

Background: Established criteria for classifying axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are lacking, and assessments of disease activity often rely on measures developed for ankylosing spondylitis (AS). There is an unmet need to systematically identify and measure efficacy of treatments for axial PsA patients (pts). Guselkumab (GUS), a selective interleukin (IL)-23p19 inhibitor, was efficacious in improving signs and symptoms of active PsA in 2 phase 3, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled studies: DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2. In a post-hoc pooled analysis of DISCOVER-1&2 pts with investigator-confirmed sacroiliitis, GUS-treated pts had greater improvements in axial symptoms compared with PBO. 1 Imaging in DISCOVER-1&2 was restricted to the sacroiliac (SI) joints, occurring prior to/at screening as confirmed by the investigator, and locally read.
Objectives: To design a new, dedicated study to evaluate the effects of GUS on axial PsA prospectively.
Methods: Cumulative evidence from DISCOVER-1&2, including exposure–response relationship, covariate adjustment for modest baseline imbalances across treatment groups, subgroup analyses, and comparisons within and across these studies, was considered in designing a new trial. Data from the pivotal registrational studies suggest similar efficacy with GUS every-4-weeks (Q4W) and Q8W regimens in treating PsA signs and symptoms, including symptoms of axial involvement. Power calculations were based on mean changes in Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) scores in DISCOVER-1&2.
Results: The phase 4, randomized, PBO-controlled STAR study is specifically designed to prospectively assess efficacy outcomes in PsA pts with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-confirmed axial inflammation. Based on observed mean (SD) changes from baseline in BASDAI score from DISCOVER-1&2 (
Power calculations for the primary endpoint in the Phase 4 STAR study.
| Historical trial data* | Observed mean (SD) change in BASDAI from W0-24 | Effect size | Power(N=135; α=0.05)** |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBO | -1.28 (2.24) | ||
| GUS 100 mg Q4W | -2.51 (2.00) | 1.23 | >99% |
| GUS 100 mg Q8W | -2.61 (2.47) | 1.33 | >99% |
* From the pooled DISCOVER-1&2 trials
**Power calculations based on N=135 per study group (1:1:1 randomization) and 2-sided significance of 0.05 using a 2-sample T-test assuming equal variances
BASDAI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; GUS, guselkumab; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; Q8W, every 8 weeks; SD, standard deviation; W, week
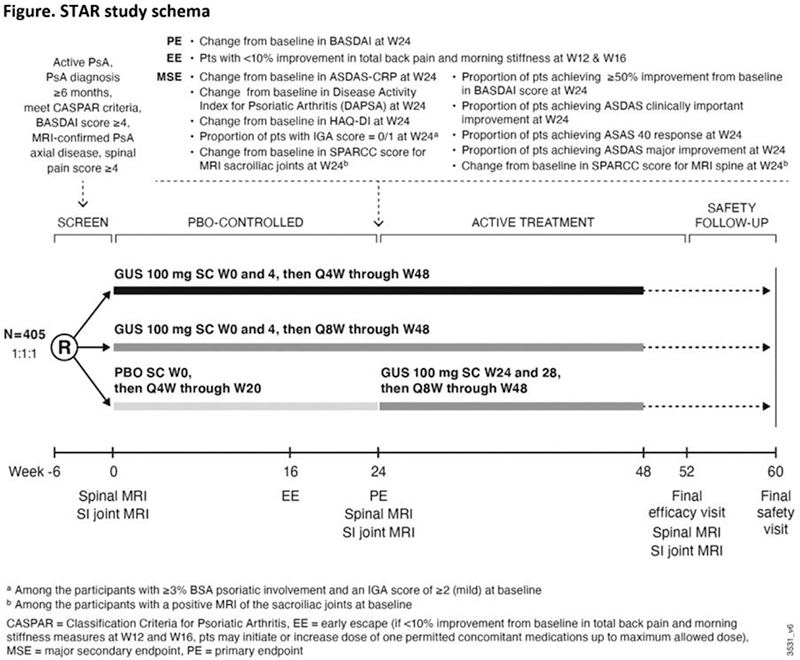
Conclusion: The phase 4 STAR study will allow for an in-depth, prospective evaluation of the effects of selectively inhibiting the IL-23p19 subunit with GUS in pts with MRI-confirmed axial PsA.
REFERENCES:
[1]Mease, et al. Lancet Rheum . 2021;3(10):e715-e723.
Disclosure of Interests: Dafna D Gladman Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, Philip J Mease Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Aclaris, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Inmagene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN Pharma, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Aclaris, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Inmagene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN Pharma, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Aclaris, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Inmagene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN Pharma, and UCB, Paul Bird Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer, Enrique Soriano Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, and Roche, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Soumya D Chakravarty Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, May Shawi Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Global Services, LLC, Stephen Xu Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Sean Quinn Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Cinty Gong Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Evan Leibowitz Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Lai-Shan Tam Consultant of: Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Lilly, Grant/research support from: Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, GSK, Novartis, and Pfizer, Philip Helliwell Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Janssen, and Novartis, Consultant of: Galapagos and Janssen, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Janssen, and Pfizer, Arthur Kavanaugh Consultant of: Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Atul Deodhar Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Glaxo Smith & Kline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Glaxo Smith & Kline, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Mikkel Østergaard Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Hospira, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Hospira, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, and Novartis, Xenofon Baraliakos Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Biocad, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Biocad, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Biocad, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB