

Background The safety of tofacitinib in patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has been demonstrated in clinical studies with up to 9.5 and 4 years (yrs) of observation, respectively. Real-world post-marketing surveillance (PMS) safety data comprised of spontaneous and voluntary adverse event (AE) reports for tofacitinib have been published for RA and ulcerative colitis, but not PsA.
Objectives To further characterise the real-world safety profile of tofacitinib in RA and PsA.
Methods AE reports were collected from 6 Nov 2012–6 Nov 2021 (RA) and 14 Dec 2017–6 Nov 2021 (PsA) from the Pfizer safety database. Tofacitinib was approved in the US for RA on 6 Nov 2012 (immediate release [IR]) and 24 Feb 2016 (extended release [XR]), and for PsA on 14 Dec 2017 (IR and XR). Safety endpoints included AEs, serious AEs (SAEs), AEs of special interest (AESI) and fatal cases. Pt years (PY) of exposure were estimated from IQVIA commercial sales data from 61 countries and 1 region. Number (N), frequency and reporting rates (RR; number of events/100 PY of estimated exposure) for each endpoint were summarised by indication (RA/PsA) and formulation (IR [5 or 10 mg twice daily], XR [11 mg once daily] or all tofacitinib [IR+XR]). A sensitivity analysis truncated the analysis period to the first 4 yrs post approval for RA (2012–16), to align with the duration of PsA data.
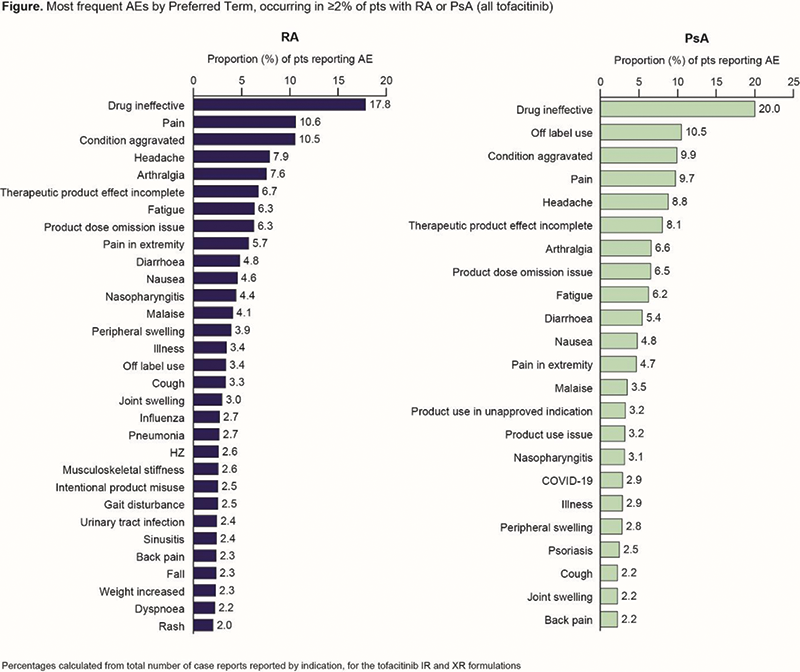
Results Of the 73 525 case reports (68 131 RA/5394 PsA), 4239/368 (6.2%/6.8%) did not report a formulation and were excluded. Most AE reports were for females (RA: 81.8%/PsA: 71.3%); around half were submitted by healthcare professionals (49.8%/63.1%) and the majority were from North America (80.1%/82.3%). Almost all XR reports (RA/PsA: 93.0%/97.0%) originated from North America (IR reports: 72.3%/68.6%). For both indications, the RR for AEs was higher with XR vs IR; RR and frequency of SAEs, AESIs and fatal cases were mostly similar between XR and IR (Table 1). The most frequently reported AEs in RA and PsA by Preferred Term included drug ineffective, pain, condition aggravated, headache and arthralgia (Figure 1). Off label use was more frequently reported in PsA than RA (Figure 1). In the first 4 yrs post approval of the IR formulation for RA (IR/XR: 49 439/2000 PY), AEs, SAEs and fatal cases RRs were 95.9/147.0, 19.1/24.5 and 0.4/0.4, respectively.
