

Background: Patients are increasingly involved in the decision process regarding their medicines, but a discrepancy exists between the information provided and preferred. Information on adverse drug reactions (ADRs) focuses on frequency, but little is known about the course and burden of ADRs.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate the course and burden of ADRs over time attributed to using TNFα-inhibitors in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRDs) and to assess whether Sankey diagrams and polar plots are suitable to provide visualization of these aspects.
Methods: We used data of the Dutch Biologic Monitor [1], in which biologic users with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease filled out bimonthly surveys about ADRs experienced and specifically the ADR course and burden. ADRs were coded according to the MedDRA terminology. ADR course was scored as worsening, improving, remaining stable or resolving over time, with room to give a description. Furthermore, it was assessed whether an ADR was recurrent or not. Patients scored burden on a scale ranging from 1 (no burden) to 5 (very high burden). We selected patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis or axial spondyloarthritis using a TNFα inhibitor (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, golimumab or infliximab). They also had to report an ADR belonging to the system organ classes ‘Infections and infestations’ or ‘Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders’, or the high-level term ‘Injection site reactions’ and completed ≥2 consecutive questionnaires (representing circa ≥4 months). These types of ADRs were chosen as they impose the highest burden for patients. [2]
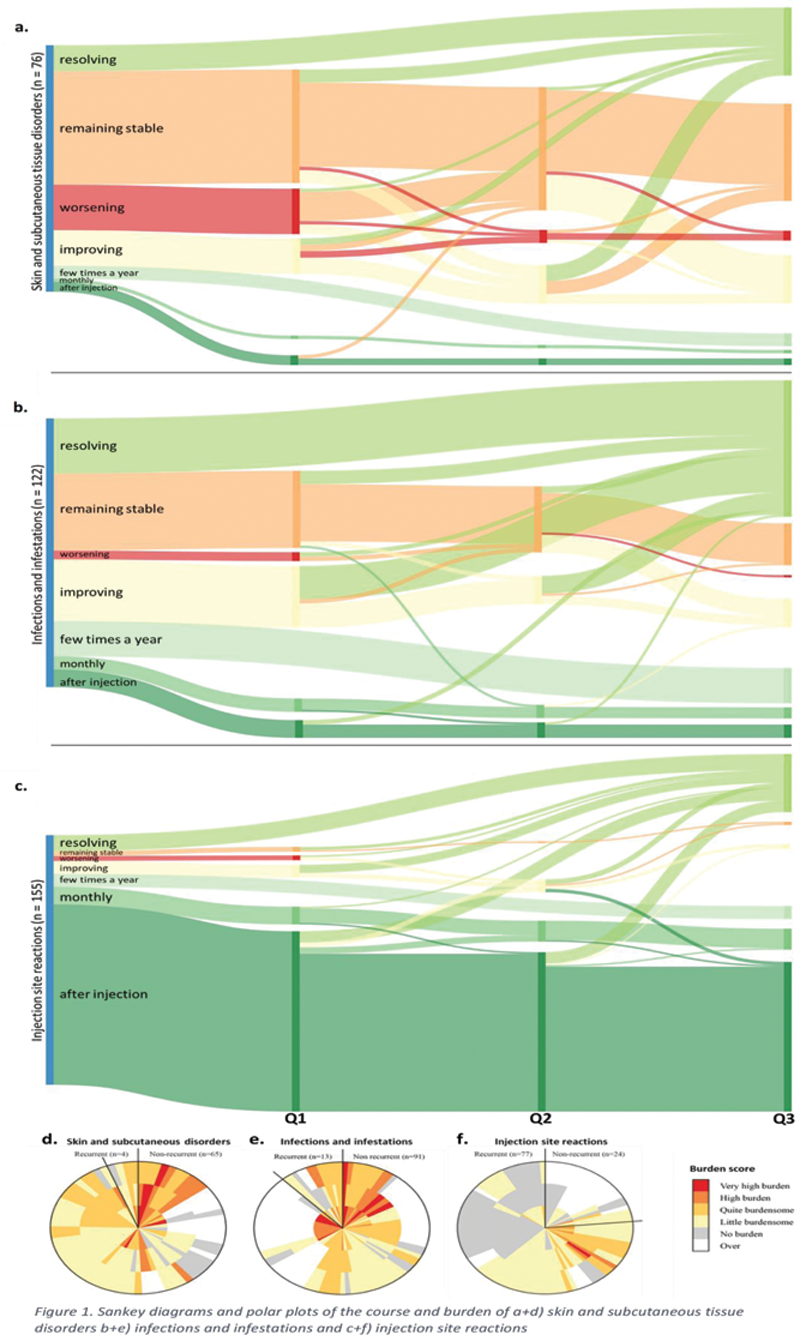
Results: A total of 202 patients met the inclusion criteria (71.8% female, mean age 54.8 years (±12.7 years)). The majority of the patients (61.9%) was diagnosed with RA. Most frequently used TNFα inhibitors were adalimumab (37.1%) and etanercept (54.0%). In total 353 ADRs were reported, of which 76 (21.5%) were categorized as ‘Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders’, 122 (34.6%) as ‘Infections and infestations’ and 155 (43.9%) as ‘Injection site reactions’. The course of the ADRs is visualized in Sankey diagrams (
Conclusion: Skin reactions attributed to the use of TNFα-inhibitors by IRD-patients show a stable course over time with a slightly diminishing burden over time. Infections have the highest burden at start but decrease over time and most of them resolve during follow-up. Injection site reactions are mostly recurrent with a low and stable burden over time. We propose that Sankey diagrams and polar plots are suitable to visualize the course and burden of ADRs over time.
REFERENCES:
[1]Kosse LJ et al. Patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases: quality of self-reported medical information in a prospective cohort event monitoring system. Rheumatology. 2020; 59(6): 1253-1261.
[2]Davelaar JF, Jessurun NT, Tas SW, Nurmohamed MT, Bemt BJF van den, Vonkeman HE. Patient-reported burden of adverse drug reactions attributed to the use of adalimumab and etanercept in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatology. 2021; 73(10).
Disclosure of Interests: Merel de Boer: None declared, Helen Gosselt: None declared, Jurriaan Jansen: None declared, Martijn van Doorn Speakers bureau: Leopharma, Novartis, Janssen-Cilag and Pfizer, Consultant of: Leopharma, Novartis, Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer and Sanofi-Genzyme, Grant/research support from: Novartis, Frank Hoentjen Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Janssen-Cilag, MSD, Takeda, Celltrion, Teva, Sandoz and Dr Falk, Consultant of: Celgene, Grant/research support from: Dr Falk, Janssen-Cilag, Abbvie, Michael Nurmohamed Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Leopharma, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme, Janssen, Novartis, Consultant of: Abbvie, Leopharma, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme, Janssen, Novarti, Grant/research support from: Novartis, Phyllis Spuls Grant/research support from: Prof. dr. Ph.I. Spuls has done consultancies in the past for Sanofi 111017 and AbbVie 041217 (unpaid), receives departmental independent research grants for TREAT NL registry, for which she is Chief Investigator (CI), from pharma companies since December 2019, is involved in performing clinical trials with many pharmaceutical industries that manufacture drugs used for the treatment of e.g. psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, for which financial compensation is paid to the department/hospital., Sander Tas Consultant of: Gebro, GSK, AbbVie, Galvani, Arthrogen, Galapagos, Grant/research support from: Pfizer, GSK, Celgene, BMS, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Harald Vonkeman Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Celgene, Celltrion, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, all outside the submitted work., Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Sanofi, Naomi Jessurun: None declared