

Background: Osteoarthritis (OA) is prevalent and is a major cause of disability, especially among the elderly. Obesity and metabolic syndrome are risk factors for OA and have been implicated in its pathogenesis. Animal studies have revealed dysbiosis in obesity and may be associated with severity of OA. Current evidence from human studies is limited.
Objectives: We aim to evaluate the differences in gut microbiome of patients with knee OA compared to healthy controls.
Methods: We used the baseline data from patients with knee OA recruited to a randomized controlled trial (NCT02176460), who gave baseline demographic variables and stool samples. Age and sex matched healthy controls (HC) were recruited from community. DNA were extracted from patients’ and HC stool samples and the gut microbiome was assessed using metagenomic profiling. Alpha and beta diversity, taxonomic and functional profiling of metagenomic analysis were compared between knee OA and HC.
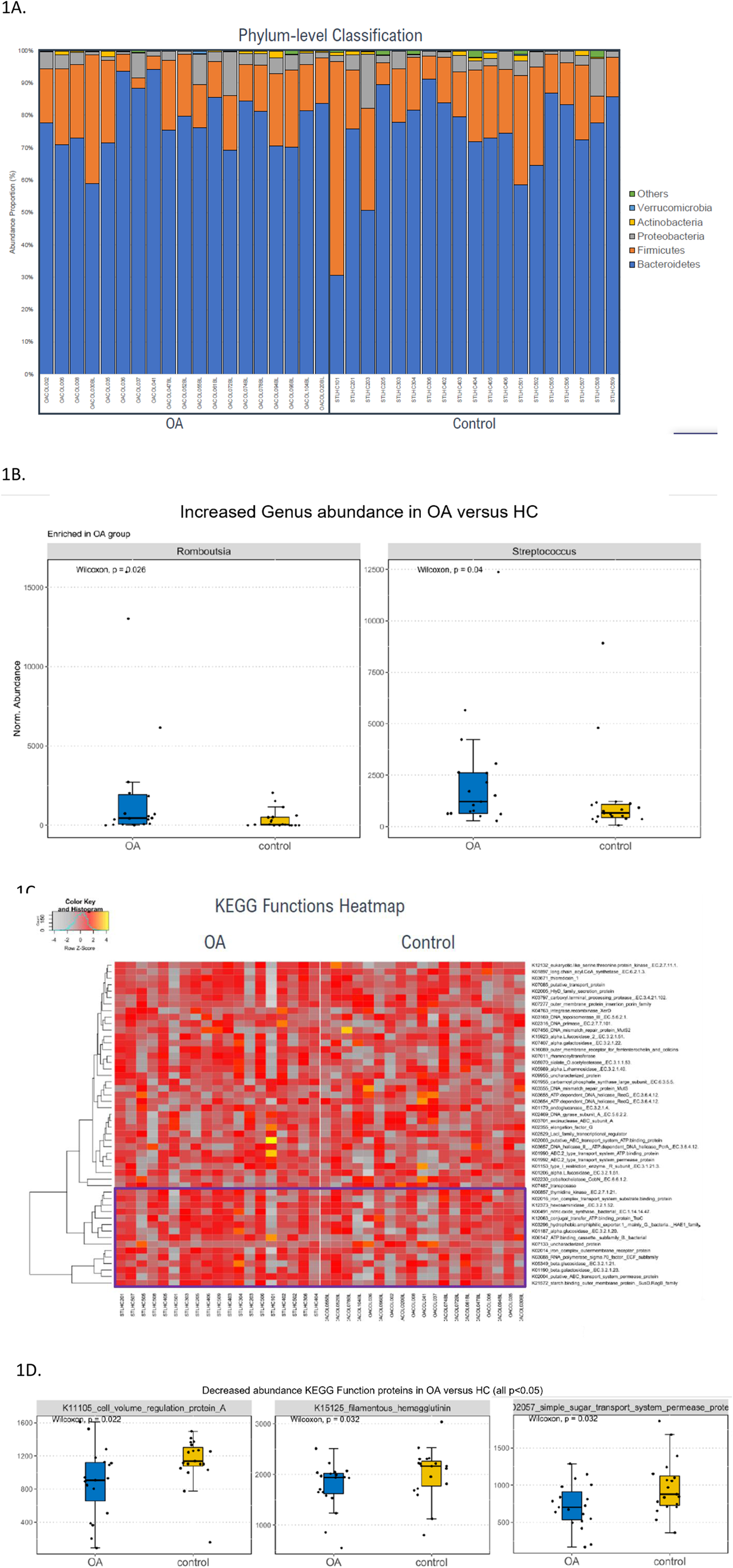
Results: Nineteen knee OA patients (100% female, mean age 57.5 years) and 19 age and sex-matched healthy controls (100% female, mean age: 56.6 years) were included (Table 1). The knee OA patients had been diagnosed with moderate to severe knee OA: 68.4% Grade 3 Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) severity and 31.6% with Grade 4 KL severity. Both knee OA patients and HC showed similar ratio of Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes at phylum level (Figure 1A). At the genus level, there was increased abundance of Romboutsia and Streptococcus genus (both p<0.05) (Figure 1B) and decreased abundance of Bilophila, Hungatella, Lachnoclostridium and Massilimicrobiota genus (all p<0.05) in knee OA patients compared to HC. At the species level, knee OA patients had increased abundance of Prevotella bivia (p<0.05), and decreased abundance of Bacteroides sp, Bilophilia sp, Blautia obeum, Hungatella sp, Clostridium sp, Parabacteroides diatasonis (all p<0.05). There were differences in expression of Kyoto Encylopedia of Genes and Genome (KEGG) functions proteins between OA patients versus HC (Figure 1C & 1D). Alpha diversity (p=0.39), and beta-diversity (p=0.09) were not significantly different between OA patients versus HC.
