

Background: Infections are the most commonly reported AE observed in patients with RA treated with immunosuppressive therapies and can be clinically significant. A recent review reported differences in the risk of infection for some biologics such as tocilizumab and TNF inhibitors. 1 Abatacept selectively modulates T-cell co-stimulation and is approved for the treatment of RA. In patients with polyarticular-course juvenile idiopathic arthritis, no association was found between higher serum abatacept exposure and the incidence of infection. 2 This has not been evaluated for adult patients with RA.
Objectives: To determine if higher serum abatacept exposure during treatment with SC abatacept was associated with increased risk of infection in adult patients with RA.
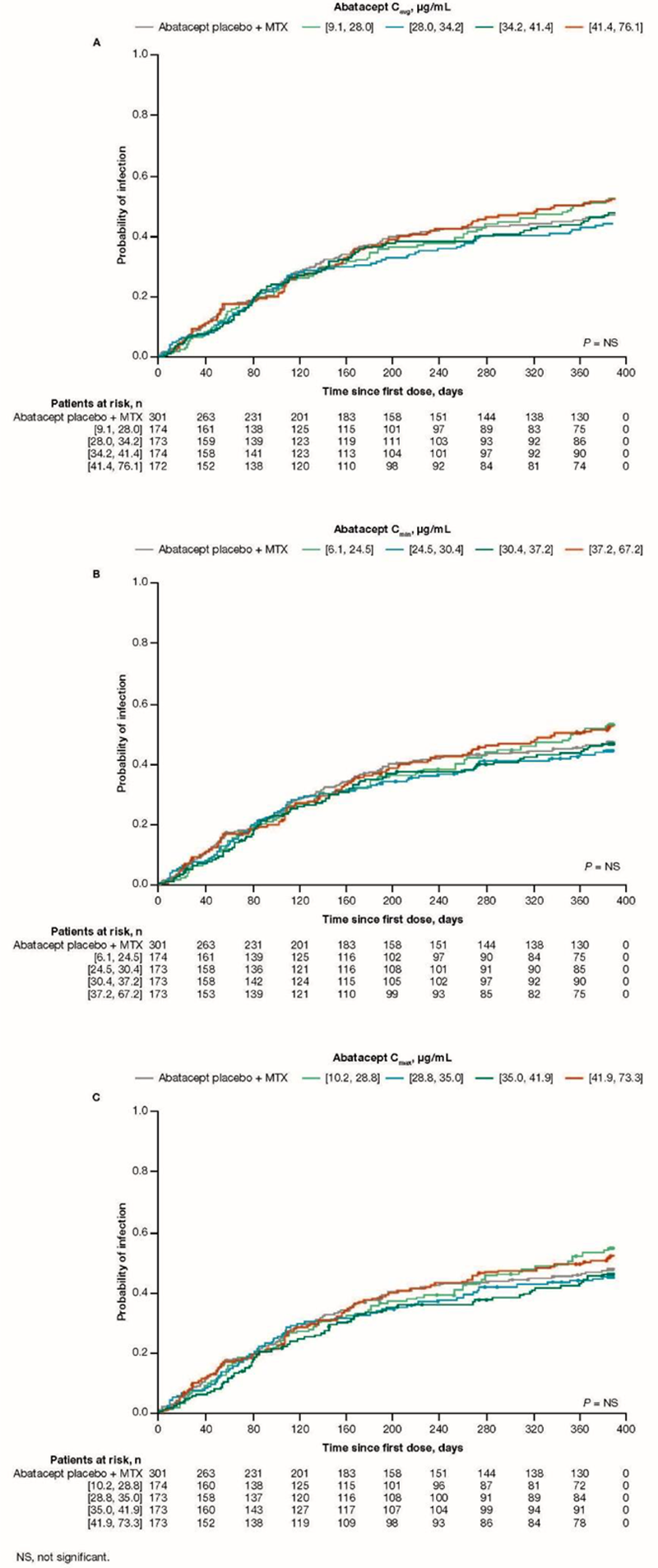
Methods: AVERT-2 ( A ssessing V ery E arly R heumatoid arthritis T reatment-2) was a randomized, placebo-controlled study of SC abatacept + MTX vs abatacept placebo + MTX in MTX-naive, anti-citrullinated protein antibody–positive patients with early, active RA. 3 A post hoc population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis was performed using PK-evaluable patient data from the induction period (year 1) of AVERT-2. Association between steady-state abatacept exposure (min plasma concentration [C min ], max plasma concentration [C max ], and average plasma concentration [C avg ]) and first infection was evaluated using Kaplan–Meier plots of probability vs time on treatment by abatacept exposure quartiles and Cox proportional-hazards models.
