

Background: Gouty arthritis is a common inflammatory arthritis caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in joints with the prevalence of 1% to 3% in China. Interleukin 1-β (IL-1β) is a key mediator of acute gouty flares, and anti-IL-1β therapy has been proven to be an important option for the treatment of gouty arthritis. However, no IL-1β inhibitors are available in China. Therefore, the effectiveness of IL-1β inhibitors in Chinese patients with gout remains unclear.
Objectives: This is a double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled phase II study to assess the efficacy and safety of SSGJ-613, a fully human anti-interleukin 1β monoclonal antibody, in Chinese patients with gout.
Methods: Key inclusion criteria were: patients aged 18 to 65 years and meeting the ACR criteria of gout; presence of an acute Gouty Arthritis flare for no longer than 7 days; baseline pain intensity ≥50 mm on the 0 to 100 mm VAS. Eligible patients were subsequently randomized 1:1:1 to the two SSGJ-613 groups and the active control group to receive a single dose of SSGJ-613, 200, or 300 mg subcutaneously; or Betamethasone 1mL Intramuscularly. The efficacy of SSGJ-613 in pain relief and flares prophylaxis was assessed by the change of VAS scores from baseline after 72 hours of dosing and the percentage of patients developing new flares within 12 weeks after single administration of SSGJ-613. Safety was assessed through monitoring of adverse events (AEs) and laboratory testing.
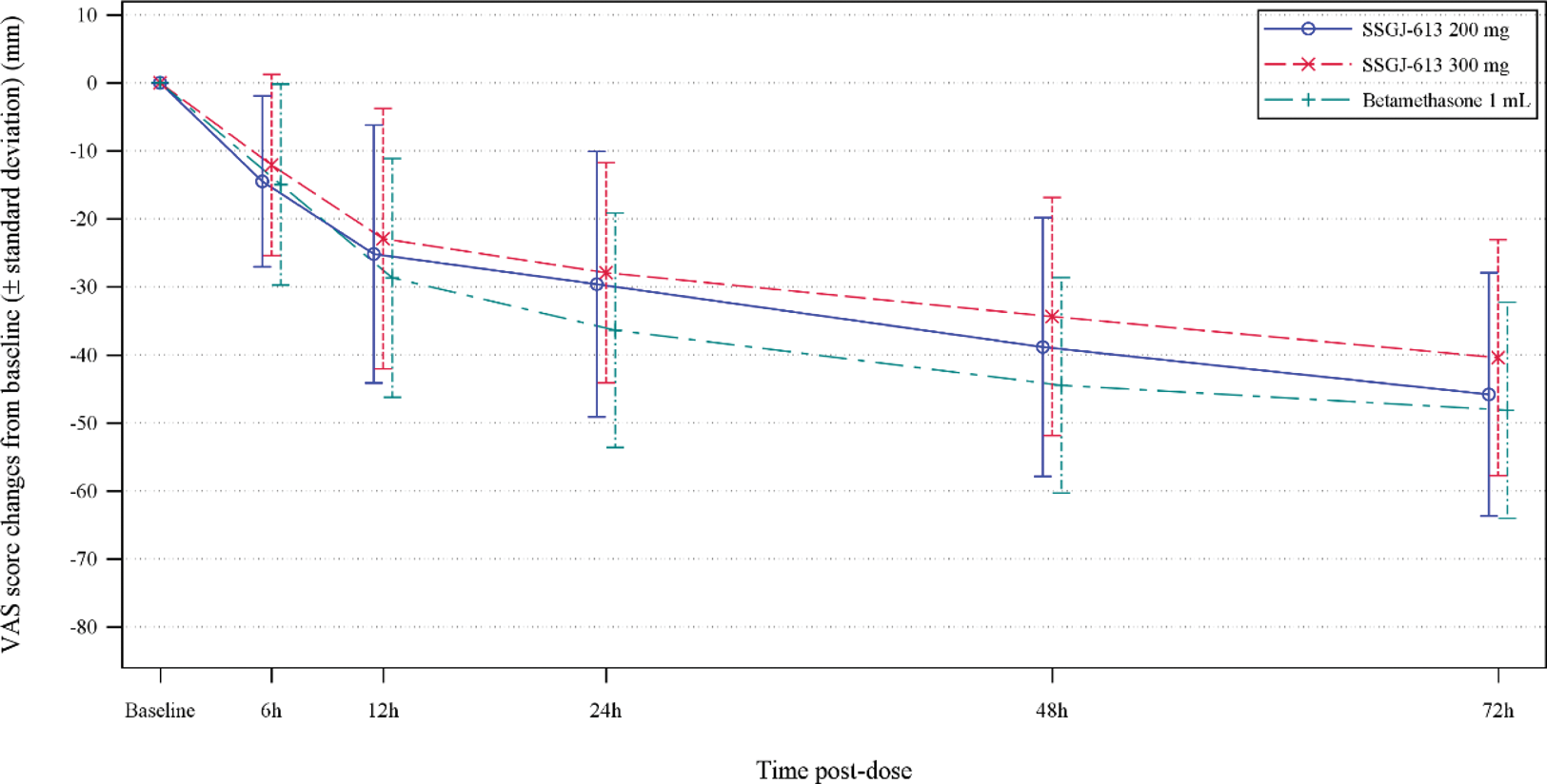
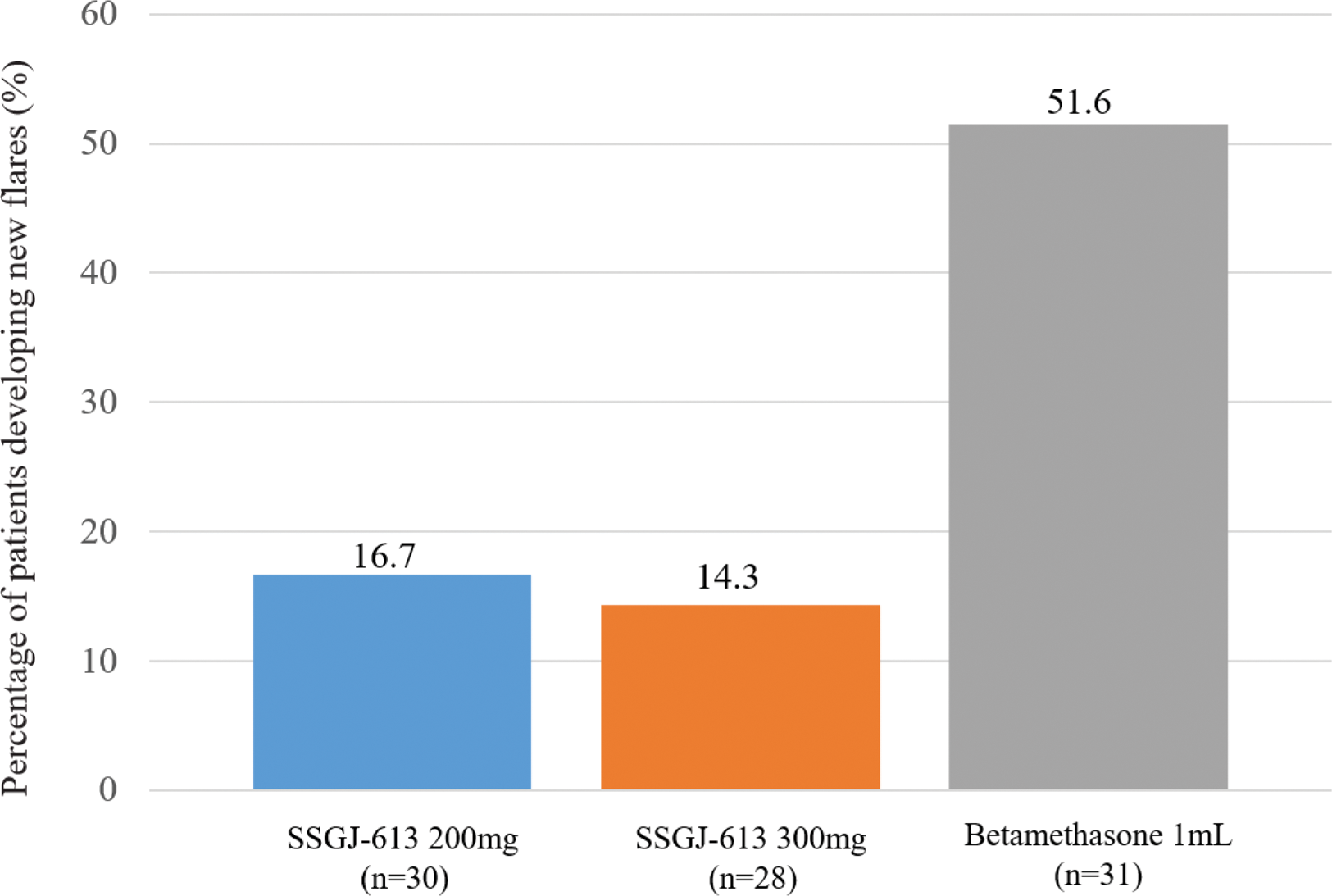
Results: A total of 90 patients were enrolled in this study. At baseline, the mean VAS scores for the targeted joints were 72.4mm, 66.8mm, and 67.4mm in the SSGJ-613 200 mg, SSGJ-613 300 mg, and Betamethasone 1mL groups, respectively. 