

Background: Elevated rheumatoid factor (RF) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with higher disease activity and increased risk for disease progression 1 .
Recent publications indicate significantly lower efficacy of TNF inhibitors (TNFi) in RA patients with high RF levels compared with low/negative RF subgroup 2,3 . Fab therapy with Certolizumab pegol (CZP), a PEGylated, Fc-free monoclonal antibody (mAb), has shown comparable efficacy and consistent serum levels irrespective of baseline RF 4 .
RF binds the Fc region of IgG1, the subtype used to engineer the majority of mAbs 5 . Formation of large immune complexes may likely explain the inceased clearance of mAbs in patients with high RF titers and reported reduced TNFi efficacy.
Objectives: We aimed to evaluate in clinical practice whether RF levels in RA patients influence serum drug levels of 3 TNFi with different molecular structures.
Methods: We evaluated retrospectively a cohort of RA patients from La Paz University Hospital (RA-Paz Registry, 1999-2019) treated with Infliximab (IFX), Adalimumab (ADA) or CZP. Clinical and demographic data were collected at baseline (T0) and after 6 months (T6) of treatment. RF titers and serum drug levels were measured at T0 and T6 using nephelometry and ELISA respectively. Association between baseline RF titers and drug levels was assessed using non-parametric test (Mann-Whitney).
Results: 168 patients were evaluated: 90 received IFX, 48 ADA and 32 CZP. Characteristics at T0 are shown in
Baseline characteristics.
| Characteristics | Total (n=168) | IFX (n=90) | ADL (n=48) | CZP (n=32) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years* | 55.5(45.3-66) | 57(46-65) | 50(42-64) | 61(47-70) | 0.08 |
| Body mass index, Kg/m 2 * | 24.5(21.7-29) | 24.2(21.8-27.7) | 24.7(21.5-30.3) | 24.6(22.2-30.3) | 0.3 |
| Male, n(%) | 28(17%) | 14(15%) | 9(19%) | 5(17%) | 0.2 |
| Disease duration, years* | 8.7(4.5-14.3) | 8.4 (4.4-14.3) | 8.8 (3.9-16) | 9.7(5-12) | 0.06 |
| Smoking status, n(%) | 0.03 | ||||
| Currently/ex-smoker | 66(39%) | 29(32%) | 22(48%) | 16(57%) | |
| Non-smoker | 96(57%) | 61(68%) | 24(52%) | 12(43%) | |
| RF, n(%) | 128(76%) | 75(83%) | 28(58%) | 25(81%) | 0.002 |
| ACPA, n(%) | 134(80%) | 73(81%) | 35(73%) | 27(84%) | 0.3 |
| DAS28** | 5.1(1.3) | 5.4(1.3) | 4.5(1.3) | 4.9(1.3) | 0.002 |
| CRP levels* | 7.8(3-21.8) | 10.3(3.2-25.2) | 5.1(1.4-10.1) | 7.8(2.3-18.2) | 0.1 |
