

Background: A better understanding of the immunological differences between psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients (pts) who are tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi)-naïve & who have inadequate response to TNFi (TNFi-IR) may guide treatment choices. In DISCOVER-1, benefit of the IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor guselkumab (GUS) every-four-weeks (Q4W) & Q8W vs placebo (PBO) in improving PsA signs & symptoms was seen in adults with active PsA. 1 The Ph3b COSMOS study of GUS Q8W vs PBO in TNFi-IR PsA pts corroborated these findings. 2
Objectives: Assess baseline (BL) molecular differences between TNFi-naïve & -IR PsA pts & investigate GUS pharmacodynamic (PD) effect on cytokine expression over time in these cohorts.
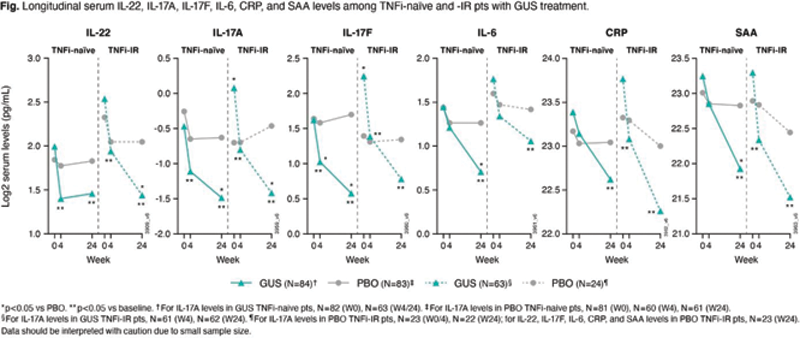
Methods: Serum samples collected from consenting biomarker substudy pts in DISCOVER-1 1 (TNFi-naïve [n=101] & -IR [n=17]), DISCOVER-2 3 (TNFi-naïve [n=150]), & COSMOS 2 (TNFi-IR [n=76]) were analyzed for selected serum cytokine levels. TNFi-IR pts in this post-hoc analysis had active PsA & discontinued 1-2 TNFi due to inadequate efficacy; these pts required a TNFi-specific washout period prior to starting GUS. PD effect of GUS Q8W on cytokine levels was assessed. Differential BL cytokine expression, associations between BL cytokine levels & clinical response (Psoriasis [PsO] Area & Severity Index 75% improvement from BL [PASI75] & American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement [ACR20]), & GUS effect on cytokine levels were analyzed with a General linear model & Spearman linear regression.
Results: BL pt demographics, disease characteristics, & conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD) use were comparable between TNFi-naïve (DISCOVER-1 & -2, N=251) & -IR (DISCOVER-1 & COSMOS, N=93) pts, with differences in mean PASI score (8.9 v 12.5), swollen joint count (SJC) (11.7 v 10.3), PsA duration (5.8 v 9.8 yrs), & PsO duration (16.7 v 20.4 yrs;
BL demographics, disease characteristics, & drug use in TNFi-naïve & -IR cohorts with available cytokine data in DISCOVER-1&2 & COSMOS.*
| TNFi-naïve (N=251) | TNFi-IR (N=93) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age [yrs] | 47.2 (11.3) | 48.5 (11.1) |
| Female, n (%) | 132 (52.6) | 46 (49.5) |
| Body mass index [kg/m 2 ] | 29.6 (6.1) | 30.3 (6.4) |
| Median (range) CRP [mg/dL] | 0.9 (0.0-12.9) | 1.0 (0.0-13.2) |
| Log2 IL-22 / TNFα [pg/mL] | 2.0 (1.4) / 1.1 (0.6) | 2.5 (1.5) / 1.9 (1.2) |
| Log2 IL-17A / F [pg/mL] | -0.4 (1.5) / 1.7 (1.5) | -0.1 (1.7) / 2.0 (1.6) |
| SJC [0-66] | 11.7 (7.1) | 10.3 (8.3) |
| TJC [0-68] | 20.3 (13.1) | 20.6 (14.2) |
| PsA duration [yrs] | 5.8 (5.9) | 9.8 (8.2) |
| PsO duration [yrs] | 16.7 (12.8) | 20.4 (12.0) |
| PsO Body surface area (%) | 14.8 (18.6) | 19.1 (21.3) |
| Investigator’s Global Assessment score [0-4] | 2.3 (0.9) | 2.3 (1.0) |
| PASI score [0-72] | 8.9 (10.6) | 12.5 (12.0) |
| Enthesitis [Y], n (%) | 160 (63.7) | 58 (62.4) |
| csDMARD use [Y], n (%) | 164 (65.3) | 62 (66.7) |
| Corticosteroid use (Y), n (%) | 45 (17.9) | 19 (20.4) |
| Methotrexate use [Y], n (%) | 136 (54.2) | 54 (58.1) |
Data are mean (SD) unless otherwise noted. *Pts with serum CRP level ≥0.3 mg/dL, SJC ≥3, & TJC ≥3 (to mimic D1 inclusion criteria 1 ). TJC = tender joint count
Conclusion: Elevated BL IL-22 expression & association between BL IL-22 levels & W24 PASI75 response, & a W24 trend for an association between upregulated BL IL-22 & ACR20 response, in TNFi-IR pts seen in this exploratory analysis may suggest increased involvement of the IL-23 pathway in TNFi-IR pts. GUS showed comparable & significant PD effects for TNFi-naïve & -IR pts, consistent with observed clinical responses.
REFERENCES:
[1]Deodhar A, et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1115-25.
[2]Coates LC, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:140-1.
[3]Mease P, et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1126-36.
Disclosure of Interests: Stefan Siebert Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Biogen, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB, Laura Coates Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Medac, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Georg Schett Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB, Siba P Raychaudhuri Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN Pharma, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN Pharma, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, SUN Pharma, and UCB, Warner Chen Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Sheng Gao Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Soumya D Chakravarty Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), May Shawi Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, Frederic Lavie Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, Elke Theander Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Marlies Neuhold Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Alexa Kollmeier Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Xie L Xu Shareholder of: Johnson & Johnson, Employee of: Janssen Research & Development, LLC (a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson), Proton Rahman Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: Janssen and Novartis, Philip J Mease Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Aclaris, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Inmagene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, and UCB, Atul Deodhar Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Aurinia, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB