

Background: Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis and occurs frequently in patients with renal disease often leading to a significant burden on quality of life and functional status. 1,2 Despite the established connection of renal disease with gout, little has been reported on the prevalence, patient characteristics, and associations of gout with other outcomes in the US hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD) population.
Objectives: This project used a large end-stage renal disease (ESRD) focused-database, Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS), to examine gout in dialysis-dependent patients.
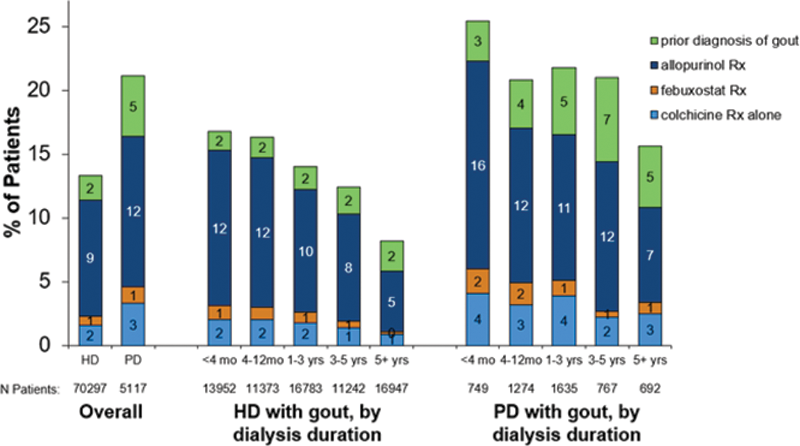
Methods: Gout patients were identified by active prescription (Rx) of (1) colchicine, (2) febuxostat, or (3) allopurinol; or by (4) prior diagnosis of gout from US cohorts of 70,297 HD (DOPPS, 2012-2020) patients and 5117 PD (Peritoneal DOPPS, 2014-2020) patients. Outcomes of HD and PD patients with and without a history of gout were compared with propensity score matching. Outcomes included erythropoietin resistance index (ERI = ESA dose/(hemoglobin*weight), cardiovascular death, all-cause mortality/hospitalization, and baseline patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
Results: Gout prevalence was 13% in HD and 21% in PD and was highest among incident dialysis patients. Of the gout patients identified, the most-commonly used gout-related medications were allopurinol (9-12%), followed by colchicine (2-3%), and then febuxostat (1%,
Gout prevalence by dialysis duration in patients undergoing HD and PD. Criteria for gout included gout diagnosis and use of a urate-lowering therapy.
HD, hemodialysis; PD, peritoneal dialysis; mo, months; Rx, prescription; yrs, years. Some patients were included in multiple gout categories.
Conclusion: Gout was common in US HD and PD patients, with a large proportion of these patients treated with drugs indicated for hyperuricemia (allopurinol and febuxostat) and gout flares (colchicine). The true prevalence of gout was likely higher than observed when considering potential under-ascertainment of gout diagnosis history in nephrology/dialysis-focused clinical settings. 3 This report provides a snapshot of gout in the US dialysis population and offers opportunities to expand on research to improve awareness and care for patients with gout and ESRD.
REFERENCES:
[1]Singh JA, Strand V. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1310–6.
[2]Singh JA, Cleveland JD. BMC Neph 2019;20:93.
[3]Roughley M, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):243.
Disclosure of Interests: Angelo Karaboyas Grant/research support from: Horizon Therapeutics, Junhui Zhao Grant/research support from: Horizon Therapeutics, Brian LaMoreaux Shareholder of: Horizon Therapeutics, Employee of: Horizon Therapeutics, Brad Marder Shareholder of: Horizon Therapeutics, Employee of: Horizon Therapeutics, Barry Gorlitsky Consultant of: AstraZenica, Davita, Horizon Therapeutics, Jensen Pharmaceuticals, KidneyAide LLC, vinicius domingues Consultant of: Abbvie, Aurinia Pharma, Exagen, Eli Lilly, Roberto Pecoits-Filho Grant/research support from: Horizon Therapeutics, Bruce Robinson Grant/research support from: Horizon Therapeutics