

Background: The long-term retention rate of a biological drug is a surrogate marker of its effectiveness and tolerability.
Objectives: We assessed the probability of golimumab retention (persistence or drug survival) and the associated factors in a large cohort of patients with rheumatic diseases, with up to 8 years of follow-up.
Methods: This was an analysis of the BIOBADASER database (Spanish registry of biological drugs of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology and the Spanish Medicines Agency) on all adult patients who had initiated golimumab for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) or axial spondyloarthritis (SpA). The probability of golimumab retention was assessed with the Kaplan-Meier method, differences between groups with the log-rank test, and factors related to retention with a Cox-regression model. Patients were right-censored if they were still treated with golimumab at the last observation for data analysis.
Results: A total of 885 patients were included, of whom 59 had received golimumab in 2 separate cycles (with a grace period of 3 months), totaling 944 cycles of treatment (286 RA, 396 axial SpA and 262 PsA). At golimumab initiation, mean (SD) age was 52 (13) years, 54% were women and median duration of disease was 7.6 (2.8-14.4) years. Golimumab was prescribed as first, second and third/subsequent biological drug in 313 (33%), 303 (32%) and 328 (35%) treatments. Concomitant medications at golimumab initiation included methotrexate (MTX) (32%), steroids (29%), leflunomide (13%) and sulphasalazine (6%). The probability of retention of golimumab since treatment initiation was 71% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 68 – 74) at year 1, 60% (95% CI: 57-63) at year 2, 54% (95% CI: 51-58) at year 3, 48% (95% CI: 44-51) at year 4, 44% (95% CI: 40-48) at year 5, 41% (95% CI: 37-45) at year 6 and 38% (95% CI: 33-42) at year 7 and at year 8. In bivariate analysis, the retention rate was higher when golimumab was used as first biological agent (p log-rank <0.001), in patients with axial SpA or PsA compared to RA (p <0.001,
Cox-regression analysis. Hazard Ratio for discontinuation of golimumab
| Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence interval | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at golimumab initiation | 1.01 | 1.00-1.02 | 0.063 |
| Gender (women vs men) | 1.23 | 0.98-1.55 | 0.079 |
| Axial SpA vs RA | 0.59 | 0.44-0.80 | <0.001 |
| PsA vs RA | 0.67 | 0.51-0.89 | 0.005 |
| Second vs first biological drug | 1.52 | 1.17-1.97 | 0.002 |
| Third or further vs first biological drug | 1.79 | 1.38-2.32 | <0.001 |
| Corticosteroids | 1.46 | 1.16-1.85 | 0.001 |
| Methotrexate | 0.79 | 0.63-0.99 | 0.041 |
| Disease activity over the median* | 1.29 | 1.05-1.59 | 0.015 |
*DAS28 > 4.3 (RA, PsA) or BASDAI > 5.6 (axial SpA) at golimumab initiation
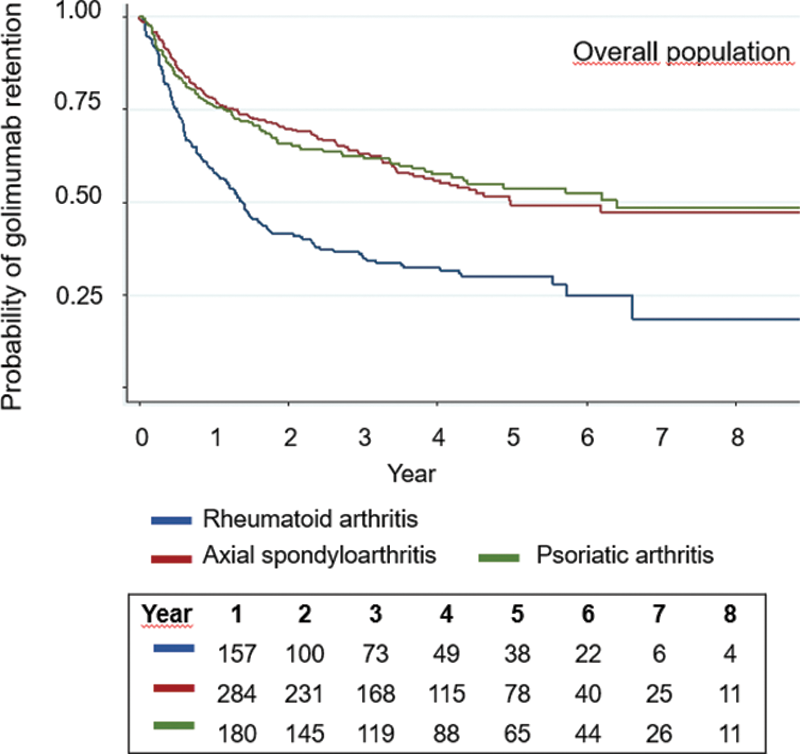
Conclusion: This study provides new information on long-term golimumab effectiveness for the treatment or rheumatic diseases, with retention rates of 71% at year 1, 44% at year 5 and 38% at year 8. The probability of golimumab retention was higher as first biological drug, in patients with PsA or axial SpA and in those treated with methotrexate, and lower in those treated with steroids or with higher disease activity at golimumab initiation.
Acknowledgements: BIOBADASER is funded by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology, the Spanish Agency of Medicines and by different pharmaceutical companies. The present study was funded by MSD, Spain.have no acknowledgements to declare.
Disclosure of Interests: Manuel Pombo-Suarez: None declared, Daniel Seoane-Mato: None declared, Luis Cea-Calvo Employee of: Medical Affairs, MSD Spain, Federico Diaz-Gonzalez: None declared, Fernando Sánchez-Alonso: None declared, Marta Sánchez-Jareño Employee of: Medical Affairs, MSD Spain, Francisco Javier Manero Ruiz: None declared, Lucía Ruiz: None declared, Vega Jovani: None declared, Isabel Castrejon: None declared