72 hours after administration, all treatment groups exhibited significant pain relief, with VAS scores changes from baseline (mean ± standard deviation) being -45.8 ± 17.88 mm, -40.4 ± 17.35 mm, and -48.2 ± 15.90 mm for the SSGJ-613 200 mg group, SSGJ-613 300 mg group, and Betamethasone, respectively. There were no statistical differences between the two SSGJ-613 doses and Betamethasone(p=0.4533 and 0.0848 for SSGJ-613 200mg and 300mg, respectively). More importantly, the percentage of patients developing new flares was remarkably lower for all SSGJ-613 groups compared with Betamethasone, with 16.7% (5/30) and 14.3% (4/28) for the SSGJ-613 200mg and 300mg doses, respectively, versus 51.6% (16/31) for Betamethasone 1mL. Regrading inflammatory factors, hsCRP, SAA, and ESR decreased rapidly in all three groups at 72 hours after dosing, with SSGJ-613 doses showing more pronounced reduction on hsCRP and SAA than Betamethasone. Safety profile was comparable between SSGJ-613 and Betamethasone, with a relatively low incidence in SSGJ-613 groups.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated that a single injection of SSGJ-613 could achieve rapid pain relief similar to that of steroids in Chinese patients with gout and provide effective prophylaxis against flares. To confirm the efficacy and safety of SSGJ-613 in Chinese gout patients, further trials will be initiated soon.
REFERENCES: NIL.
VAS score changes for baseline.
The percentage of patients developing new flares within 12 weeks after single administration of SSGJ-613.
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: Hejian Zou: None declared, Yu Xue: None declared, Qinghong Zhou Employed Sunshine Guojian Pharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd, Yuyu Xu Employed by Sunshine Guojian Pharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Haomin Huang Employed by Sunshine Guojian Pharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.