| RA | Tofacitinib IR 312 632 PY | Tofacitinib XR 126 738 PY | All tofacitinib 439 370 PY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | RR | N | % | RR | N | % | RR | |
| AEs | 137 476 | 44.0 | 82 153 | 64.8 | 219 629 | 50.0 | |||
| SAEs | 24 966 | 18.2 | 8.0 | 11 978 | 14.6 | 9.5 | 36 944 | 16.8 | 8.4 |
| Serious infections | 4944 | 3.6 | 1.6 | 2467 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 7411 | 3.4 | 1.7 |
| HZ | 1194 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 529 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1723 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| CV eventsa | 773 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 413 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1186 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Malignancyb | 941 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 429 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1370 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| VTE | 318 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 150 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 468 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Fatal cases | 839 | 2.1c | 0.3 | 279 | 1.2c | 0.2 | 1118 | 1.8c | 0.3 |
| PsA | Tofacitinib IR 14 000 PY | Tofacitinib XR 6706 PY | All tofacitinib 20 706 PY | ||||||
| N | % | RR | N | % | RR | N | % | RR | |
| AEs | 8349 | 59.6 | 7602 | 113.4 | 15 951 | 77.0 | |||
| SAEs | 1136 | 13.6 | 8.1 | 912 | 12.0 | 13.6 | 2048 | 12.8 | 9.9 |
| Serious infections | 239 | 2.9 | 1.7 | 200 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 439 | 2.8 | 2.1 |
| HZ | 49 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 35 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 84 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| CV eventsa | 44 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 25 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 69 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Malignancyb | 30 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 27 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 57 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| VTE | 27 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 12 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 39 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Fatal cases | 22 | 0.9c | 0.2 | 19 | 0.8c | 0.3 | 41 | 0.8c | 0.2 |
All cases reported ≥1 AE and ≥0 SAE
aIncludes Standardised MedDRA Queries: central nervous system vascular disorders, myocardial infarction and associated terms, ischaemic heart disease and associated terms; and Preferred Terms: cardiac death, cardiac failure congestive, sudden cardiac death and pulmonary embolism
bExcluding non-melanoma skin cancer
cBased on total case reports by formulation: RA, 39 744 IR/24 148 XR; PsA: 2601 IR/2425 XR
CV, cardiovascular; HZ, herpes zoster; MedDRA, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities; VTE, venous thromboembolism
Image/graph:
Conclusion Tofacitinib PMS safety data from submitted AE reports were consistent for RA and PsA and aligned with the established safety profile. Reporting bias, reporter identity, regional differences in formulation use and exposure data (lower XR vs IR; estimation from commercial sales data) limit interpretation.
Acknowledgements This study was sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support, under the direction of the authors, was provided by Julia King, PhD, CMC Connect, a division of IPG Health Medical Communications, and was funded by Pfizer, New York, NY, USA, in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP 2022) guidelines (Ann Intern Med 2022; 175: 1298-1304).
Disclosure of Interests Gerd Rüdiger Burmester Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Galapagos, Novartis, Pfizer Inc and Sanofi, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Galapagos, Novartis, Pfizer Inc and Sanofi, Laura Coates Speakers bureau: AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Janssen, Medac, Novartis, Pfizer Inc and UCB, Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer Inc and UCB, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc and UCB, Stanley B. Cohen Consultant of: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead Sciences, Merck and Pfizer Inc, Yoshiya Tanaka Speakers bureau: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Mitsubishi-Tanabe and Pfizer Inc, Grant/research support from: AbbVie, Asahi-Kasei, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai and Takeda, Ivana Vranic Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Edward Nagy Shareholder of: Pfizer Ltd, Employee of: Pfizer Ltd, All-shine Chen Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Irina Lazariciu Employee of: IQVIA, who were paid contractors to Pfizer Inc in the development of this abstract and in providing statistical support, Kenneth Kwok Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Lara Fallon Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc, Cassandra Kinch Shareholder of: Pfizer Inc, Employee of: Pfizer Inc.
Keywords: Safety, Targeted synthetic drugs, Real-world evidence
DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2023-eular.1722