Results: PK of SC abatacept was defined as a linear 2-compartment model with first-order absorption and first-order elimination. The findings of the updated PK analysis were consistent with those reported in prior population analyses of abatacept PK in adults with RA. The final model included effects of baseline body weight, estimated glomerular filtration rate, sex, age, albumin, MTX use, NSAID use, SJC, and race on abatacept clearance. The only covariate with a clinically relevant effect was higher body weight, which caused an increase in clearance and volume. Infections occurred in a total of 330/693 (47.6%; serious, 1.6%) patients treated with abatacept, and 134/301 (44.5%; serious, 1.3%) with placebo during the first year of AVERT-2. In patients taking abatacept, the mean (SD) study exposure to abatacept was 376 (60) days, while mean (SD) prednisone equivalent dose was 6.7 (3.8) mg/day and mean (SD) MTX dose was 9.6 (3.0) mg/week. No exposure–response relationship was observed between the probability of first infection and steady-state abatacept exposure quartiles (C
avg
, C
min
, and C
max
), or compared with placebo (
Conclusion: No association was found between initial infection and steady-state abatacept exposure (C avg , C min , C max ) or MTX and glucocorticoid use in patients with RA treated with SC abatacept.
REFERENCES:
[1]Jani M, et al. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2019;31:285–92.
[2]Ruperto N, et al. J Rheumatol 2021;48:1073–81.
[3]Emery P, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71(suppl 10):L11.
Acknowledgements: This study was sponsored by Bristol Myers Squibb. Writing and editorial assistance were provided by Fiona Boswell, PhD, of Caudex, and was funded by Bristol Myers Squibb. Support was provided by Sandra Overfield as Protocol Manager, and Prema Sukumar and Renfang Hwang as Data Science Leads.
Disclosure of Interests: Paul Emery Consultant of: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung, Roy Fleischmann Consultant of: Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, Grant/research support from: Amgen, AbbVie, Arthrosi, Biosplice, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Horizon, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, TEVA, UCB, Robert Wong Shareholder of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Karissa Lozenski Shareholder of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Yoshiya Tanaka Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Mitsubishi Tanabe, YL Biologics, Consultant of: AbbVie, Ayumi, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Taisho, Sanofi, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Asahi Kasei, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Corrona, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Kowa, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Takeda, Vivian Bykerk Consultant of: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genzyme Corporation, Gilead, Regeneron, UCB, Grant/research support from: Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genzyme Corporation, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Aventis, UCB, Clifton Bingham Consultant of: AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Grant/research support from: Bristol Myers Squibb, Thomas Huizinga Speakers bureau: Abblynx, Abbott, Biotest AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, Crescendo Bioscience, Eli Lilly, Epirus, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi- Aventis, UCB, Consultant of: Abblynx, Abbott, Biotest AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, Crescendo Bioscience, Eli Lilly, Epirus, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi- Aventis, UCB, Grant/research support from: Abblynx, Abbott, Biotest AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, Crescendo Bioscience, Eli Lilly, Epirus, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi- Aventis, UCB, Gustavo Citera Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Sandoz, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Grant/research support from: Pfizer, Yedid Elbez Consultant of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Signifience, Vidya Perera Shareholder of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Bindu Murthy Shareholder of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Kelly Maxwell Consultant of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Cognigen Corporation, Julie Passarell Consultant of: Bristol Myers Squibb, Employee of: Cognigen Corporation, William Hedrich: None declared, Daphne Williams Consultant of: Black Diamond Network, Joule, Syneos, Employee of: Bristol Myers Squibb.