Conclusion: There are differences in gut microbiome composition between patients with knee OA and healthy controls. The dysbiosis in patients with knee OA may suggest possible link to pathogenesis.
REFERENCES: NIL.
Baseline characteristics of knee OA patients and healthy controls
| Knee OA
| Healthy Controls (n=19) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Age (SD), years | 57.5 (8.21) | 56.6 (7.7) | |
| Female, % | 100 | 100 | |
| Chinese ethnicity, n (%) | 19 (100) | 19 (100) | |
| BMI, (SD) | 29.7 (5.8) | 23.3 (7.1) | |
| History of | |||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 3 (15.8) | |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 3 (15.8) | 1 (5.3) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 1 (5.3) | 0 | |
| Mean duration of knee OA, years (SD) | 13.3 (4.7) | - | |
| Severity of Knee OA (Kellgren-Lawrence scale) | |||
| Grade 3, n (%) | 13 (68.4) | - | |
| Grade 4, n (%) | 6 (31.6) | - | |
| WOMAC pain (0-100) | 56.1 (16.5) | - | |
| WOMAC stiffness (0-100) | 49.9 (28.2) | - | |
| WOMAC function (0-100) | 51.5 (22.6) | - | |
| WOMAC total (0-100) | 52.5 (19.5) | - | |
| Alpha diversity (Shannon Weaver index) between OA versus HC | p=0.39 | ||
| Beta diversity (Bray-Curtis index) between OA versus HC | p=0.09 | ||
All data in mean (standard deviation, SD) unless otherwise stated.
BMI Body Mass Index, HC Healthy controls, OA Osteoarthritis, WOMAC Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index
1A. Knee OA patients and HC showed similar ratio of Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes at phylum level analysis. 1B. Increased abundance of Romboutsia and Streptococcus genus in knee OA patients versus HC. 1C. KEGG functions heatmap showing increased expression of genes related to alpha-glucosidase, beta-glucosidase, beta-galactosidase, starch-binding outer membrane protein in gut microbiome of knee OA patients versus HC. 1D. Decreased abundance of cell volume regulation protein A, filamentous hemaglutinin and simple sugar transport system in KEGG function protein gene expression in knee OA patients versus HC. HC healthy controls, KEGG Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome, OA osteoarthritis
Acknowledgements: NIL.
Disclosure of Interests: None declared.