

Background: Janus Kinases (JAK) can promote cytokine production in immune and hematopoietic cells. The JAK-2 (V617F) mutation is the most frequently detected mutation in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) which include essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV), primary myelofibrosis (PMF) and undifferenciated MPN. JAK-2 (V617F) mutation displays a pro-inflammatory phenotype that may be associated to a higher risk of immune mediated diseases (IMID).
Objectives: In a wide series of JAK2 (V617F) mutation, we assess the presence of a) IMID (rheumatic and non-rheumatic), b) treatment of rheumatic IMID.
Methods: We studied all the patients diagnosed with a positive JAK-2 (V16F) mutation in a single University Hospital from January 2004 to December 2019. JAK-2 (V16F) mutation was detected by using both peripheral blood and bone marrow samples. Associated IMID and treatment of rheumatic IMID were evaluated.
Results: We included 130 patients (73 men/57 women; mean age, 70.1±14.5 years). All of them were diagnosed of MPN; ET (n=64, 49.2%), PV 46 (35.4%), undifferentiated MPN (n=12, 9.2%) and PMF (n=8, 6.1%). In 10 of these 130 patients (7.7%) a rheumatic IMID was diagnosed: rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n=4; 40%), polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) (n=3; 30%), Sjögren syndrome (SS) (n=1; 10%), antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) (n=1; 10%) and autoinflammatory syndrome (WDR1 mutation) (n=1; 10%). Patients with RA, SS, PmR, and APS were clinically mild. RA patients were seronegative, non-erosive and without extraarticular involvement. Treatment and response are summarized in
Conclusion: Except in autoinflammatory syndrome, most rheumatic IMID associated to JAK-2 (V16F) mutation are clinically mild, and treatment and response of patients seems similar or even better than those without this mutation.
Treatment of 10 patients with rheumatic IMIDs and JAK-2 (V16F) mutation.
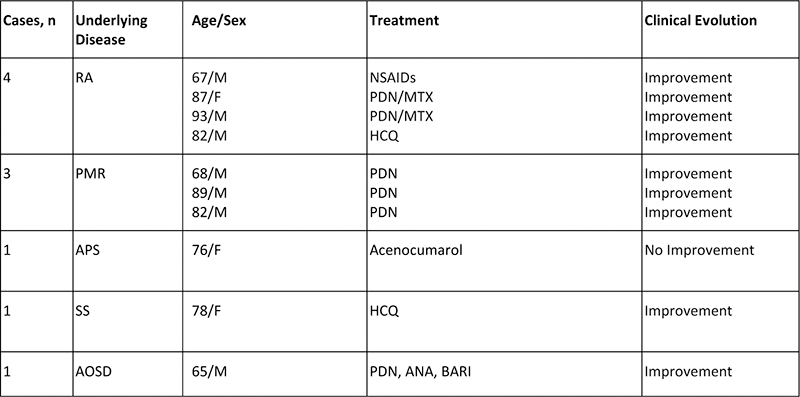
Abbreviation: ANA: anakinra, BARI: baricitinib, NSAIDs: Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs, PDN: prdnisone, RA: Rheumatoid arthritis, SS: Sjögren syndrome, PMR: polymyalgia rheumatica.
Disclosure of Interests: Carmen Álvarez-Reguera: None declared, Lara Sanchez-Bilbao: None declared, Sara Fernández López: None declared, Ana Batlle-López: None declared, Alba Herrero-Morant: None declared, David Martínez-López: None declared, Miguel Á. González-Gay Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Janssen, Lilly and MSD, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and MSD., Ricardo Blanco Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Pfizer, Roche, Bristol-Myers, Janssen, Lilly and MSD., Grant/research support from: Abbvie, MSD and Roche.