

Background: Isoniazid (INH) is used to treat latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI), and hepatotoxicity is one of the most frequent adverse effect. Several Disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs) can also cause hepatotoxicity. Many patients with rheumatic immune mediated diseases (R-IMID) receive INH prior to DMARDs for prophylaxis of LTBI. This risk of hepatotoxicity with DMARDs after hepatotoxicity with INH is unknown.
Objectives: To assess the risk of hepatotoxicity with DMARDs in patients who have presented hepatotoxicity with INH.
Methods: Study of all consecutive R-IMID patients evaluated in the last five years (2016-2020) in a University Hospital, who presented hepatotoxicity after INH and later received DMARDs. We study if they also presented hepatotoxicity with DMARDs.
Hepatotoxicity was defined as an elevation of liver enzymes (ALT and/or AST) upper the high limit after the introduction of the treatment.
Results: INH was used in 232 of 7218 patients with R-IMID. We finally included 64 patients (45 women; 70.3%; mean age 53.4±10.5 years), who had hepatotoxicity due to INH (
Main characteristics of 64 patients with rheumatic immune-mediated diseases (R-IMID) that presented hepatotoxicity after receiving isoniazid (INH).
| Variables | Patients (n=64 ) |
|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ±SD | 53.4±10.5 |
| Sex (women), n (%) | 45 (70.3) |
| R-IMID | |
| - SpA / PsA | 36 (56.3%) |
| - RA | 21 (32.8%) |
| - SSc | 3 (4.7%) |
| - Conectivopathies | 3 (4.7%) |
| - Other | 2 (3.2%) |
| Liver enzyme elevation over baseline (INH)* | |
| - x2 | 64 (100) |
| - x3 | 22 (34.4) |
| - x4 or higher | 13 (20.3) |
| csDMARDs | |
| - MTX | 34 (53.1%) |
| - HCQ | 15 (23.4) |
| - LFN | 13 (20.3) |
| - SSZ | 10 (15.6) |
| bDMARDs | 47 (73.4%) |
| Targeted synthetic DMARDs (Jakinib ) | 8 (12.5) |
ABA: Abatacept; AZA: Azathioprine, HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine; INH: Isoniazid; LFN: Leflunomide; MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil, MTX: Methotrexate; PsA: Psoriatic arthritis, RA: Rheumatoid arthritis, RTX: Rituximab; SpA: Axial spondyloarthritis; SSc: Systemic sclerosis; TCZ: Tocilizumab; TNFi: TNF inhibitors
* Patients with higher liver enzyme elevation are included in the previous groups.
The most frequent R-IMIDs were rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Methotrexate (MTX) (n=34, 53.1%) and TNF inhibitors (n=27, 42.2%) were the conventional and biologic-DMARD more frequently used, respectively.
Hepatotoxicity was higher with MTX (14 of 34, 41.2%), and lower with the other DMARDs (
Hepatotoxicity with different DMARDs in 64 patients with previous hepatotoxicity with INH
* Patients with higher liver enzyme elevation are included in the previous groups.
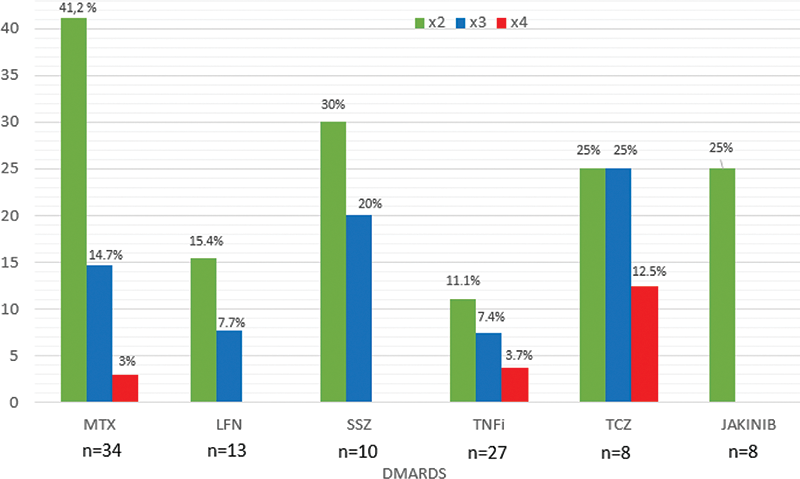
Conclusion: In patients with previous hepatotoxicity with INH, we observed an increased risk with different DMARDs, especially with MTX.
Disclosure of Interests: David Martínez-López: None declared, Joy Osorio-Chavez: None declared, Virginia Portilla: None declared, Carmen Álvarez-Reguera: None declared, Alba Herrero-Morant: None declared, Lara Sanchez-Bilbao: None declared, Iñigo Gonzalez-Mazon: None declared, Miguel A González-Gay Speakers bureau: Consultation fees/participation in company-sponsored speaker´s bureau from Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, and MSD, Grant/research support from: Dr. Miguel A. Gonzalez-Gay received grants/research supports from Abbvie, MSD, and Roche, Ricardo Blanco Speakers bureau: Consultation fees/participation in company-sponsored speaker´s bureau from Abbvie, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Janssen, and MSD., Grant/research support from: Dr. Ricardo Blanco received grants/research supports from Abbvie, MSD, and Roche