

Background: A significant number of Systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP) experience digital ischemic complications (DICs-digital ulcers, digital pitting/scars, gangrene and/or amputation).
Objectives: We reviewed the prevalence & risk factors for DICs in SSc-RP and compared treatment patterns among patients with & without DICs.
Methods: SSc patients meeting ACR/EULAR 2013 classification criteria that underwent an upper extremity arterial study between 2001-2018 were included. Clinical characteristics, treatment for RP, use of antiplatelet (aspirin 81 mg), statin therapy & occurrence of DICs, digital occlusive arterial disease (DOAD) on laser doppler flowmetry (LDF) and macrovascular disease (MVD) on duplex US were abstracted. Risk factors for DICs and their associations with therapy were evaluated.
Results: We identified 273 SSc patients (mean age 57±13 y, 81% F, 93% Caucasian, mean disease duration 4.8 ± 7.1 y). Cohort characteristics are described in
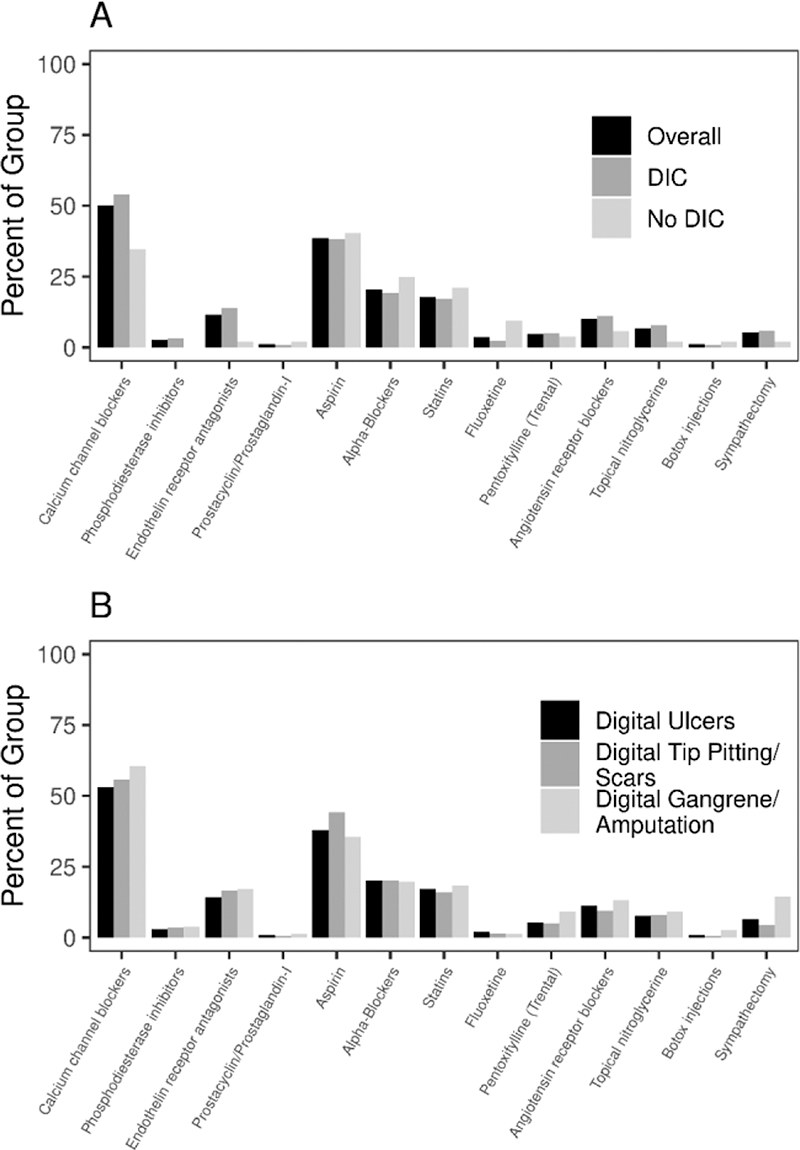
Treatment patterns are described in
Conclusion: Our study confirms a high prevalence of DICs in SSc, with digital ulcers occurring in nearly 75% patients. A higher risk of DICs is associated with DOAD, MVD, ILD, calcinosis and pericardial effusion. While there is a significantly higher utilization of vasodilators among patients with DICs, the utilization of antiplatelet therapy and statins was not different among these groups. Whether this suggests a lack of evidence supporting their use in clinical practice, or inefficacy in preventing DICs remains unclear and warrants further study.
| Overall (N=273 ) | DICs (N=217 ) | No DICs (N=56 ) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age at procedure(y); mean (SD) | 57.5 (13.3) | 56.9 (13.6) | 59.4 (11.8) | 0.25 |
| Sex (Female) | 220 (81%) | 173 (80%) | 47 (84%) | 0.48 |
| Race (White) | 253 (93%) | 199 (92%) | 54 (96%) | 0.73 |
| BMI (kg/m 2 ) at study; mean (SD) | 26.6 (6.1) | 26.3 (6.1) | 27.4 (6.1) | 0.14 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| Never | 154 (56%) | 120 (55%) | 34 (61%) | 0.76 |
| Former | 102 (37%) | 83 (38%) | 19 (34%) | |
| Current | 17 (6%) | 14 (6%) | 3 (5%) | |
| Disease characteristics | ||||
| SSc subtype: | ||||
| Limited | 211 (77%) | 166 (76%) | 45 (80%) | 0.18 |
| Diffuse | 59 (22%) | 49 (23%) | 10 (18%) | |
| Time from SSc diagnosis to duplex US (months) mean (SD) | 57.9 (85.7) | 63.5 (91.5) | 36.1 (52.9) | 0.04 |
| Digital occlusive arterial disease | 223 (82%) | 193 (89%) | 30 (54%) | <0.001 |
| Macrovascular disease | 74 (27%) | 69 (32%) | 5 (9%) | <0.001 |
| Ulnar Occlusive disease | 68 (25%) | 63 (29%) | 5 (9%) | 0.002 |
| Telangiectasias | 239 (88%) | 192 (89%) | 47 (84%) | 0.27 |
| Calcinosis | 102 (43%) | 95 (49%) | 7 (16%) | <0.001 |
| Interstitial lung disease | 105 (38%) | 90 (41%) | 15 (27%) | 0.04 |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 50 (18%) | 43 (20%) | 7 (12%) | 0.21 |
| Pericardial effusion | 61 (22%) | 54 (25%) | 7 (12%) | 0.047 |
| Gastrointestinal dysmotility | 194 (71%) | 159 (73%) | 35 (62%) | 0.11 |
| Renal crisis | 17 (6%) | 12 (6%) | 5 (9%) | 0.35 |
| SSc specific antibodies: | 175 (68%) | 138 (67%) | 38 (69%) | 0.77 |
| Centromere | 116 (63%) | 95 (63%) | 21 (64%) | 0.97 |
| Scl-70 | 48 (19%) | 36 (18%) | 12 (22%) | 0.57 |
| RNA-Polymerase | 19 (20%) | 14 (19%) | 5 (22%) | 0.79 |
Disclosure of Interests: None declared