

Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a low-prevalent autoimmune disease with a heterogeneous presentation. Skin involvement is the most frequent symptom and its treatment is orphan, only attending at Raynaud’s phenomenon and classic immunosuppressive therapy for fibrosis. Lung implication is still remaining as the first cause of death. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the most frequent presentation and treatments most used includes cyclophosphamide and mycophenolate. 1 In 2021, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first biologic therapy for ILD-SSc, tocilizumab (TCZ), based on 2 clinical trials. 2,3
Objectives: To assess TCZ efficacy in SSc, either in ILD or skin involvement.
Methods: A systematic literature review was made using Medline, Embase, Cochrane Library and the Web of Science databases. Search strategy focused in synonyms of SSc and TCZ, also including MeSH terms. A random-effects model meta-analysis was performed to evaluate TCZ efficacy, when comparable measures were found. Clinical trials, observational studies and case-series were eligible.
Results: Search strategy identified 1036 articles, finally 13 studies were eligible for the review. Regarding the effect of TCZ in SSc skin involvement, measured by the modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS), a non-significant 40% improvement in mRSS and change in mean mRSS was reported (OR 1.22 [0.74-2.01], p=0.43 and SMD -0.69 [-1,48-0.10], p=0.09, respectively). About ILD-SSc, a significant non-worsening 10% Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) was reported in patients treated with TCZ (OR 0.45 [0.23-0.86), p=0.02) (
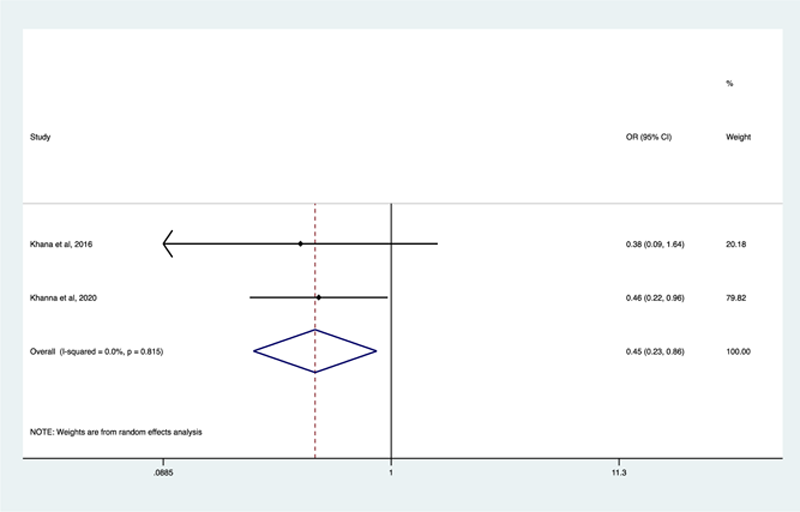
Conclusion: Our study is the first review and meta-analysis of SSc patients treated with TCZ. This results show that TCZ could delay the worsening of ILD-SSc, being one therapeutic alternative to classical immunosuppressive therapy. Further studies are needed for better disease understanding and TCZ implications in other organ impairment.
REFERENCES:
[1]Desbois AC, Cacoub P. Systemic sclerosis: An update in 2016. Autoinmun Rev. 2016 May; 15 (5): 417-26.
[2]Khanna D, Denton CP, Jahreis A, et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (fascinate): a phase 2, randomized, controlled trial. Lancet, 2016;387(10038):2630-2640.
[3]Khanna D, Lin CJF, Furst DE, et al. Tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(10):963-974.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared