

Background: Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, the BNT162b2 (manufactured by Pfizer—BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (manufactured by Moderna Inc) vaccines have demonstrated an acceptable safety profile and a high degree of effectiveness in preventing severe COVID-19 outcomes in healthy individuals. However, it remains to be determined if similar benefits can be replicated in immunocompromised patients, who were largely excluded from Phase III clinical trials. Preliminary data on vaccine immunogenicity among lupus patients reveal blunted humoral responses, particularly in those using prednisone and/or mycophenolate (1-2).
Objectives: This study sought to measure the antibody responses following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with SLE and to identify clinical and laboratory parameters associated with low antibody responses.
Methods: We prospectively enrolled SLE patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Cohort (BIDLC). The patients received two doses of either BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 and were tested for the SARS-CoV-2 IgG spike antibody at least 4 weeks after the second vaccine dose. Patients with evidence of prior COVID-19 infection were excluded. The primary goal of this study was to measure the prevalence of a weak IgG spike antibody response and identify predictive clinical-laboratory factors. We first measured the antibody responses in a healthy control group and defined a low antibody titer as values that fell below the 25% percentile of this reference group (<6). We then used simple logistic regression to assess for associations between different predictive variables and our predefined dichotomous outcome: <6 vs ≥6 IgG spike antibody titer. To account for potential cofounders, a multiple logistic regression model was performed. Risk ratios were calculated with the Log Binomial regression. Significance level was set at p <0.05.
Results: A total of 71 patients were included in the study. At the time of vaccination, patients were on various immune modulator and suppressive medications, including: Hydroxychloroquine 87%, Prednisone 38%, Mycophenolate 38%, Azathioprine 18% and Belimumab 7%. The proportion of patients who received BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 were 58% and 42%, respectively. Overall, 63% of patients had a high IgG spike antibody titer (≥ 6) and 37% of patients had a low IgG spike antibody titer (<6). Univariate logistic regression demonstrated that a SLEDAI ≥6 (OR: 4.55,
p = 0.02
), the use of azathioprine (OR: 3.55,
p = 0.04
) and receiving the BNT162b2 vaccine vs. mRNA-1273 (OR: 3.80,
P = 0.01
) were independent predictors of antibody titers <6. After controlling for age, sex, race, time to spike testing and use of immunosuppressive drugs, the association between a high SLEDAI score or receiving the BNT162b2 vaccine and a weak antibody response remained significant (
Logistic regression plot
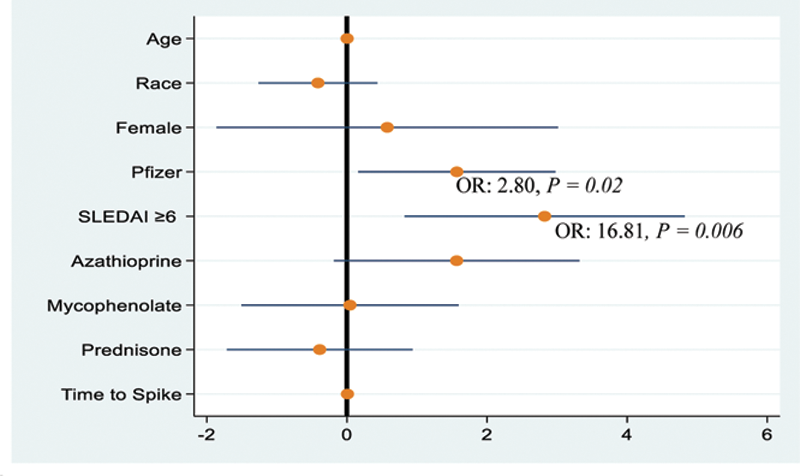
Conclusion: In patients with SLE, Azathioprine use independently predicts reduced antibody titers. More importantly, we demonstrated that a pre-vaccine high disease activity score or receiving BNT162b2 (Pfizer—BioNTech) increases the risk of impaired immune response to the COVID-19 vaccine.
REFERENCES:
[1]Ammitzbøll, C., et al (2021). Impaired antibody response to the BNT162b2 messenger RNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. ACR open rheumatology , 3 (9), 622-628.
[2]Izmirly, P. M., et al (2021). Evaluation of Immune Response and Disease Status in SLE Patients Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. Arthritis & Rheumatology
Disclosure of Interests: Christine Parsons: None declared, Jose Rubio: None declared, Afroditi Boulougoura: None declared, Vasileios Kyttaris Grant/research support from: Dr. Kyttaris is a grant recipient of Exagen Diagnostics, Employee of: Dr. Kyttaris serves on the advisory board of Aurinia Pharmaceuticals