

Background: Booster doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines have emerged as an important strategy for containing the pandemic and may be especially important to rituximab treated patients. B-cell depletion has been associated with worse outcomes from COVID-19 infection, and many rituximab treated patients demonstrate an inadequate serologic response to the initial vaccine series (1). Strategies to optimize serologic response to COVID-19 vaccine boosters in previously serologically unresponsive patients is, therefore, of particular relevance.
Objectives: To assess factors associated with serologic response to COVID-19 booster vaccines in rituximab treated patients previously serologically unresponsive to the initial vaccine series.
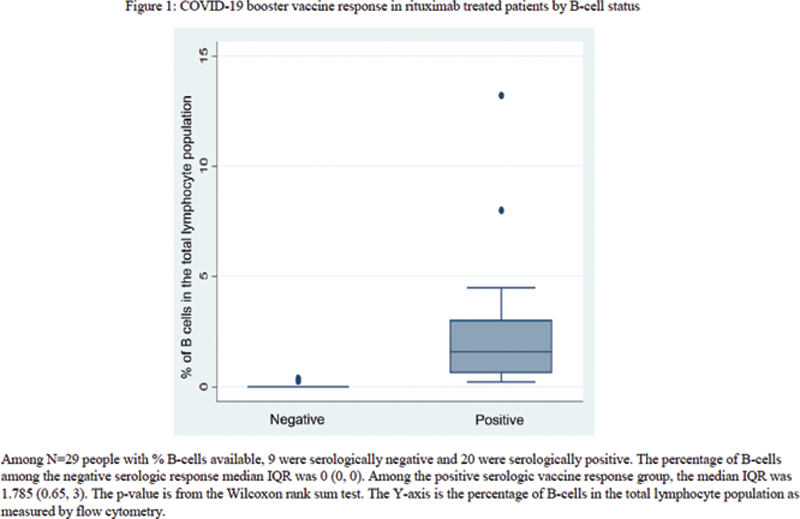
Methods: A retrospective chart review of rituximab treated patients who failed to demonstrate a serologic response to the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccination series and subsequently received an mRNA vaccine booster was performed. Serologic response four weeks or more after the booster was the primary outcome. T-tests, Fisher’s exact tests, and Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used for comparisons. Box and whisker plots were constructed to visualize differences between serologic response.
Results: In 31 rituximab treated patients who were seronegative following the initial vaccine series, demographic characteristics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine (
Bivariate comparisons between seronegative and seropositive patients to the COVID-19 booster vaccine by patient characteristics and demographics
| Factor | Value | Negative | Positive | p-value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 31 | 10 | 21 | |
| Age, median (IQR ) | 64 (51, 72) | 63 (51, 69) | 65 (51, 73) | 0.75 |
| Sex | 1.00 | |||
| Female | 23 (74%) | 7 (70%) | 16 (76%) | |
| Male | 8 (26%) | 3 (30%) | 5 (24%) | |
| Any immunosuppressant b | 9 (29%) | 3 (30%) | 6 (29%) | 1.00 |
| Corticosteroid | 5 (16%) | 1 (10%) | 4 (19%) | 1.00 |
| 3 rd Vaccine dose type | 0.24 | |||
| Pfizer | 19 (61%) | 8 (80%) | 11 (52%) | |
| Moderna | 12 (39%) | 2 (20%) | 10 (48%) | |
| Dichotomous B-cell status around booster dose | <0.001 | |||
| No detectable B-cells | 7 (23%) | 7 (70%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Detectable B-cells | 22 (71%) | 2 (20%) | 20 (95%) | |
| Missing | 2 (6%) | 1 (10%) | 1 (5%) | |
| Time from last RTX infusion to booster, median (IQR ) | 260 (216, 379) | 188 (169, 245) | 301 (251, 368) | 0.030 |
| Time from last RTX infusion to booster dose | 0.10 | |||
| <6months | 8 (25.81%) | 5 (50%) | 3 (14%) | |
| 6-12 months | 15 (48.39%) | 3 (30%) | 12 (57%) | |
| >12 months | 8 (25.81%) | 2 (20%) | 6 (29%) | |
a P-values are from Fisher’s exact test, Student’s T-test and Wilcoxon rank sum tests
b Immunosuppressants included Leflunomide, Azathioprine, Methotrexate, Mycophenolate Mofetil, and Tocilizumab
IQR= Interquartile range
Conclusion: Presence of detectable B-cells and longer time from last rituximab were associated with the development of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibodies following the booster vaccine. These factors should be considered in timing of administration of booster vaccine doses in previously unresponsive rituximab treated patients.
REFERENCES:
[1]Levavi H, Lancman G, Gabriolove J. Impact of rituximab on COVID-19 outcomes. Ann Hematol 2021;100:2805-12.
Disclosure of Interests: Kaitlin Schultz: None declared, Deanna Jannat-Khah Shareholder of: Cytodyn, Astrazeneca, Walgreens, Robert Spiera Consultant of: AbbVie, Regeneron, Sanofi, Chemomab, Formation Biologics, GSK, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Chemocentryx, Grant/research support from: GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Formation Biologics, InflaRx, Kadmon, Astrazeneca, AbbVie, Sanofi, Genentech/Roche, Principia, Novartis