| Prior bDMARDs, n(%) | 26(15%) | 10 (11%) | 10 (21%) | 6(20%) | 0.2 |
| Monotherapy, n(%) | 16(10%) | 8(9%) | 8(17%) | 0 | 0.2 |
| csDMARDS, n(%) | 152(90%) | 82(91%) | 82(91%) | 32(100%) | |
| Methotrexate, n(%) | 112(67%) | 64(78%) | 33(83%) | 17(53%) | 0.2 |
| Other csDMARDs, n(%) | 24(24%) | 18(22%) | 7(18%) | 15(50%) | 0.0008 |
| Prednisone, n(%) | 85(51%) | 49(54%) | 21(44%) | 16(50%) | 0.6 |
*Median and interquartile range;**mean and standard deviation
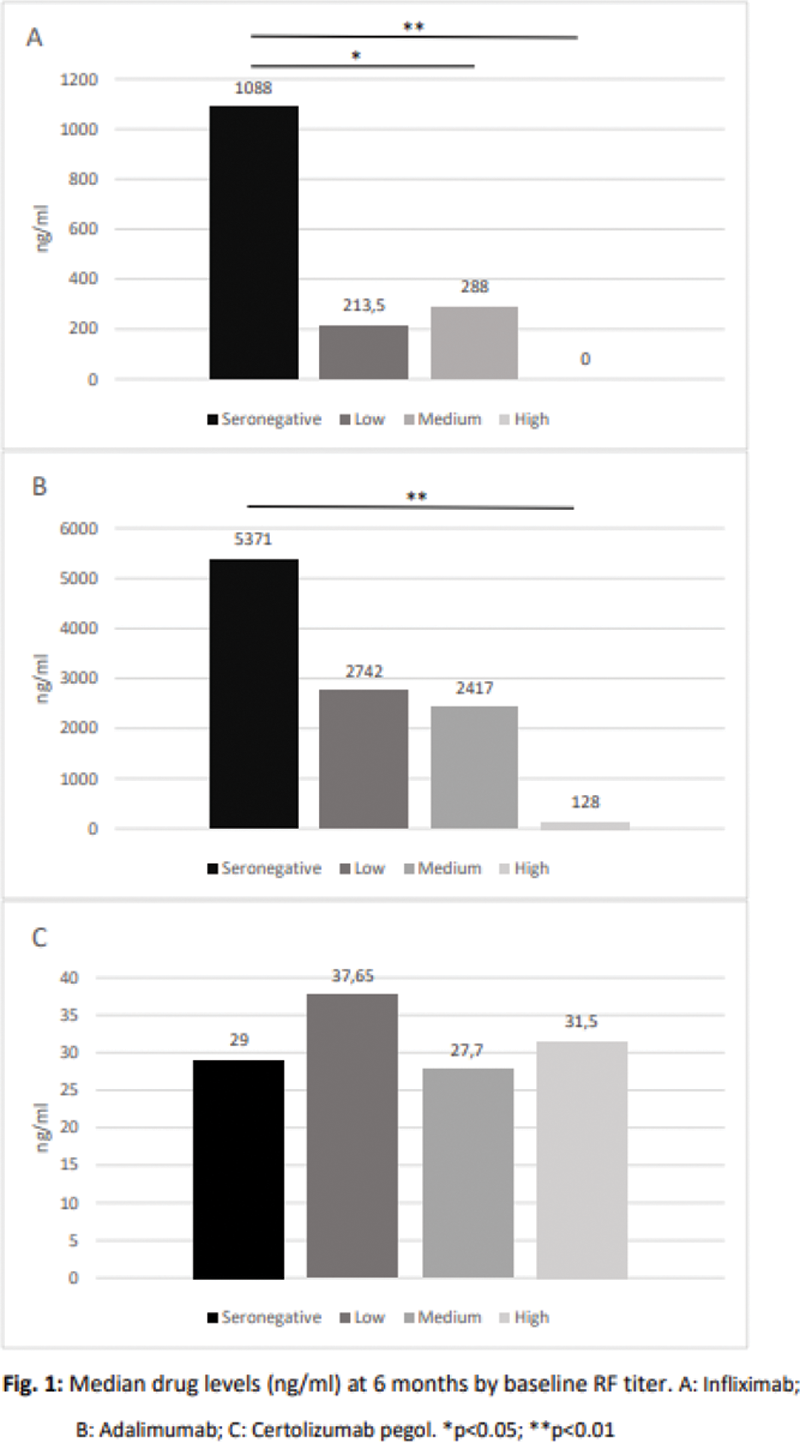
Drug levels of IFX and ADA at T6 were significantly lower in those patients who had higher RF titers at T0 compared to seronegative. In contrast, CZP levels remained stable irrespectively of baseline RF titers, without significant differences among quartiles (
Conclusion: Higher baseline RF titers are associated with lower IFX and ADA levels at T6 in a cohort of RA patients. A concentration-response association has been clearly established for TNFi, and baseline RF levels appear to influence drug levels.
Reduced immune complexes formation with CZP may result in a limited impact of baseline RF titers on drug levels.
REFERENCES:
[1]Aletaha D. Arthritis Res Ther2015;17(1):229.
[2]Bobbio-Pallavicini F. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66(3):302–7.
[3]Potter C. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68(1):69–74.
[4]Tanaka Y. APLAR 2020. Oral Communication.
[5]Levy RA. Immunotherapy 2016;8(12):1427-1436.
Acknowledgements: This study was funded by an anrestricted reserch grant from UCB pharma.
Disclosure of Interests: ANA MARTÍNEZ-FEITO: None declared, Borja Hernández-Breijo: None declared, Marta Novella-Navarro Grant/research support from: UCB, Alejandro Villalba: None declared, Diana Peiteado: None declared, Pilar Nozal: None declared, DORA PASCUAL-SALCEDO Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda, Menarini and MSD., Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda, Menarini and MSD., Alejandro Balsa Speakers bureau: Pfizer, AbbVie, Galapagos, Lilly, Gilead, UCB, Nordic, Sandoz, Consultant of: Galapagos, Pfizer, AbbVie, Lilly, UCB, Nordic, Grant/research support from: Pfizer, Abbvie, UCB, Chamaida Plasencia Speakers bureau: Abbvie, Pfizer, UCB, Sandoz, Sanofi, Biogen, Lilly, Roche and Novartis, Grant/research support from: Abbvie, Pfizer, UCB, Sandoz, Sanofi, Biogen, Lilly, Roche and Novartis