

Background: Inflammatory ocular pathology (IOP) includes internal and external involvement. IOP may be severe ocular conditions refractory to conventional immunosuppressants and even biological therapy. Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKINIB) had shown efficacy in refractory cases of different immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID).
Objectives: In patients with refractory IOP treated with JAKINIB our aims were a ) to assess the patients of Spanish referral centers, b ) Literature review.
Methods: Multicenter study of 6 patients with refractory IOP treated with JAKINIB. For Literature review a search was conducted in PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane library from their inception to 1 st January 2022, and conference proceedings from four major rheumatology conferences. In addition, a therapeutical approach of refractory IOP is proposed.
Results: We have identified 6 cases in five University Hospitals and 11 cases in the literature review. These 17 patients (14 women/ 3 men) (24 affected eyes), mean age 35.5±23.4 years had different refractory IOP (uveitis=11; scleritis= 3, PUK= 3).
Most of IOP were associated with IMID (n=13, 76.5%). The main underlying IMID were juvenile idiopathic arthritis (n=5, 29.4%), rheumatoid arthritis (n=2, 11.8%) and spondyloarthritis (n=2; 11.8%) (
Cases reports and Literature review
| Study, year | Cases | Age/ Sex | Underlying IMID | JAKINIB | Ocular involvement | Previous immunosuppressive treatment | Ocular Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Ref ) | |||||||
| Meadow et al. 2014 | 1 | 59, F | RA | TOFA | PUK | MTX, ABA, ivMP | Partial (PI) |
| (1) | |||||||
| Bauermann et al. 2018 | 1 | 22, F | JIA | TOFA | A. uveitis, CME | MTX, ADA, RTX, GOLI, IFX, CsA, TCZ, MMF | Complete (CI) |
| (2) | |||||||
| Paley et al. 2019 | 2 | 1.40, F | 1.Idiopathic | 1.TOFA | 1.Scleritis | 1.MTX, MMF, AZA, CYP | 1.CI |
| (3) | 2.45, F | 2.Idiopathic | 2.TOFA | 2.A. uveitis, CME | 2.MTX, LFN, AZA, MMF, ADA, IFX, CZP, intravitreal fluocinolone ac. | 2.CI | |
| Liu J et al. 2020 | 1 | 30, M | Behçet dis | TOFA | Scleritis | SSZ, MTX, AZA, LFN, THD, COL, GLM | PI |
| (4) | |||||||
| Majumder et al. 2020 | 1 | 26, F | Vogt-Koyanagi- Harada dis | TOFA | P. uveitis | ivMP | CI |
| (5) | |||||||
| Miserocchi et al. 2020 | 4 | 1. 9, F | JIA | 1. TOFA | 1. Panuv | 1. IFX, ADA, LFN, ABA, RTX, TCZ. | 1. CI |
| 2. 1, F | 2. BARI | 2. Panuv | 2. MTX, ADA, IFX, RTX, ABA. | 2. CI | |||
| (6) | 3. 2, F | 3. BARI | 3. Panuv | 3. MTX, AZA, IFX, ADA, TCZ. | 3. CI | ||
| 4. 10, M | 4. BARI | 4. Panuv | 4. ETN, MTX, CsA, IFX, ADA, ABA, TCZ, RTX. | 4. CI | |||
| Pyare et al. 2020 | 1 | 45, F | Idiopathic | TOFA | Necrotizing scleritis | MMF | CI |
| (7) | |||||||
| Present study, 2022 | 6 | 1. 25, F | 1. Blau Syndrome | 1. TOFA/BARI | 1. Panuv | 1.MTX, ETN, ANA, ABA | 1. CI |
| 2. 85, F | 2. RA | 2. BARI | 2. PUK | 2.MTX, LFN, CZP, ADA, iv MP. | 2. CI | ||
| 3. 41, F | 3. Relapsing polychondritis | 3. BARI | 3. PUK | 3. MTX, CsA, SSZ, MMF, AZA, IFX, TCZ, CZP, ABA, ADA. | 3. CI | ||
| 4. 65, F | 4. Idiopathic | 4. BARI | 4. Panuv | 4. MTX, AZA | 4. CI | ||
| 5. 59, M | 5. AS | 5. UPA | 5. A. uveitis | 5. MTX, ADA | 5. CI | ||
| 6. 40, F | 6. SpA and ulcerative colitis | 6. TOFA | 6. A. uveitis | 6. MTX, AZA, ADA | 6. CI |
Uveitis (n=11) followed by ocular surface pathology (n=6) were the most frequent subtypes of IOP. Patterns of uveitis were panuveitis (n=6), anterior uveitis (n=4; 2 of them with Cystoid macular edema) and posterior (n=1). Ocular surface pathology was due to scleritis (n=3) and PUK (n=3).
Besides systemic corticosteroids, before JAKINIB, conventional (n= 16; 94.1%) and biological immunosuppressive drugs (n=13; 76.5%) were required. The JAKINIB most widely used was tofacitinib (n= 10; 58.8%) followed by baricitinib (n=7; 41.2%). In only one patient with Blau Syndrome and uveitis, tofacitinib was switched to baricitinib due to severe lymphopenia.
After starting JAKINIB treatment, all patients presented clinical improvement, complete (n=15, 88.2%) or partial (n= 2; 11.8%).
Based on these data a therapeutical approach of refractory IOP was proposed (
Therapeutical approach
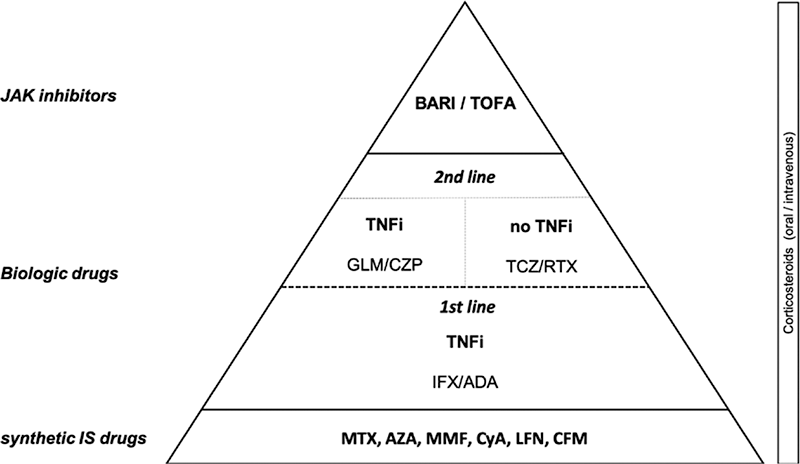
Conclusion: JAKINIB may be an effective and safe therapy in IOP refractory to conventional or even biological immunosuppressive therapy.
REFERENCES:
[1]Meadow PB. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2014.
[2]Bauermann P. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2019.
[3]Paley MA. Am J Ophthalmol Case Reports. 2019.
[4]Liu J. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020.
[5]D Majumder. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020.
[6]Miserocchi E. Clin Rheumatol. 2020.
[7]Pyare E. Indian J Ophtalmol, 2020.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared