusion: In our study, LEF was comparable to RTX for achievement of ACR20/50/70 responses at 24 weeks. LEF can be considered as an add-on option to MTX instead of more expensive biologic agents in MTX refractory RA. Larger studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis.
REFERENCES:
[1]Sergeant JC, Hyrich KL, Anderson J, et al. Prediction of primary non-response to methotrexate therapy using demographic, clinical and psychosocial variables: results from the UK Rheumatoid Arthritis Medication Study (RAMS). Arthritis Res Ther . 2018;20(1):147. Published 2018 Jul 13.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared