

Background: In the SENSCIS trial in subjects with SSc-ILD, nintedanib reduced the rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) over 52 weeks by 44% compared with placebo.
Objectives: To investigate the effects of nintedanib on circulating biomarkers of extracellular matrix (ECM) turnover, epithelial injury and inflammation in the SENSCIS trial.
Methods: Subjects had SSc with first non-Raynaud symptom in the prior ≤7 years, extent of fibrotic ILD on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) ≥10% and FVC ≥40% predicted. Patients were randomised to receive nintedanib or placebo stratified by anti-topoisomerase I antibody (ATA). Blood samples were taken at baseline and at weeks 4, 24 and 52. Fold changes in adjusted mean levels of circulating biomarkers were analyzed using a linear mixed model for repeated measures. Data were log 10 transformed before analysis and estimates of change from baseline were back-transformed.
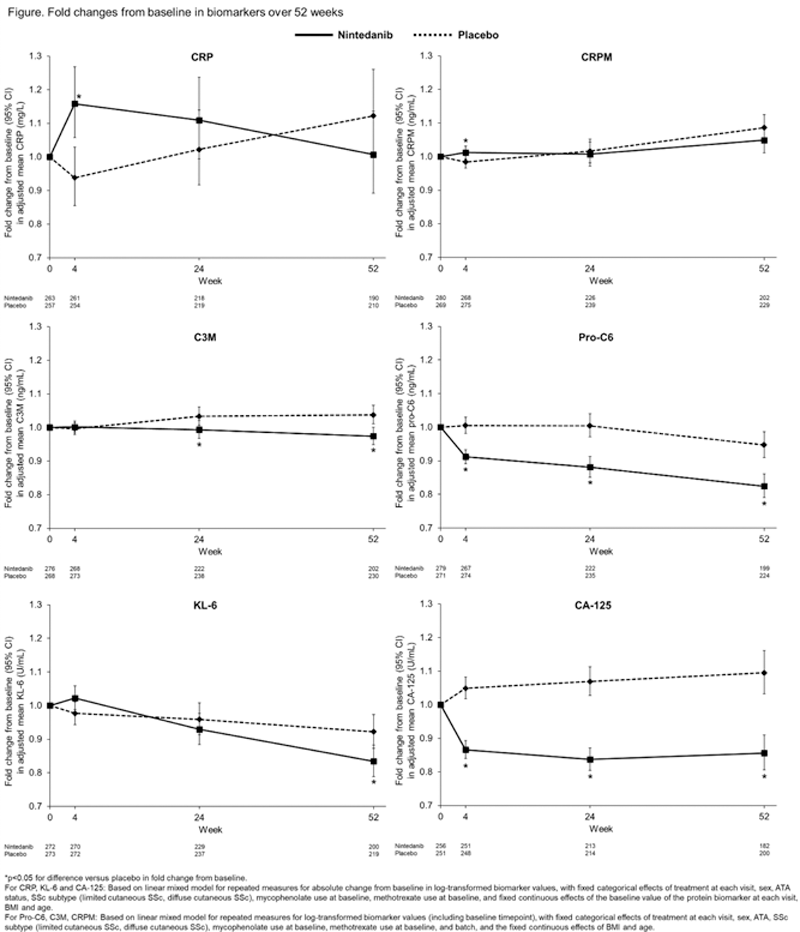
Results: A total of 576 subjects received trial drug (288 nintedanib, 288 placebo). A transient increase in fold change from baseline in C-reactive protein (CRP) (a marker of inflammation) was observed in subjects who received nintedanib versus placebo at week 4. After an initial increase at week 4 in the fold change from baseline in CRP degraded by MMP-1/8 (CRPM) (a marker of ECM turnover), a trend to decreasing levels was observed in subjects who received nintedanib compared with placebo at week 52. Decreases in the fold change from baseline in collagen 3 degraded by MMP-9 (C3M) and N-terminal propeptide of type VI collagen (pro-C6) (markers of ECM turnover) were observed in subjects who received nintedanib compared with placebo from week 24 and week 4, respectively. A decrease in fold change from baseline in Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) (a marker of epithelial injury) was observed in subjects who received nintedanib versus placebo at week 52. A decrease in fold change from baseline in cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) (a marker of epithelial injury) was observed in subjects who received nintedanib versus placebo from week 4 (
Conclusion: Data from the SENSCIS trial suggest that nintedanib reduced circulating levels of markers of ECM turnover and epithelial injury in subjects with SSc-ILD.
Acknowledgements: The SENSCIS trial was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim. Masataka Kuwana, Toby M Maher and Oliver Distler were members of the SENSCIS trial Steering Committe.
Disclosure of Interests: Shervin Assassi Speakers bureau: On speaker bureau for Integrity Continuing Education, Consultant of: Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, CSL Behring, Novartis, Grant/research support from: Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Masataka Kuwana Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Nippon Shinyaku, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Ono Pharmaceuticals, Consultant of: AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, Mochida
Kissei, Grant/research support from: Boehringer Ingelheim, MBL, Ono Pharmaceuticals, Christopher P Denton Speakers bureau: Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Consultant of: Abbvie, Acceleron, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, CSL Behring, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Grant/research support from: ARXX Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Horizon Therapeutics, Servier, Toby Maher Speakers bureau: Boehringer Ingelheim, Galapagos, Genentech, Consultant of: AstraZeneca, Bayer, Blade Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Galecto, GlaxoSmithKline R&D, IQVIA, Pliant, Respivant, Roche, Theravance and Veracyte, Grant/research support from: AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Claudia Diefenbach Employee of: Claudia Diefenbach is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim, Carina Ittrich Employee of: Carina Ittrich is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim, Martina Gahlemann Employee of: Martina Gahlemann is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim, Oliver Distler Speakers bureau: OD has/had relationships with the following companies in the area of potential treatments for systemic sclerosis and its complications in the last three calendar years:
Speaker fee: Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Medscape, Consultant of: OD has/had relationships with the following companies in the area of potential treatments for systemic sclerosis and its complications in the last three calendar years:
Consultancy fee: Abbvie, Acceleron, Alcimed, Amgen, AnaMar, Arxx, AstraZeneca, Baecon, Blade, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, CSL Behring, 4P Science, Galapagos, Glenmark, Horizon, Inventiva, Kymera, Lupin, Miltenyi Biotec, Mitsubishi Tanabe, MSD, Novartis, Prometheus, Roivant, Sanofi and Topadur
OD has/had relationships with the following companies in the area of potential treatments for arthritides in the last three calendar years:
Consultancy fee: Abbvie, Grant/research support from: OD has/had relationships with the following companies in the area of potential treatments for systemic sclerosis and its complications in the last three calendar years:
Research Grants: Boehringer Ingelheim, Kymera, Mitsubishi Tanabe,