

Background: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are recommended as first-line treatment of axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are effective in the management of patients refractory to NSAIDs. However, in some cases the introduction of bDMARDs is limited by absolute contraindications or patient opposition. Beyond the well-known anti-osteoclastic properties, bisphosphonates (BPs) can exert their benefits through other mechanisms, including reduction of proinflammatory cytokines (such as IL6 and TNFα), and modulation of macrophage and osteoblast activity.
Objectives: To examine the potential therapeutic properties of a BP, IV neridronate (IVNer), in patients with axSpA refractory to NSAIDs and not eligible for a second-line therapy with bDMARDs.
Methods: We retrospectively collected data of patients affected by axSpA according to ASAS classification criteria, treated with IVNer, referred to a tertiary Rheumatology Centre between Sept 2015 and Dec 2021. Patients with active disease, as defined by a BASDAI score ≥4, with active sacroileitis (SI) on MRI (according to ASAS MRI definition of active SI), who had failed/were intolerant to NSAIDs and not eligible for bDMARDs, were recruited. IVNer (100 mg) was given intravenously on Days 1, 4, 7, and 10, over 3 h in 500 ml of 0.9% saline. Response to IVNer was evaluated after 60 days from the last infusion as the mean change from baseline of BASDAI and visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score, and the improvement of MRI imaging.
Results: We included 30 patients (77% females, mean age±SD 39.0±16.8 yrs, and mean disease duration of 24±14.4 months (range 1.0-298). Fourteen had ankylosing spondylitis (AS), six had undifferentiated SpA, two had enteropathic arthritis, one had non-radiographic axSpA, and seven had axial psoriatic arthritis. 50% had axial involvement, 30% axial and peripheral arthritis, and 20% had axial and enthesis involvement. Eleven were HLA-B27 positive. On MRI evaluation, 43% had monolateral SI, 57% bilateral SI and 7% had erosions. Among the reasons of ineligibility to bDMARDs, 6 patients have concurrent solid tumor, 11 had comorbidities contraindicating bDMARDs, and 12 preferred not to undergo to bDMARDs. Mean BASDAI significantly decrease after IVNer (5.86±1.98 vs 3.52±2.39, p=0.0002,
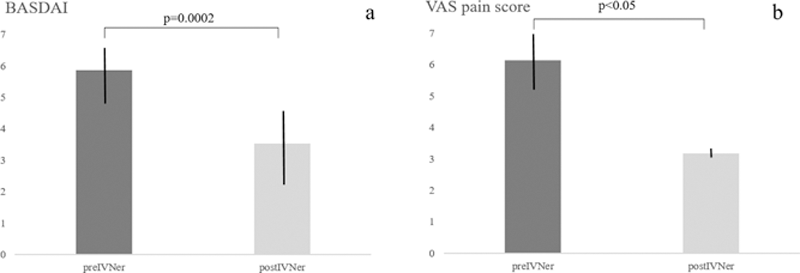
Conclusion: IVNer was effective in reducing disease activity measured by BASDAI and VAS pain score in patients with axSpA refractory to NSAIDs and not eligible for bDMARDs. When recommended second-line treatments are contraindicated or according to patients’ preference, IVNer can be considered as a potential alternative therapeutic option. Further evaluations in controlled trials are needed to confirm these results.
REFERENCES:
[1]Varenna M, Rheumatology 2014.
[2]Maksymowych WP et al, Ann Rheum Dis. 2019
Disclosure of Interests: None declared