

Background: Neuropsychiatric (NP) disease is more common in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) than in the general population. 1 Increased incidence of NP events (depression and suicidality) has been reported with biologic therapies, including SLE therapies. 2 Depression and suicidality were evaluated in patients with SLE treated with anifrolumab, a type I interferon receptor antibody, in the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 trials. 3,4
Objectives: To understand the impact of anifrolumab treatment on NP manifestations (depression and suicidality) in patients with SLE relative to standard therapy using pooled data from the TULIP trials.
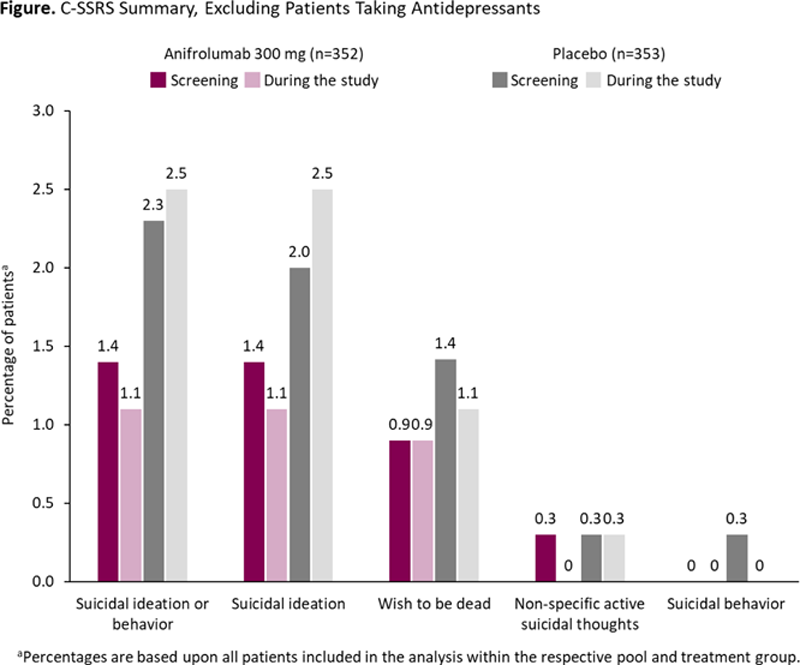
Methods: TULIP-1/-2 were randomized, placebo-controlled, 52-week trials of intravenous anifrolumab every 4 weeks in patients with moderate to severe SLE despite standard therapy. 3,4 Patients with active severe or unstable NP SLE were excluded. Patients who received ≥1 dose of anifrolumab 300 mg or placebo were analyzed for depression and suicidality. 3,4 The Personal Health Questionnaire Depression Scale-8 (PHQ-8) and Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) were used to assess clinical depression and suicidal ideation and behavior, respectively. Incidence of adverse events (AEs) within the standardized Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities query of depression (excluding suicide and self-injury) and antidepressant use at baseline and during the study were also assessed.
Results: In the TULIP pooled analysis, 360 patients received anifrolumab and 365 received placebo. Mean PHQ-8 scores were in the mild range (≥5 to <10); 9.7 in both groups at baseline (
PHQ-8 Summary
| All patients | Excluding patients taking antidepressants | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anifrolumab 300 mg N=360 | Placebo N=365 | Anifrolumab 300 mg N=360 | Placebo N=365 | |||||||||||||
| n | Mean a | SD | Change b | n | Mean a | SD | Change b | n | Mean a | SD | Change b | n | Mean a | SD | Change b | |
| Baseline | 341 | 9.7 | 6.26 | – | 348 | 9.7 | 6.11 | – | 335 | 9.5 | 6.21 | – | 338 | 9.7 | 6.09 | – |
| Week 24 | 295 | 7.6 | 5.89 | –2.1 | 303 | 8.0 | 6.00 | –1.5 | 289 | 7.5 | 5.84 | –2.1 | 293 | 8.1 | 6.00 | –1.5 |
| Week 52 | 266 | 7.8 | 5.99 | –2.0 | 261 | 7.9 | 6.03 | –1.3 | 262 | 7.7 | 6.00 | –2.0 | 252 | 7.9 | 5.96 | –1.2 |
SD, standard deviation.
a PHQ-8 classifications: 0–4 = none, 5–9 = mild, 10–14 = moderate, 15–19 = moderately severe, and 20–24 = severe.
b Mean change from baseline.
Conclusion: Patients with SLE treated with anifrolumab did not experience increased depression, suicidality, or need for antidepressants when compared with standard therapy, irrespective of baseline antidepressant use.
REFERENCES:
[1]Zhang L, et al. BMC Psychiatry . 2017;17:70.
[2]Benlysta (belimumab) [prescribing information]. Philadelphia, PA: GlaxoSmithKline; 2021.
[3]Furie RA, et al. Lancet Rheumatol . 2019;1:e208–19.
[4]Morand EF, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:211–21.
Acknowledgements: Writing assistance by Andrea Y. Angstadt, PhD (Fishawack Health). This study was sponsored by AstraZeneca.
Disclosure of Interests: Susan Manzi Speakers bureau: AstraZeneca, Consultant of: AstraZeneca, Exagen Diagnostics, Inc, Cugene, GSK, Lilly, Lupus Foundation of America, UCB Advisory Board, Grant/research support from: HGS/GSK, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Catharina Lindholm Employee of: AstraZeneca, Ihor Hupka Employee of: AstraZeneca, Lijin (Jinny) Zhang Shareholder of: AstraZeneca, Employee of: AstraZeneca, Manish Shroff Employee of: AstraZeneca, Gabriel Abreu Employee of: AstraZeneca AB, Shanti Werther Shareholder of: AstraZeneca, Employee of: AstraZeneca, Raj Tummala Shareholder of: AstraZeneca, Employee of: AstraZeneca